AQA GCSE Reflection of Waves(Physics)
Reflection of Waves
All waves can be reflected.
Reflection is when a wave hits a boundary in a medium and bounces off the surface, without changing speed or wavelength.
Reflection of Light waves using a Mirror.
The diagram below is a very common practical that is carried out. First the equipment is set up as shown in the diagram below.
You will need a protractor to measure the angle of incidence and angle of reflection.

To show you clearly how to carry out the practical some of the label lines have been removed in the diagram below.
The ray box is moved so that different angles of incidence are selected.
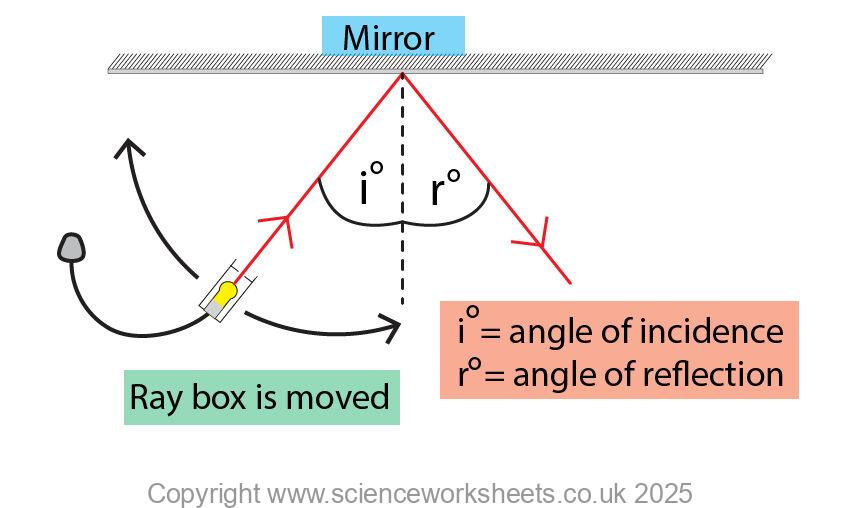
At each angle of incidence, the angle of reflection is measured and recorded in the table below.
| Angle of incidence, io | Angle of reflection, ro |
|---|---|
| 10 | 10 |
| 20 | 20 |
| 30 | 30 |
| 40 | 40 |
| 50 | 50 |
The pattern that you need to notice is that the angle of incidence = angle of reflection. This is known as the law of reflection!
Reflection with wavefronts and wavelengths on the diagram
The diagram with the incident and reflected ray can also be shown with the wavefronts and wavelength.
Distance between two wavefronts is one wavelength.
Notice that the wavelength is the same on both the incident and reflected wave.

Practice Question
1.State what is meant by the term reflection
2. State the law of reflection
3. Write a method explaining how you can prove the law of reflection.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque