AQA GCSE Resolving Forces(Physics)
Resolving Forces
A single force can be resolved into two components acting at right angles to each other.
Lets look at a single diagonal force on a free body diagram.
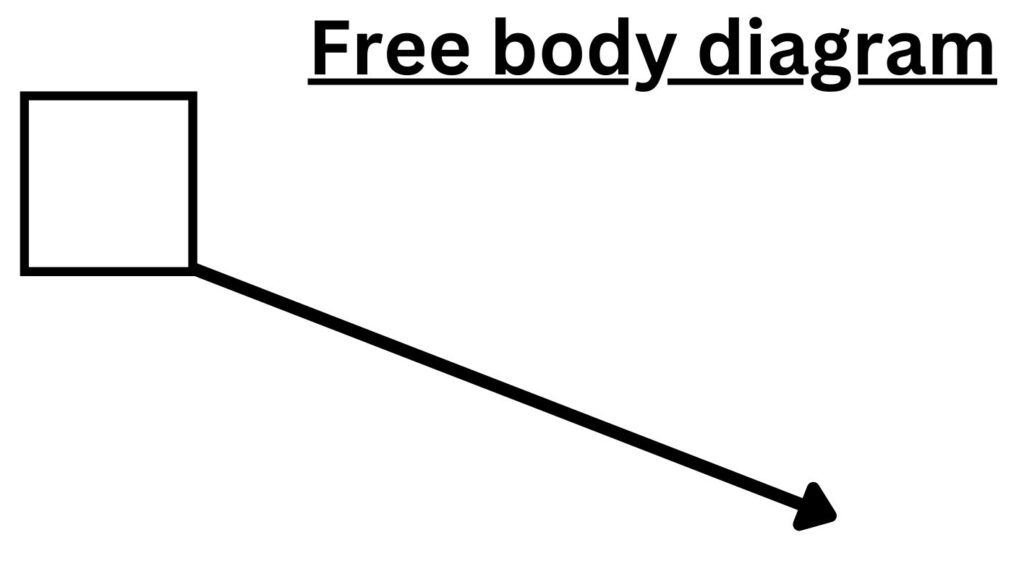
This single diagonal force can be split into a horizontal and vertical components as show below:
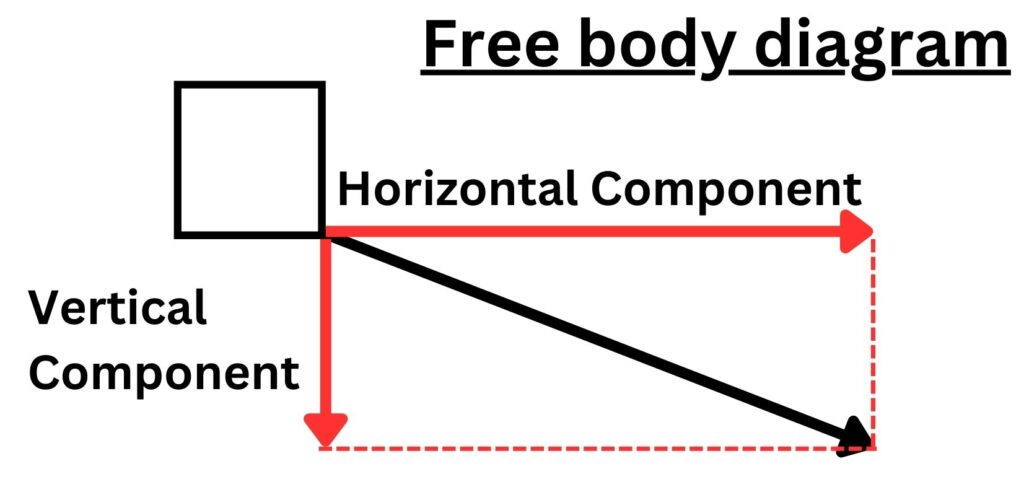
The two component forces together have the same effect as the single force.
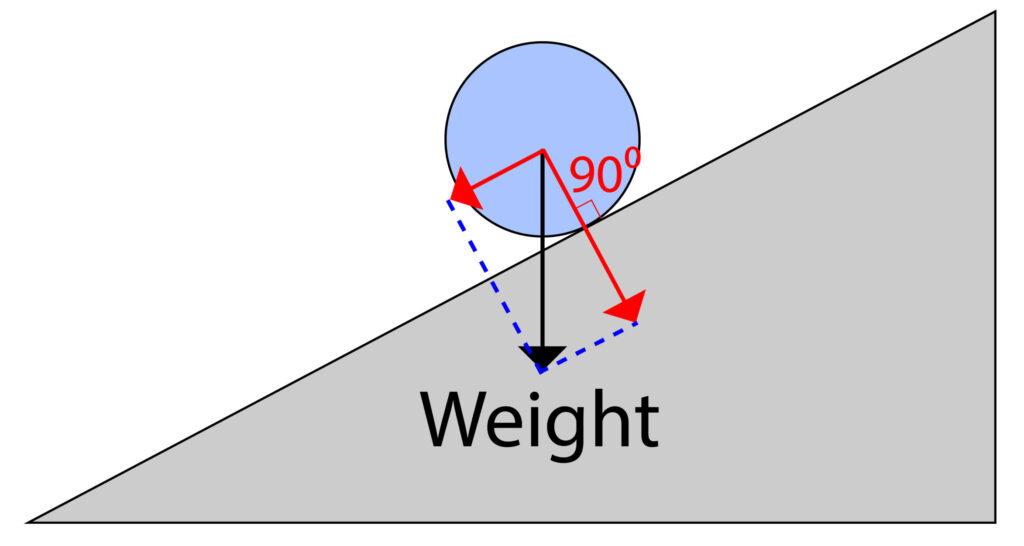
Ball rolling down a slope
When a ball rolls down a slope, its weight acts directly downwards as shown by the force arrow on the diagram below:
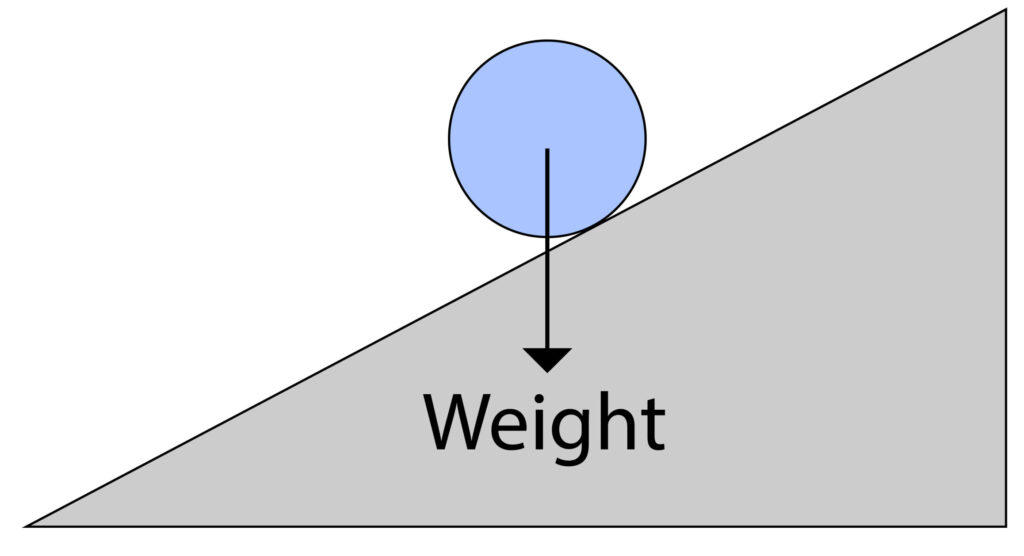
This weight force can be split into two component forces a horizontal one and a vertical one.
Draw an arrow from where the weight arrow starts and ensure that the arrow has a 90 degree angle with the surface of the ramp. This will give the vertical component.
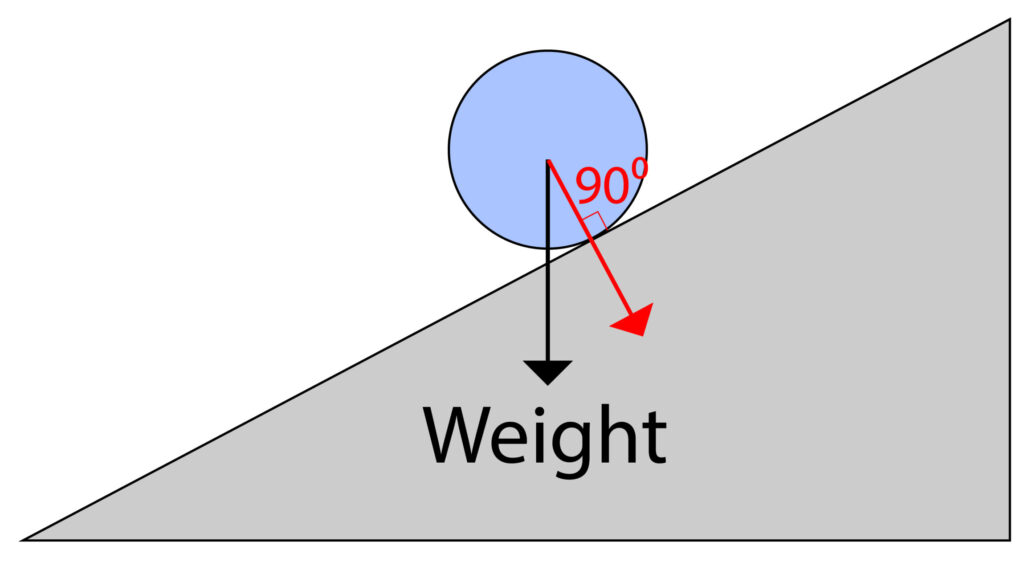
Now draw an arrow from where the weight arrow starts and ensure the arrow line is parallel with the ramp slope to give the horizontal component. Then you can connect all 3 arrows with dotted lines.
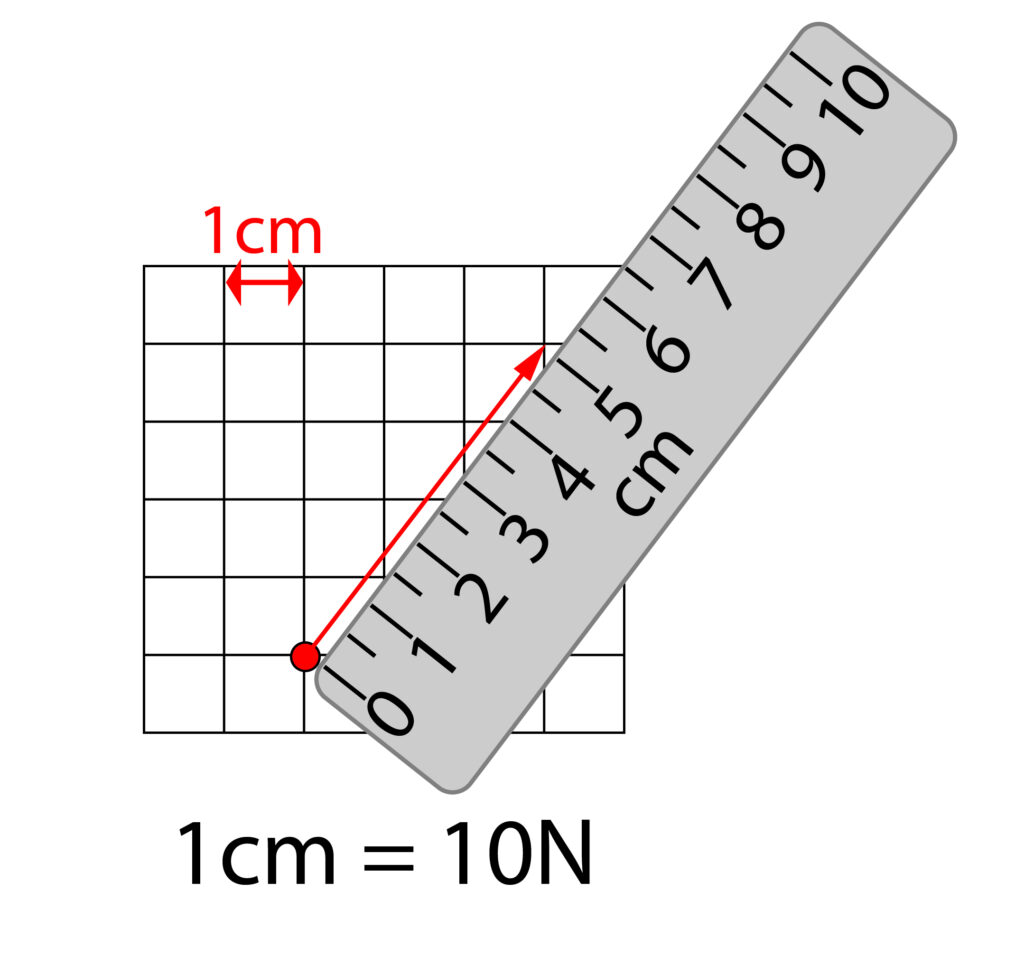
Resolving forces and scale diagrams
A force arrow has been drawn on the grid below. The force arrow is 5cm long in the diagonal direction. Using the scale on the diagram 1cm = 10N. This means that this force arrow is 50N.
Now we will remove the ruler, resolve the force to draw the horizontal and vertical components.
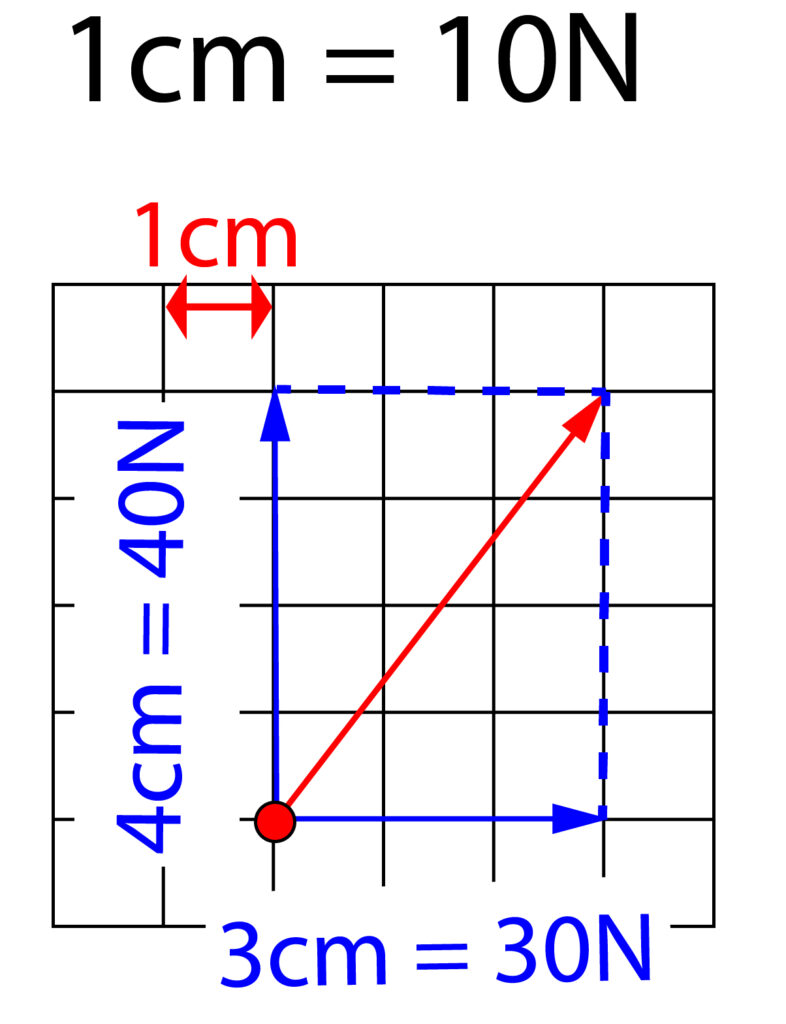
After drawning the dotted lines to complete the shape and using the scale of 1cm per box = 10N, the vertical component is 40N and the horizontal component is 30N.
Practice Questions
1.How can you use a scale diagram to resolve a force of 50 N acting at 45° to the horizontal?
2. Describe how a free-body diagram helps in resolving forces.
3.What is meant by the term resolving a force?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque