AQA GCSE Parallel Circuits(Physics)
Parallel Circuits
A parallel circuit contains electrical components that are in a branched circuit.
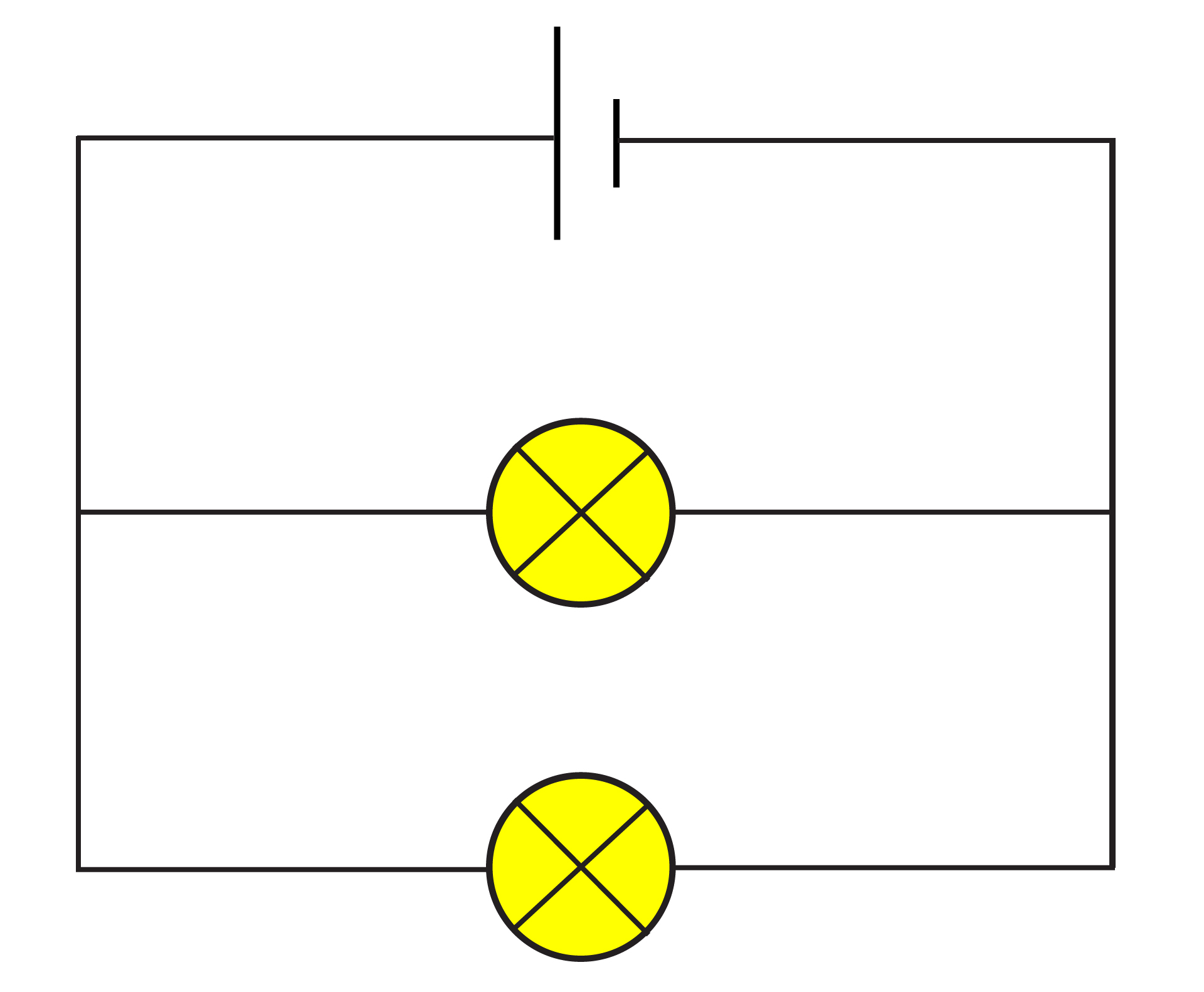
Rules for Parallel Circuit diagram
Rule 1: The potential difference is the same across each component in a parallel circuit
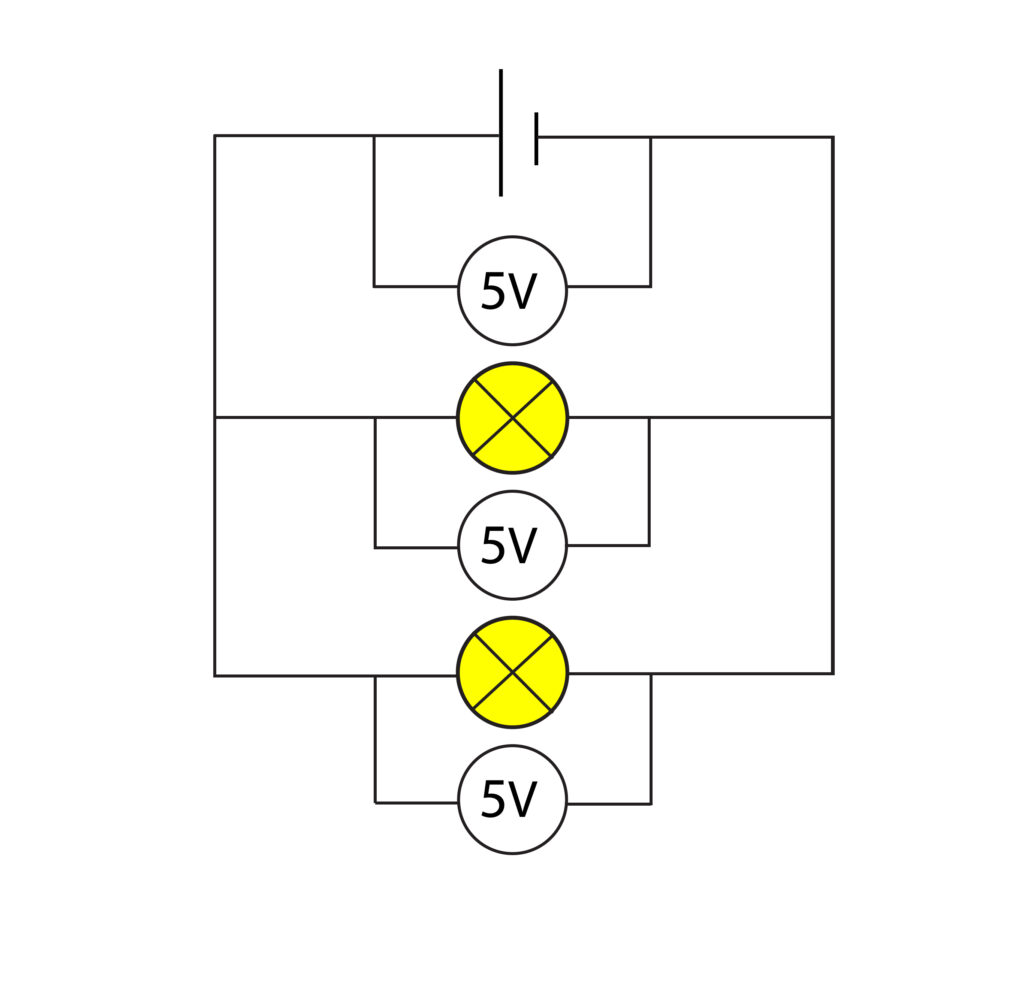
In the circuit above, the potential difference is the same across all components
Rule 2: In a parallel circuit, total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the
currents through the separate components.
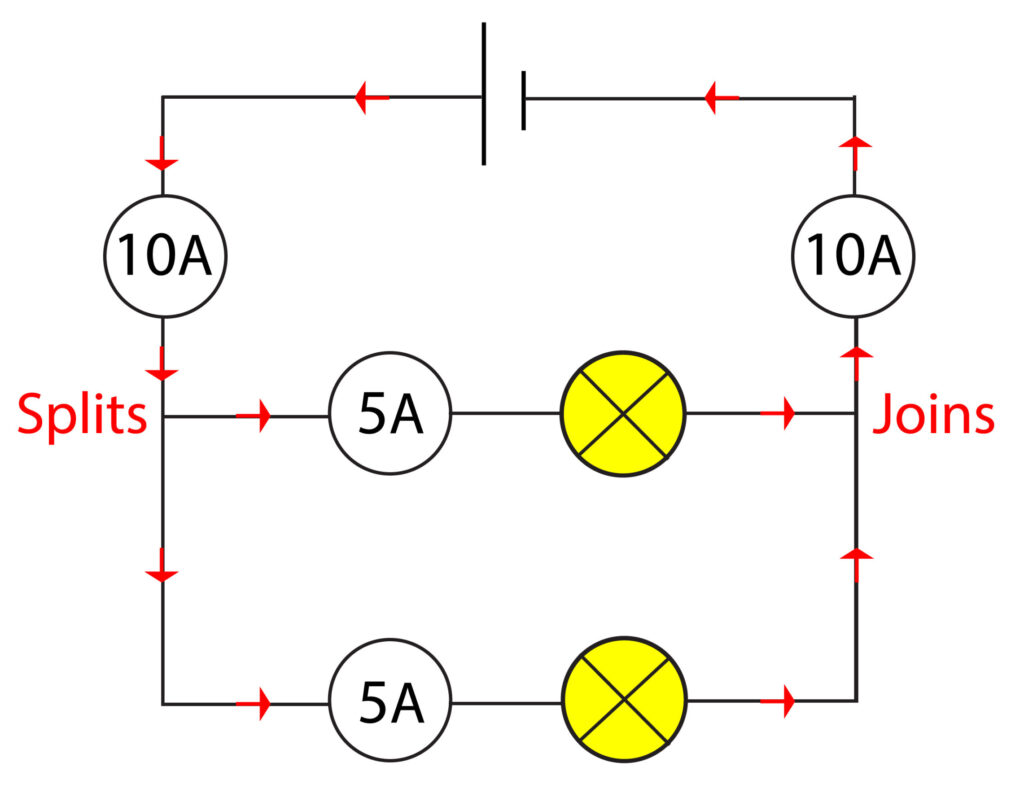
This means that at a junction, the current splits. Think of this just like the water flow splits in a pipe at a junction.
Rule 3: The total resistance in a parallel circuit is less than the value of resistance for the lowest single resistor.
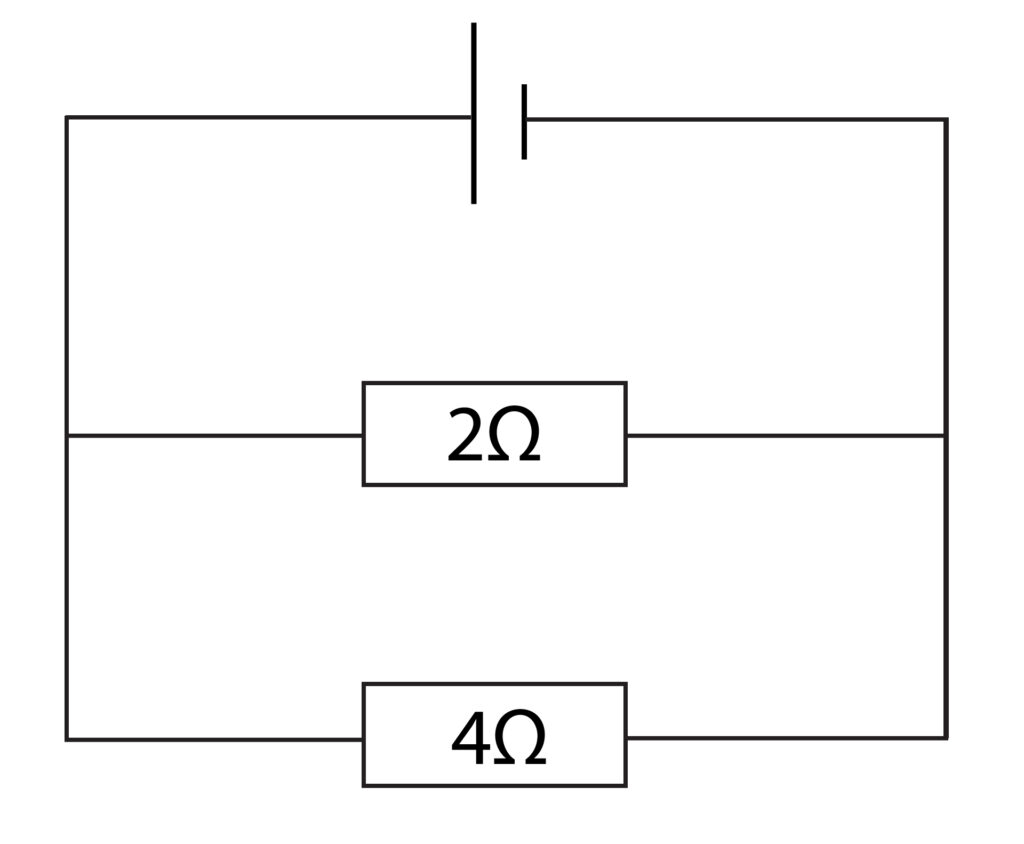
In the circuit diagram above the total resistance will be lower than the resistor with the least value. In this case, total resistance is < 2 ohms.
You do not need to know how to calculate the exact value on AQA.
You do need to know that as more resistors are added in parallel, total resistance decreases because this is adding more branches to the circuit, so there are more routes for the current to flow.
Practice Questions
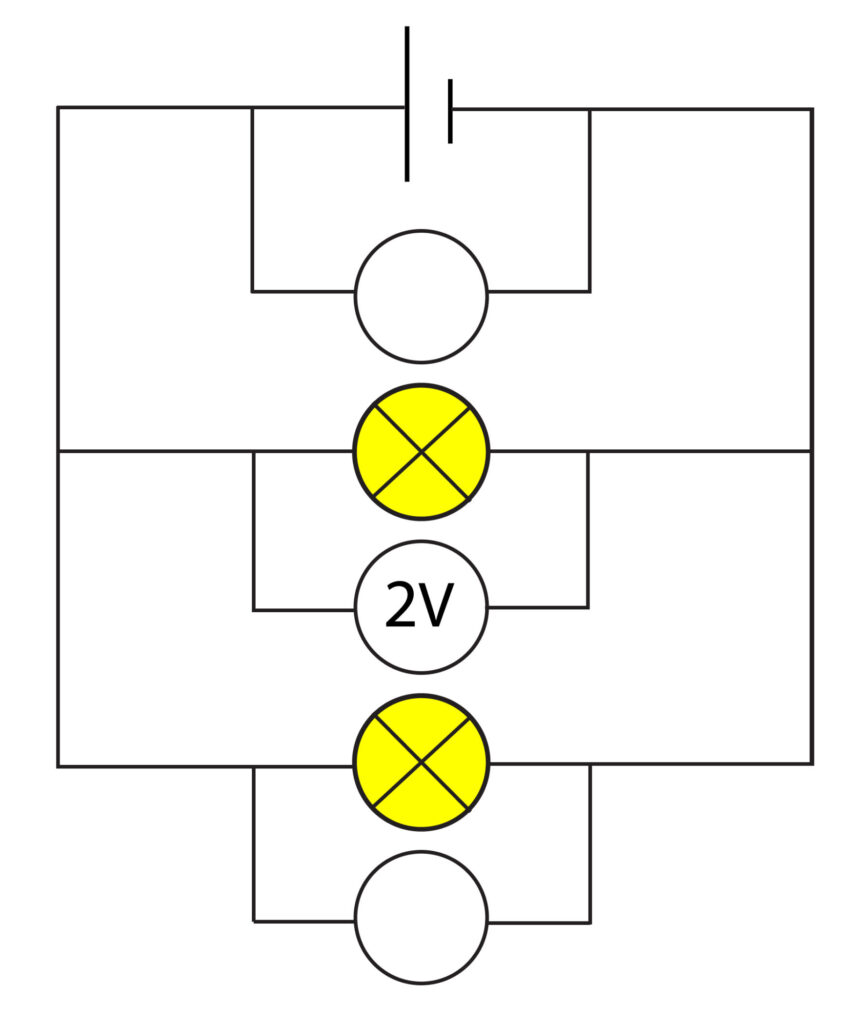
1.In the circuit below calculate the value for the potential difference across both the cell and one of the bulbs.
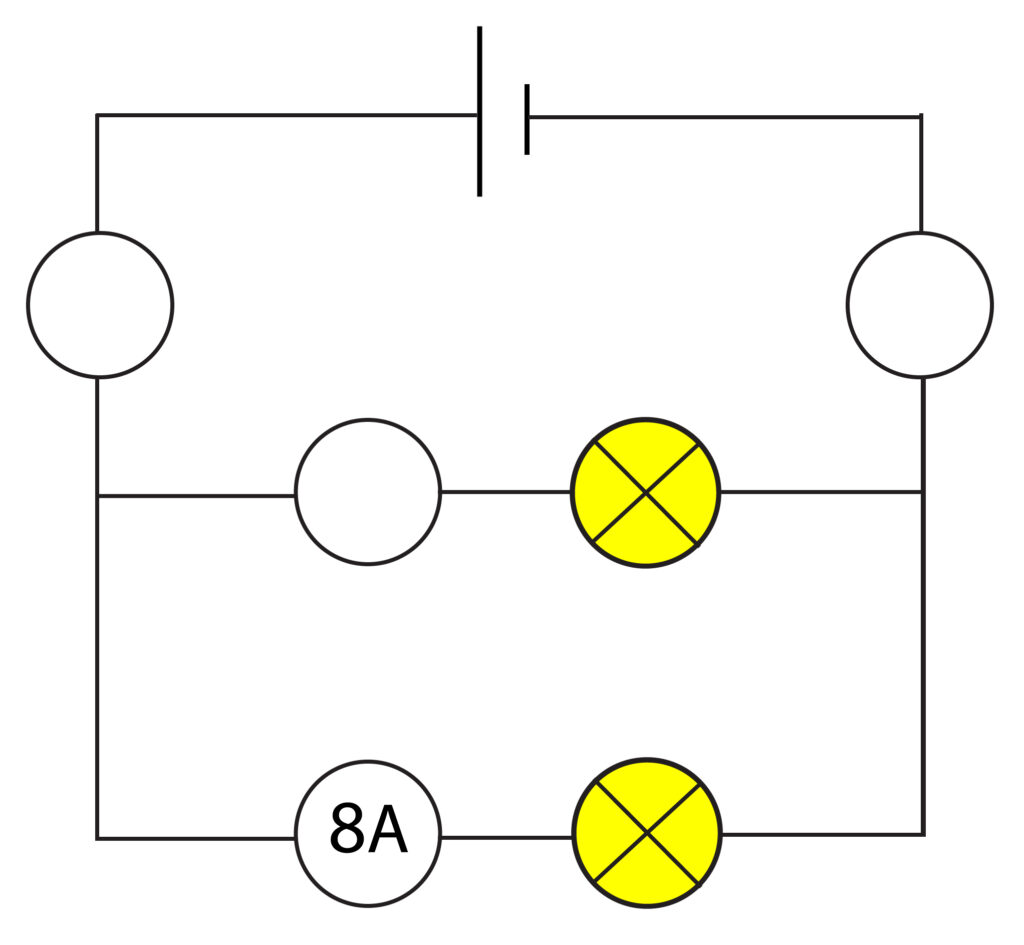
2. Calculate the missing value for current for the ammeters in the circuit below. Assume that all bulbs are identical.
3. A parallel circuit contains 3 resistors, wired in parallel 10 ohm, 5 ohm and 4 ohm resistor. State the value for the total resistance of the circuit.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque