AQA GCSE Understanding Black body radiation(Physics)
Black body radiation
In physics we often use the term body to represent an object.
All bodies, regardless of the temperature, emit and absorb infrared radiation.
Infrared radation is thermal energy.
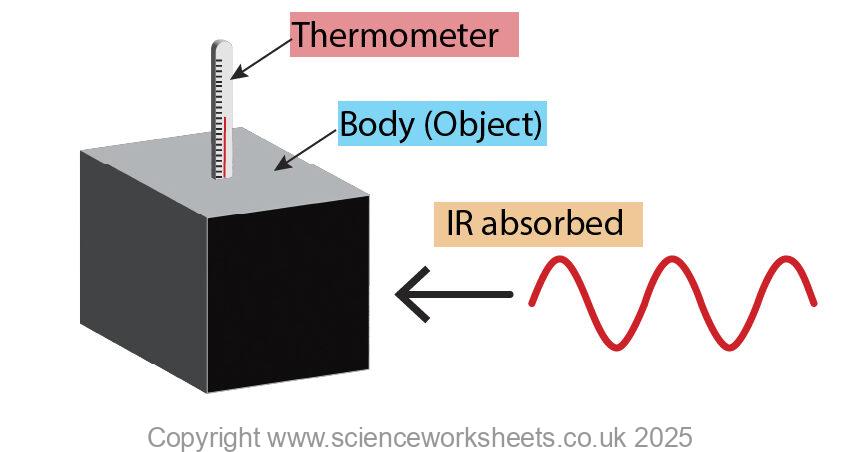
Body absorbing Infrared
When a body absorbs Infrared its temperature increases, so its thermal energy store will increase.
In the diagram below, the temperature on the thermometer is increasing as the body absorbs infrared.
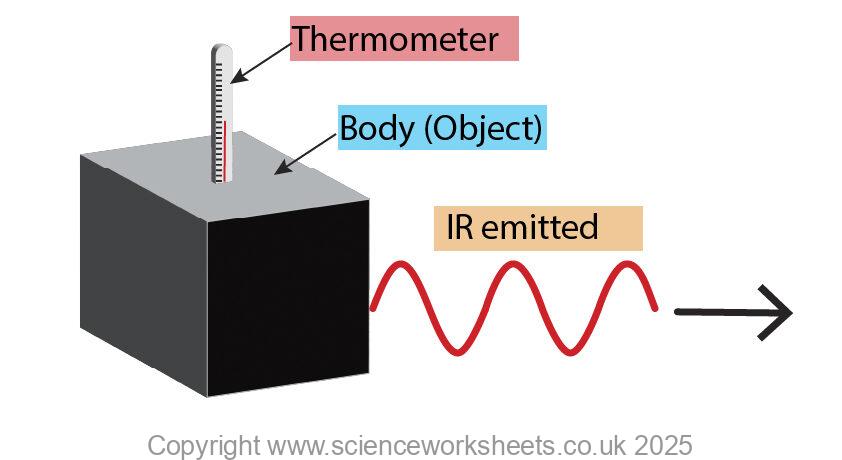
Body emitting Infrared
When a body emits Infrared its temperature decreases, so its thermal energy store will decrease.
In the diagram below, the temperature on the theremometer is decreasing as the body absorbs infrared.
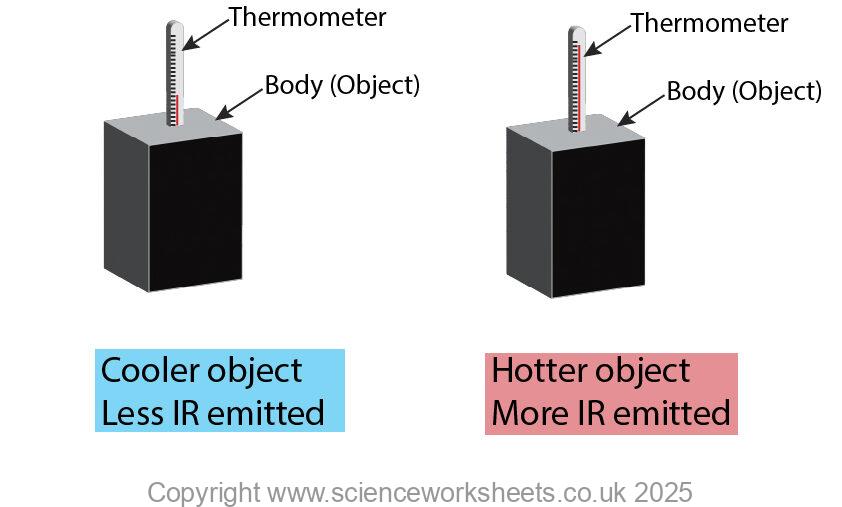
Temperature of the object and amount of IR emitted
The higher the temperature of the object, the more IR emitted in a given time. This is shown in the diagram below.
Look at the graph below, there are three important deductions that you need to learn.
1. If an object has a constant temperature it will emit radiation across a range of wavelengths. In most cases these wavelengths will correspond to IR, but they can correspond to other electromagnetic wave regions such as visible light.
2. The higher the temperture the greater the intensity of radiation that is emitted at a range of wavelengths. You can see that the line for the higher temperature object is higher compared to the line for the lower temperature object.
3.The peak intensity has a smaller wavelength at a higher temperature. Look at the position of peak intensity for 900⁰C, it is to the left of the peak intensity for the 700⁰C.
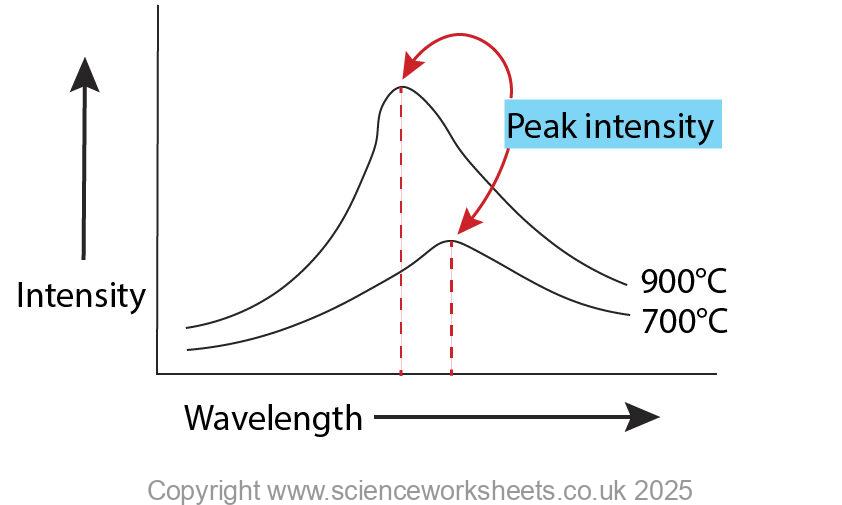
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy of the wave.
Practice Question
1.In physics what is meant by the term body?
2. If a body emits infrared to the surroundings, what will happen to the temperature of the surroundings?
3. As a hot object cools down, describe how the intensity of radiation emitted changes and also how the peak intensity of radiation changes.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque