AQA GCSE Using Ultrasound Waves for Industrial Imaging(Physics)
Industrial imaging using Ultrasound.
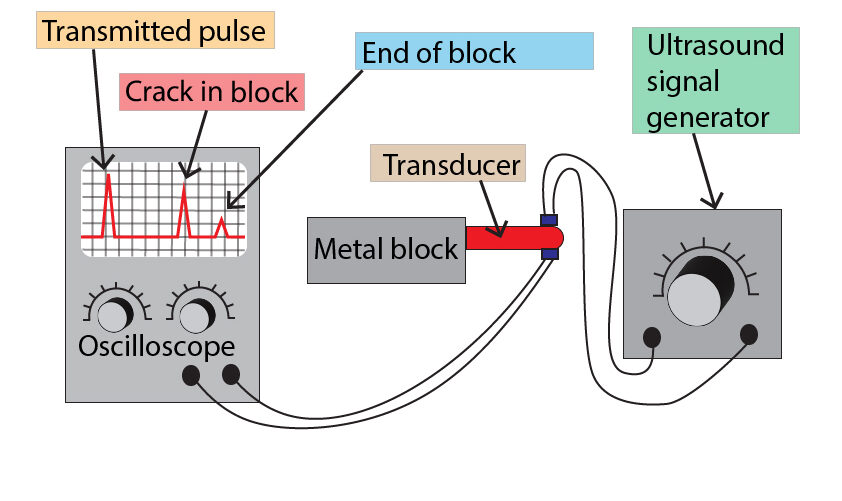
Ultrasound waves can be used to find cracks(flaws) in metal structures.
The signal generator will produce a high frequency sound wave (ultrasound), which the transducer sends through the metal block.
The oscilloscope will record a peak when the wave enters the metal block, because some of the wave is reflected back towards the transducer when the wave hits the metal boundary.
The wave then passes through the metal structure when it reaches a crack the oscilloscope will record a 2nd peak, again because some of the wave is reflected back to the transducer
Eventually, the wave will reach the end of the block and a 3rd peak is recorded on the oscilloscope screen, due to some of the wave being reflected back to the transducer.
Calculating distance to the crack in a metal object.
You may have to calculate the depth of the crack in the metal’s internal structure.
The grid on the oscilloscope has a time scale. In this case each box is 0.00005 seconds as shown below.
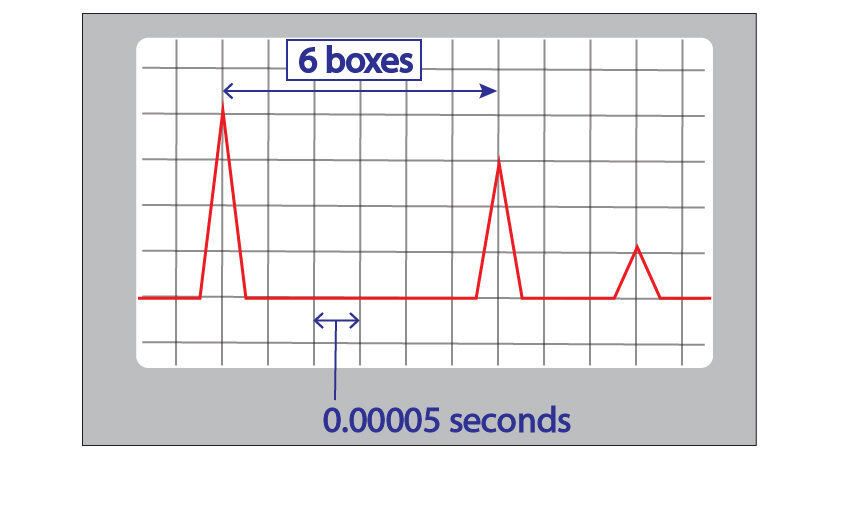
The transmission peak is on the far left and the peak due to the crack is the peak that is between the other two peaks.
The grid on the oscilloscope has a time scale. In this case each box is 0.00005 seconds as shown above.
There are 6 boxes between the transmission peak and the peak due to the crack. So, the total time taken for the wave to travel to the crack is:
6 x 0.00005 second = 3 x 10-4 seconds.
We are going to assume that the speed of ultrasound wave in metal is 5000m/s.
Distance (depth of crack) = Speed x time
Distance (depth of crack) = 3 x 10-4 x 5000 = 1.5m
Practice Question
1.Suggest why ultrasound might be useful to an aircraft maintenance company.
2. Ultrasound waves have been used to detect cracks in a metal structure. The oscilloscope screen has 5 peaks in it. Calculate how many cracks are present in the metal structure
3. Explain how ultrasound is used to detect cracks in a metal structure.
4. Ultrasound waves travel through metal X at a speed of 7000m/s. The time scale on the oscilloscope is set to 0.00010 seconds per box. There is a difference of 4 boxes between the transmitted peak and the peak due to a crack. Calculate the depth of the crack.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque