AQA GCSE The Generator Effect (Physics)
The Generator Effect
The generator effect is a term used to explain an induced potential difference across the ends of a conductor (wire) when either of the following occurs:
1.An electrical conductor (wire) moves relative to a magnetic field. This can include:
-moving a wire through a magnetic field
-moving a magnet through a coil of wire
2. A change in the magnetic field around a conductor
– When a magnet is moved into or out of a coil of wire, there is a change in the magnetic field.
In both cases, if the conductor(wire) is part of a complete circuit and a potential difference is induced, then a current will flow.
Electrical conductor (wire) moving relative to the magnetic field
In the diagram below, the black wire is being moved up and down through the magnetic field.
The wire will cut the blue field lines, which will induce a potential difference across the ends of the wire, if the wire is part of a complete circuit then a current will flow.
If the direction of the wire is reversed, then the direction of the current reverses.
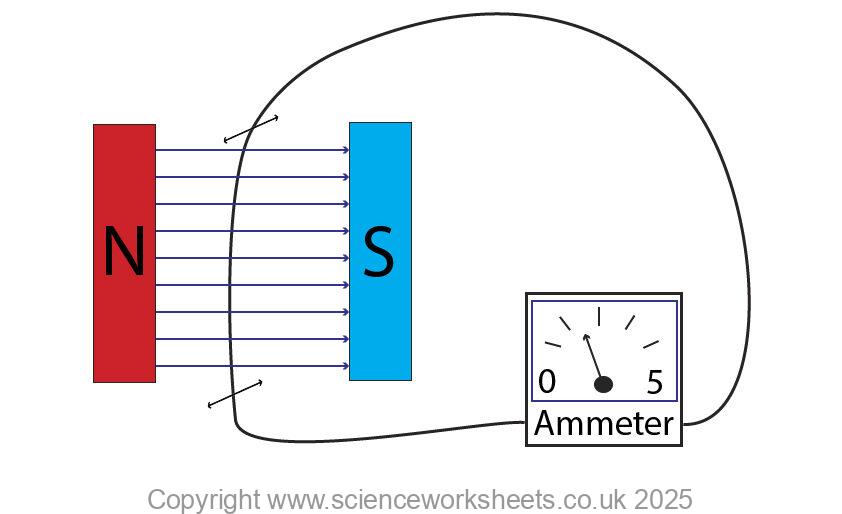
In the diagram below a bar magnet is moving in and out of a coil of wire.
As the bar magnet moves through the coil of wire, the coil of wire of wire cuts the magnetic field lines and a potential difference is induced across the end of the wire. If wire is part of a complete circuit, then a current will flow.
If the direction of the magnet is reversed, then the direction of current reverses.

A change in the magnetic field around a conductor(wire)
When the magnet is moved in and out of the coil of wire, a change in magnetic field occurs.

Pushing the magnet into the coil
When a magnet is pushed into the coil, the magnetic field inside the coil increases.
That change in magnetic field induces a potential difference across the ends of the coil.
If the coil is part of a complete circuit, this potential difference causes a current to flow.
Pulling the magnet out of the coil
When a magnet is pulled out of the coil, the magnetic field inside the coil decreases.
That change in magnetic field induces a potential difference across the ends of the coil.
If the coil is part of a complete circuit, this potential difference causes a current to flow.
Factors that affect the size of the induced potential difference or current.
1. Faster the movement of the conductor or magnet, the greater rate of change in magnetic field. This increases the size of the induced potential difference or current.
2.A stronger magnetic field produces a larger induced voltage because more magnetic field lines are being cut.
3.More turns (loops) of wire then more area for the magnetic field to pass through. The induced voltage is proportional to the number of turns. If there are more turns, then there is a greater induced potential diffference or current.
4.The longer the wire exposed to the magnetic field, the more field lines are cut, so the greater the induced voltage or current.
5.The maximum voltage is induced when the wire cuts the magnetic field at 90° (perpendicular). If the wire moves parallel to the field, no voltage is induced.
Practice Question
1.Describe what is meant by the term a generator effect
2. State two ways that the generator effect can occur
3. List three factors that affect the size of the induced voltage.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque