AQA GCSE Forces and Elasticity(Physics)
Forces and Elasticity
Definition of a force: A force is a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object.
Forces can change the shape of an object by:
1.Compression of object
2.Bending of object
3.Stretching of object

Compression
Objects can be squashed when a compression force acts on the object.

A compression force acts downwards on the can. In response the table exerts an upwards reaction force that is the same size as the compression force, but in the opposite direction on the can.
As a result the can is crushed.
There are other forces involved in this example, but they have been removed for simplicity.
Stretching
In the case of a man pulling on a rope. He will exert an applied pull force on the rope. In response the rope will have a tension force which acts in the opposite direction.

Bending
A spoon can be bent by applying forces to the straw.

The straw is bent by applying two downward forces to the ends of the straw, whilst applying an upward force to the inside part of the straw.
Inelastic and Elastic Deformation.
Deformation is when an object changes its shape.
There are two types of deformation:
1.Inelastic deformation
2.Elastic deformation.
Inelastic deformation
When a stretching force is applied to an object it will be deformed (change shape).
When the stretching force is removed, if the object does not return to its original length and shape, then inelastic deformation has occurred.
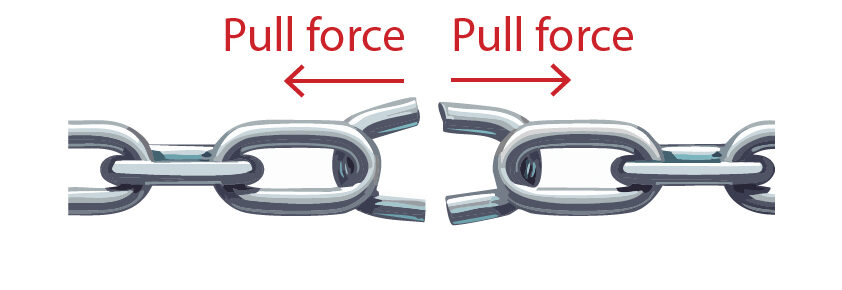
Due to the stretching forces, the metal chain has been permanently deformed and when those pulling forces are removed the chain will not return to its original length and shape, so inelastic deformation occurs.
Elastic deformation
When a stretching force is applied, the object will be deformed. However, when that stretching force is removed the object will return to its original length and shape.
An example is a rubber bungee cord. During the person’s downward fall, the bungee cord stretches, but then recoils.

Once the person has removed the bungee cord after the jump, the bungee cord returns to its original length and shape to be used again.
Practice Questions
1.Define the term force
2.How do forces affect the shape of an object?
3. Explain the difference between elastic and inelastic deformation
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque