AQA GCSE Hydroelectric, Wave and Tidal(Physics)
Hydroelectric
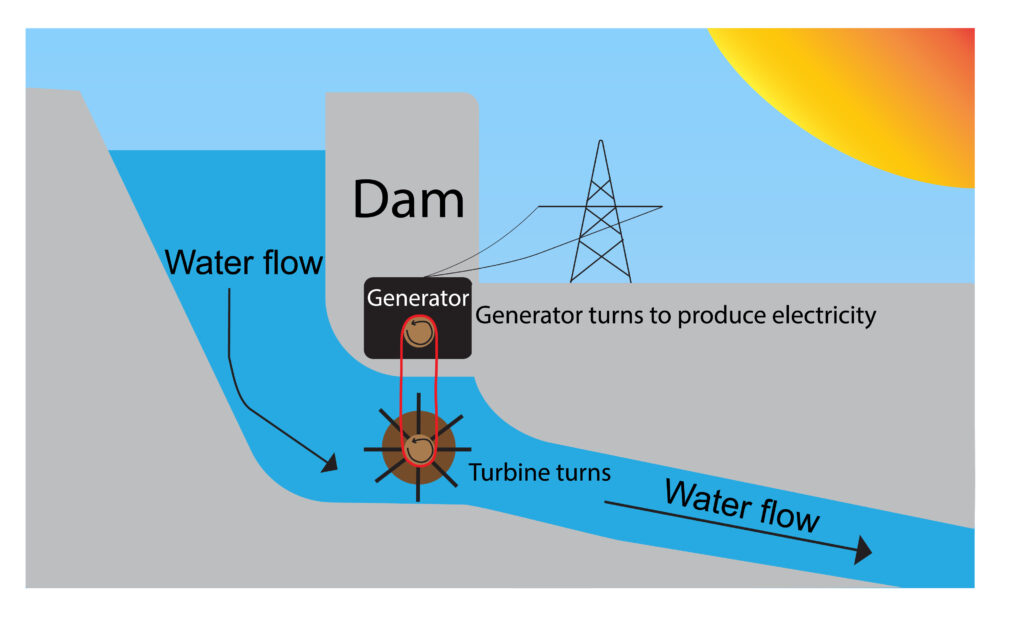
Water is stored at height in a reservoir, allowed to flow downhill, which turns a turbine, turning a generator to produce electricity.
Hydroelectric can be used as pumped storage, so during periods of excess electricity due to solar, a water pump is used to pump the water back up to the top reservoir, then during periods of high demand the water is allowed to flow back down hill again to meet surges in demand.
| Advantages to Hydroelectric | Disadvantages to hydroelectric |
|---|---|
| Renewable resource | Flooding can occur before or after dam |
| Short start up time, can be used to meet surges in demand | Low power output |
| Stores energy for later use, using pumped storage | High set up cost |
Wave

As the waves move in one direction the wave generator will move up and down on the surface of the water. As the generator moves, it rotates on surface of water causing electricity to be produced.
| Advantages to Wave Power | Disadvantages to Wave Power |
|---|---|
| Renewable resource | Cables need to connect wave machine to the mainland |
| No carbon dioxide produced | Construction problems due to building in water |
Tidal
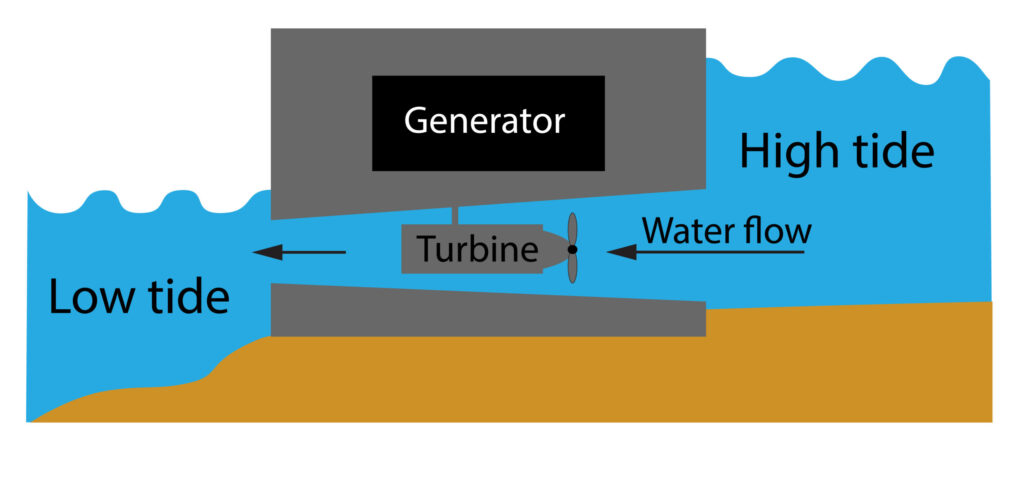
A tidal barrage is normally located in an estuary where the river meets the sea. As the tide moves in and out it will cause the turbines to turn, which turns a generator to produce electricity.
| Advantages to Tidal Power | Disadvantages to Tidal Power |
|---|---|
| Renewable resource | Restricts access for boats |
| No carbon dioxide produced | Construction problems due to building in water |
| Tide only occurs twice a day |
Practice Questions
1.Explain how hydroelectric can help to meet our energy requirements during peak periods of use
2.In the UK, we are surrounded by water, but wave power is not commonly used. Suggest reasons why it is not commonly used.
3.Suggest why tidal power could be considered both as a reliable energy resource and an unreliable energy resource
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque