AQA GCSE Upthrust(Physics)
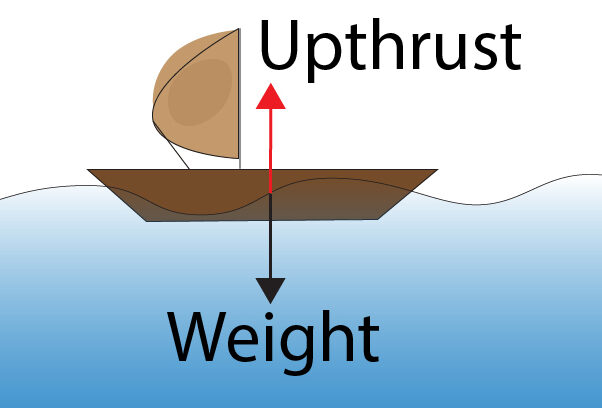
Upthrust
Upthrust is an upward force on an object that a fluid exerts
Fluids can be liquids or gases. We will look at examples of objects in liquids here.
In the image below a box is suspended in water. Pressure on the object increases with depth of water. The pressure increases deeper into the water because the density of the water increases as depth increases, due to increased weight of water from above.
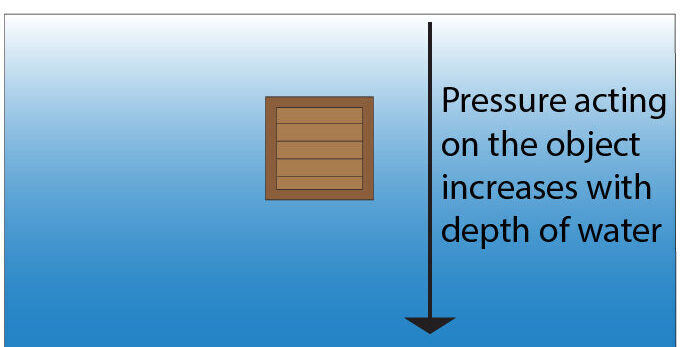
This means that a higher pressure will act on the bottom of the box, compared to the top of the box.
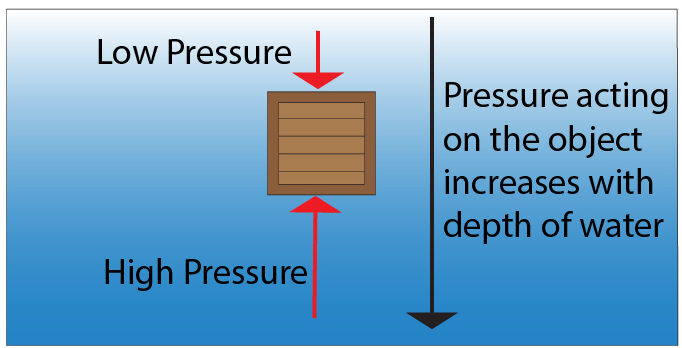
Pressure is the amount of force over a certain area, so that means that the upward force on bottom of object is greater than downward force on the object. The resultant force, formed as a result of both of these forces will give an upthrust (Upward force) on the object.
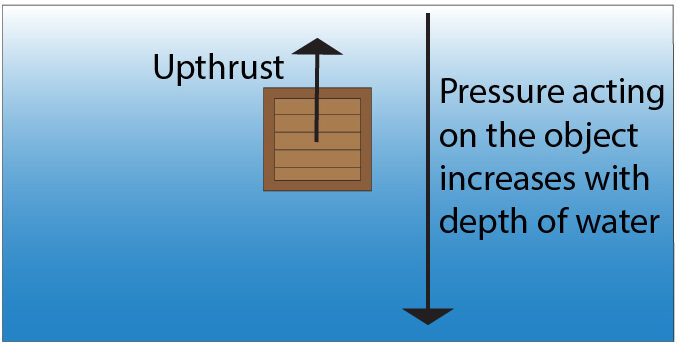
Floating or Sinking.
An object will sink if its weight is greater than the upthrust as shown below.
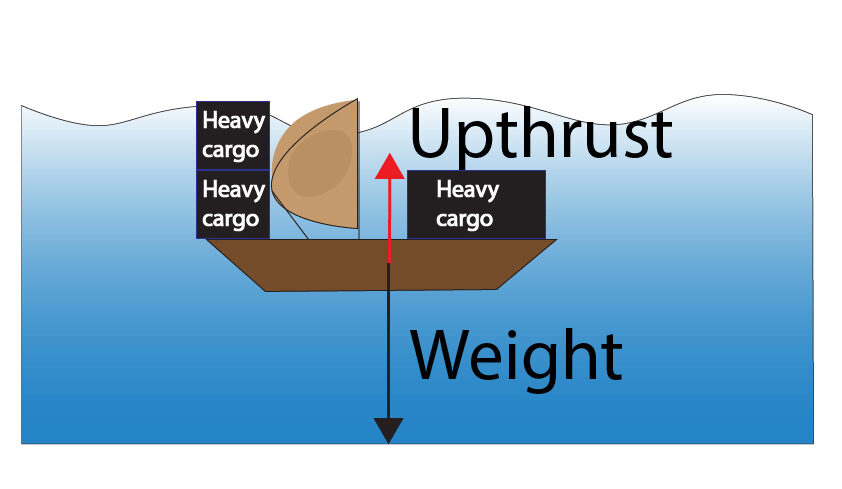
An object will float if its weight is equal to the upthrust as shown below.
Role of Density in floating or sinking.
In the diagram below an object is lowered into water. In the measuring cylinder on the right the water level has risen because the object displaced some of the water as shown below.
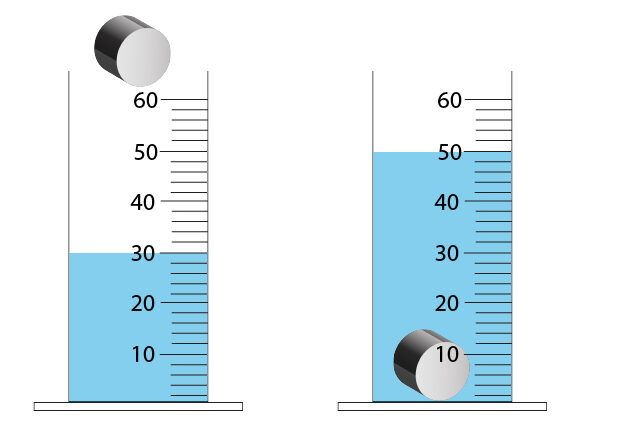
As the object is lowered into the water it will displace a certain weight of water. This weight of water displaced will be equal to the upthrust force.
Objects that are less dense than water.
The box that is partly submerged in the water below has a density of less than water. As a result it floats. Notice how the object is only part submerged.
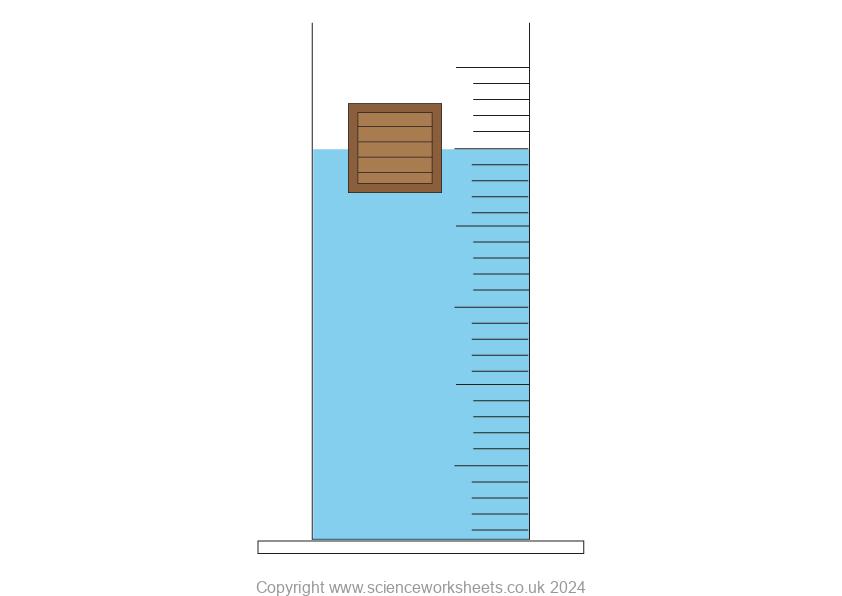
As the box is less dense than water, the object’s weight will be equal to the weight of the water displaced. Therefore the weight of the object is equal to the upthrust of the liquid. So, it floats.
Objects with the same density as water.
The top of the box is now level with the surface of the water. This is because the box has a density that is equal to the density of water.
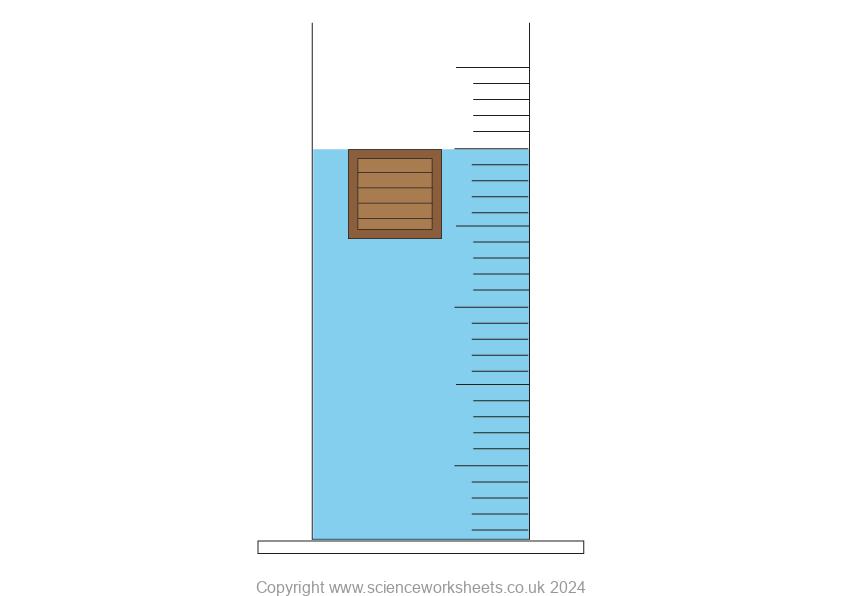
As the box has a density that is equal to the density of the water, the object’s weight will be equal to the weight of the water displaced. Therefore the weight of the object is equal to the upthrust of the liquid.
Objects with a greater density than water.
When the object is more dense than water, the object will sink.
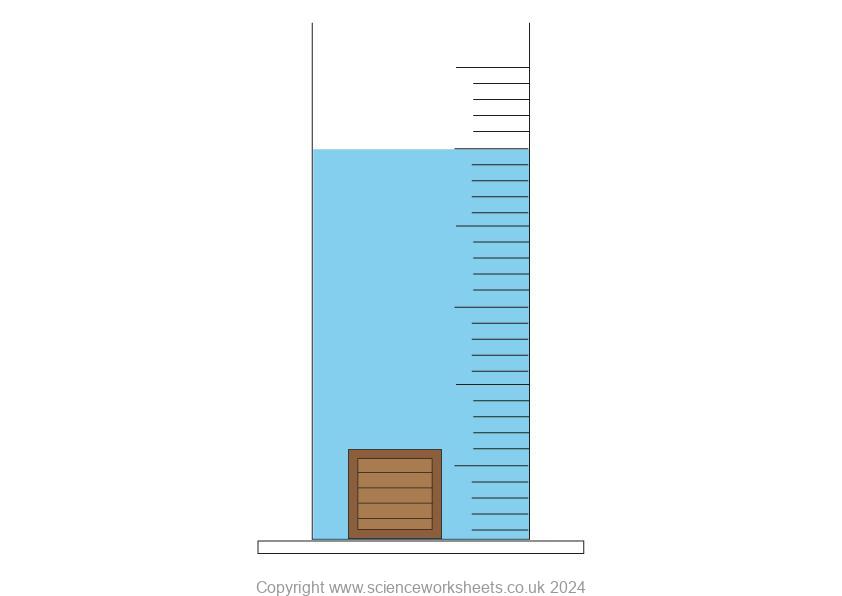
As the box has a density that is greater than the density of the water, the object’s weight will be more than the weight of the water displaced. Therefore the weight of the object is greater than the upthrust of the liquid. So, the object sinks.
Practice Questions
1. State the definition of upthrust
2. Describe how pressure changes with depth of liquid.
3. Explain how an upthrust force is formed on a beach ball that is submerged in the water.
4. Delete the two incorrect words in the brackets to make the following sentence correct:
For an object to float its weight must be (less than, equal, greater than) the upthrust of water.
5. Explain why an object that is less dense than water will float on the surface of water.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque