AQA GCSE Temperature of Bodies(Physics)
Temperature of Bodies
A body is an object.
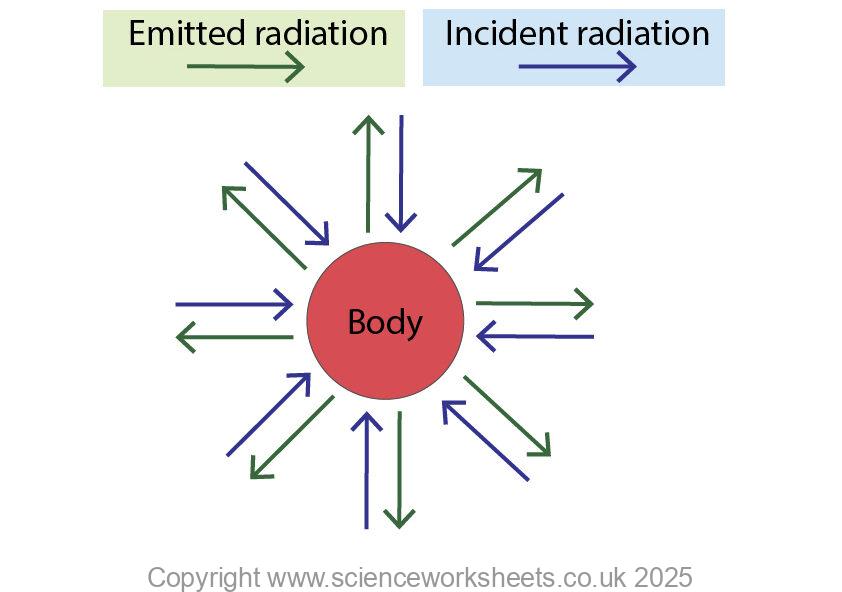
A body will have a constant temperature if the incident radiation that it absorbs is equal to the emitted radiation.
In the diagram below the rate of incident radiation will equal the rate of emitted radiation, so the temperature remains constant.
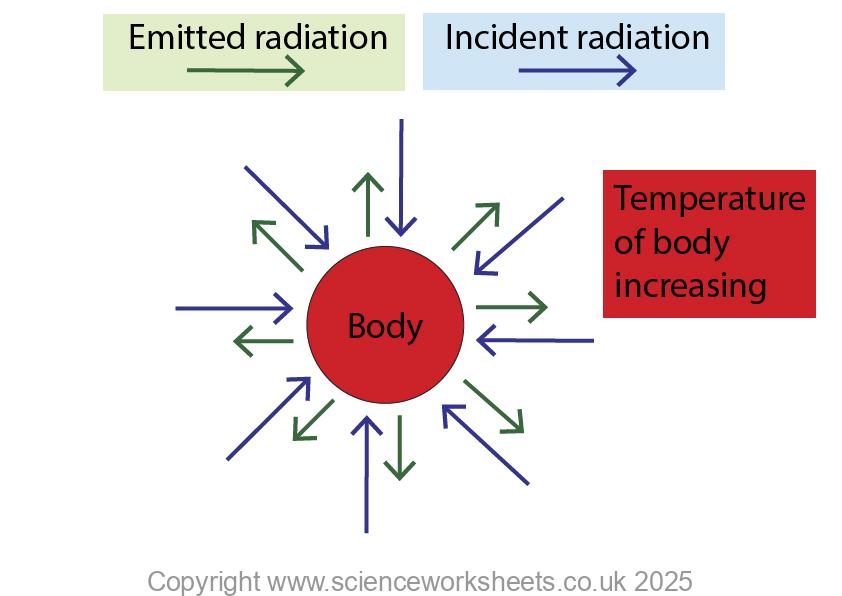
Temperature of body increasing
If the rate of incident radiation is greater than the rate of emitted radiation, the temperature of the body will increase as shown below.
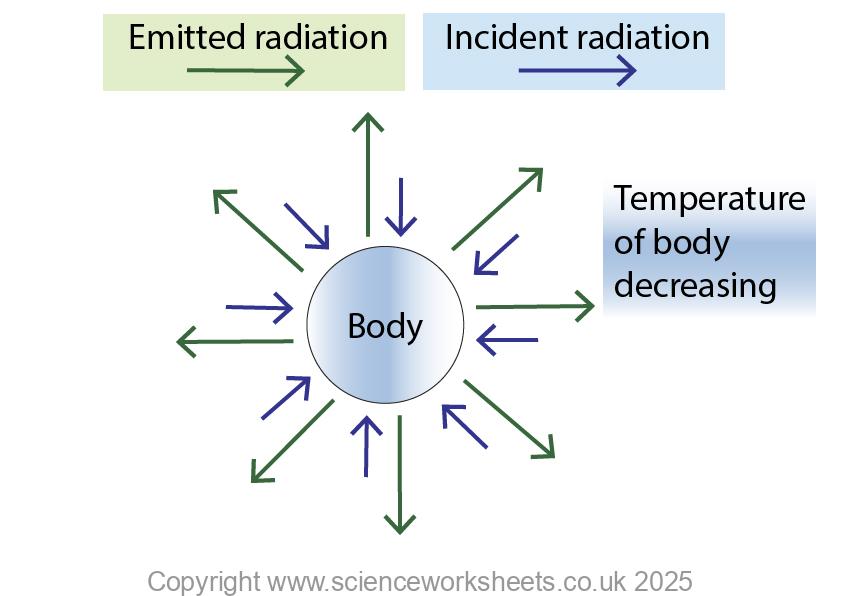
Temperature of the body decreasing
If the body emits radiation at a faster rate than the rate of absorption, then the temperature of the body will decrease.
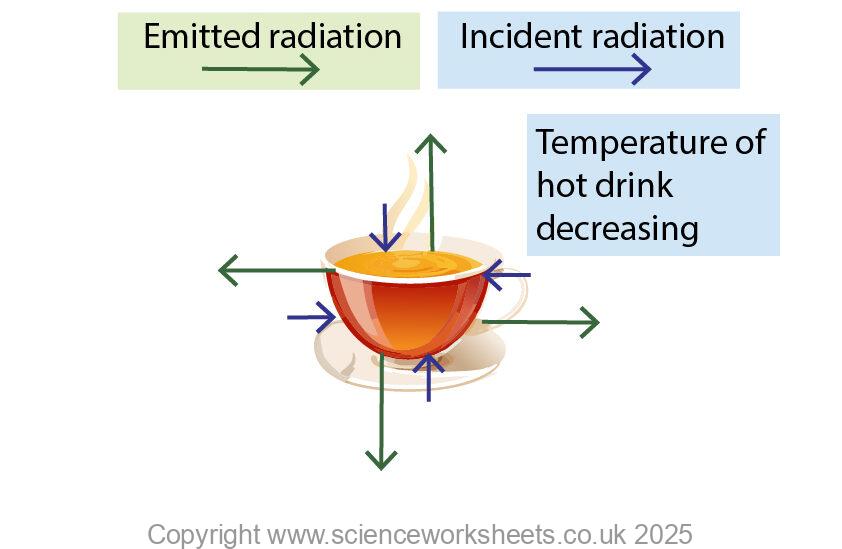
Everyday objects changing temperature.
You need to be able to apply the ideas to everyday examples. In the diagram below a cup of tea is decreasing its temperature because it emits radiation at a greater rate than it absorbs radiation
Practice Question
1.During the day, the temperature of the sand on a beach increases. Explain the temperature increase in terms of incident radiation and emitted radiation
2. The temperature of a refrigerator is kept constant. Explain how this is possible in terms of incident radiation and emitted radiation
3. When liquid water is placed into a freezer it changes into ice. Explain this change in terms of incident and emitted radiation.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque