AQA GCSE Alternating and Direct Electrical Circuits(Physics)
Alternating and Direct Circuits
Circuits are either classed as alternating, or direct.
A circuit can have either:
1.Direct potential difference and Direct current
2.Alternating potential difference and alternating current
Direct
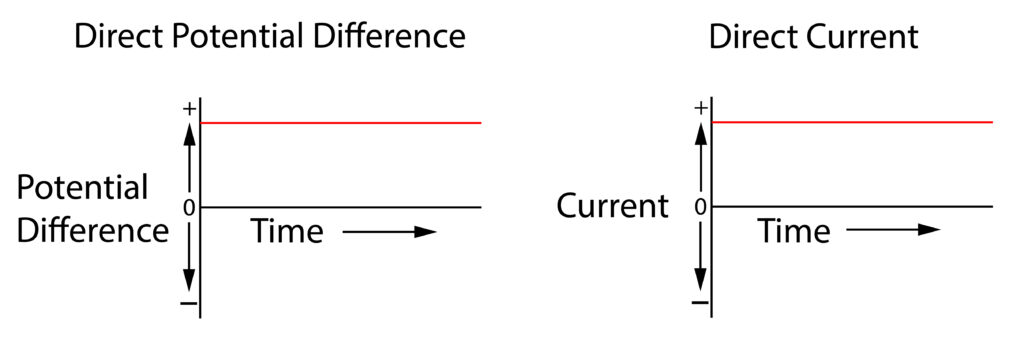
A direct potential difference is in one direction only.
This means that when the power source provides a direct potential difference a direct current will flow, this means that the current flows in only one direction around the circuit.

The direct current will flow from the positive terminal of the cell to the negative terminal of the cell.
Note the design of the cell terminals, compare to the alternating one below
An oscilloscope can be used to illustrate a direct potential difference and direct current
Sources of direct current for an electrical circuit would be a cell or battery.
Alternating
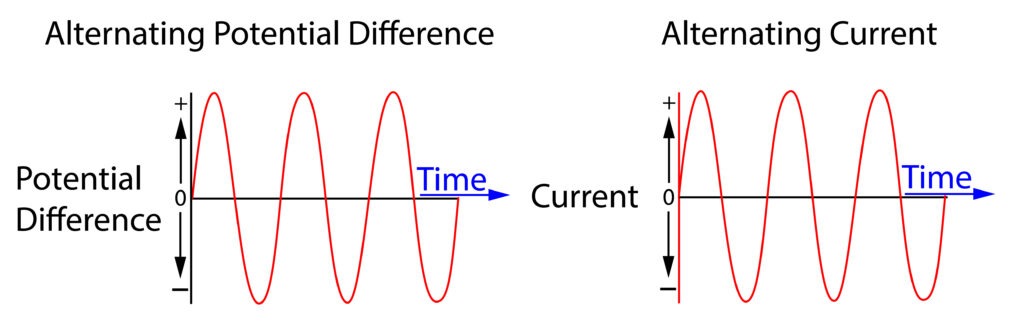
An alternating potential difference will continuously changes its direction.
An alternating potential difference will cause an alternating current to flow in a complete circuit.
An alternating current will continously change direction.
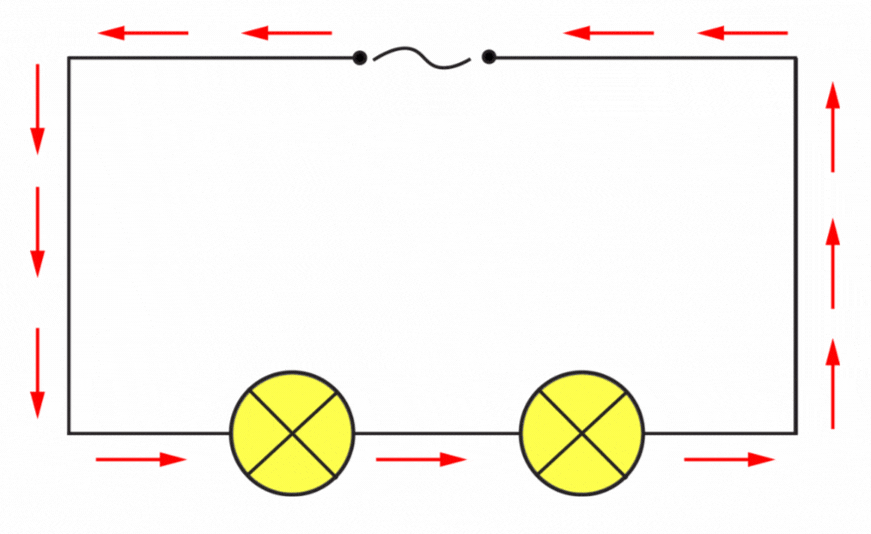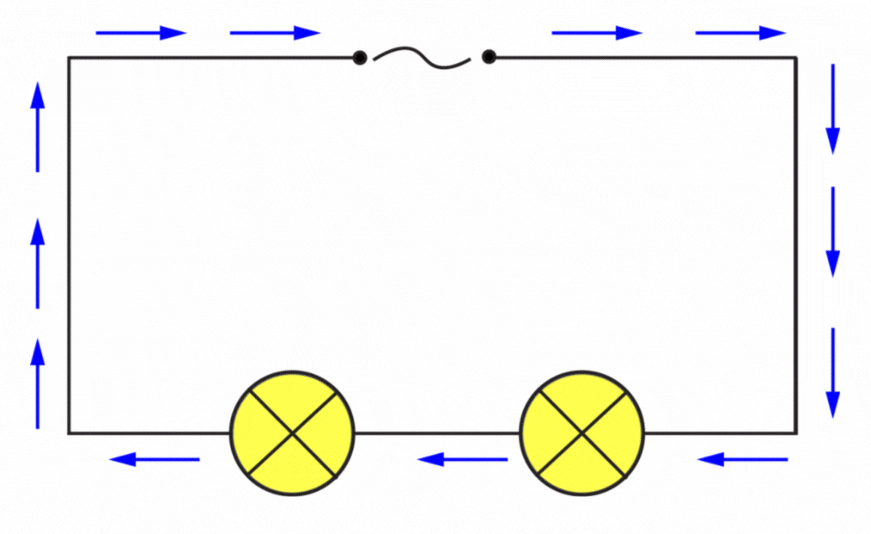
In the diagram above notice how the terminals have changed.
An oscilloscope can be used to show an alternating potential difference and alternating current
Sources of alternating current include generators and mains electricity
Practice Questions
1.Draw the circuit symbol to represent the terminals for:
(a)Circuit that has a direct potential difference
(b)Alternating potential difference
2. State two sources of:
(a) direct potential difference
(b)Alternating potential difference
3. State the name of the device which can be used to graphically show a direct current, or direct potential difference.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque