AQA GCSE Real or Virtual images (Physics)
Real and virtual images
A real image is formed when the light rays converge to form an image which can be projected onto a screen.
Real images are always inverted by a lens.
A virtual image is an image that looks like it’s coming from behind a mirror or lens, but it’s not really there. You can see it, but you can’t project it onto a screen because the light rays do not actually meet.
| Type of lens | Type of images that can be formed |
|---|---|
| Convex(Converging) | Real or Virtual |
| Concave(Diverging) | Virtual only |
Convex(Converging) Lens to form a Real image
F is the Focal point, so the distance between F and centre of lens is focal length.
2F is the distance of two focal lengths from the centre of the lens.
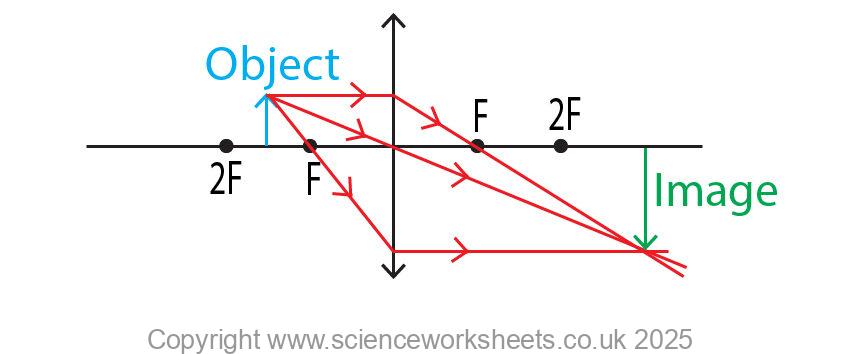
The object in the image below has been placed between F and 2F. Rays of light from the image are refracted by the convex lens to form an image that is :
1. Inverted (arrow has changed direction, it is now pointing down rather than up)
2.Image is larger than the object
3. A real image has been formed on the opposite side of the lens.
Now the object has been placed at 2F in the diagram below.
The image formed is still real and inverted, but do you notice that it is smaller than the previous image, now that the object has been moved slightly left.
The image formed at 2F is actually the same size as the object at 2F.

Now the object is beyond 2F
Again notice how when the object is moved to the left, the image becomes smaller.
The image formed is inverted, real and smaller than the object.

Convex lens (converging) to form a virtual image.
When the object is placed between the convex lens and F, a real image is not formed. Instead a virtual image is formed on the same side of the lens, which is upright and larger than the object as shown in the diagram below.

Concave lens (diverging) to form a virtual image
The object is just beyond F, it will form a virtual image that is upright, smaller than the object between F and the lens, on the same side of the lens as shown in the diagram below.

| Type of lens | Position of object | Real or virtual | Image upright or inverted | Size of image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convex | between lens and F | Virtual | Upright | Larger than object |
| Convex | between F and 2F | Real | Inverted | Larger than object |
| Convex | At 2F | Real | Inverted | Same size as object |
| Convex | Beyond 2F | Real | Inverted | Smaller than object |
| Concave | Between F and 2F | Virtual | Upright | Smaller than object |
Practice Question
1.Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual image.
2. What type of lens would you use to from a real inverted inverted image that is smaller than the object?
3.What type of lens would you use to for a virtual image that is smaller than the object?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque