AQA GCSE Transformers (Physics)
Transformers
A transformer is used to either increase or decrease the size of an alternating potential difference.
A transformer works using the principle of electromagnetic induction.
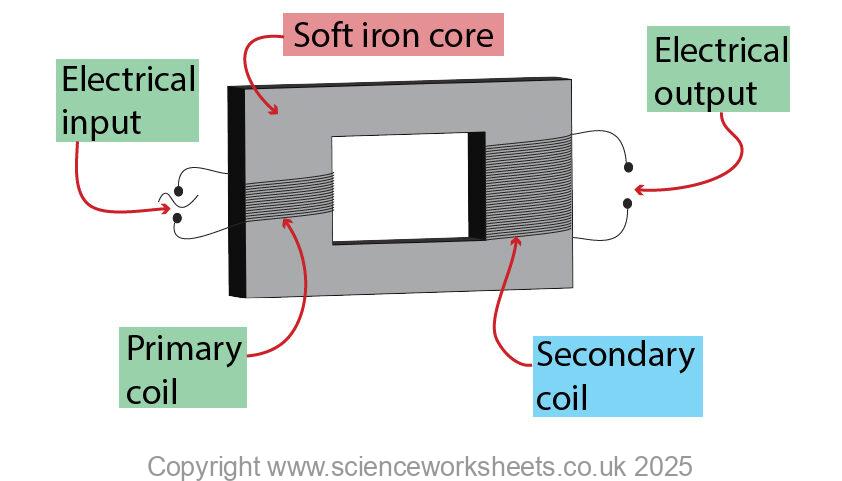
Every transformer will contain a primary coil, secondary coil and iron core.
Both of the coils are wound around the soft iron core as shown below.
Iron is used for the core because it is magnetically soft, this means it is easy to magnetise and demagnetise.
Step up and Step down transformers
Below are images of a step up and step down transformer

| Step up transformer | Step down transformer |
|---|---|
| Few turns on primary coil | More turns on primary coil |
| More turns on secondary coil | Few turns on secondary coil |
| Small alternating potential difference supplied | Large alternating potential difference supplied |
| Large output alternating potential difference | Small output alternating potential difference |
How a transformer works
When an alternating potential difference is applied across the primary coil, an alternating current will flow in the primary coil.
This alternating current through primary coil, will cause a changing magnetic field through the soft iron core.
The magnetic field lines will cut the secondary coil, inducing an alternating potential difference across the ends of the coil.
If the secondary coil is part of a complete circuit, then an alternating current will flow.
Practice Questions
1.State what a transformer is used for
2. Describe the construction of a transformer
3. Explain how a transformer can increase the size of an alternating potential difference.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque