AQA GCSE Radioactive Decay(Physics)
Radioactive Decay
The nuclei of some atoms are unstable, so they undergo radioactive decay to try to become more stable.
Remember the term isotope?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element, with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
Some isotopes have stable nuclei, others unstable.
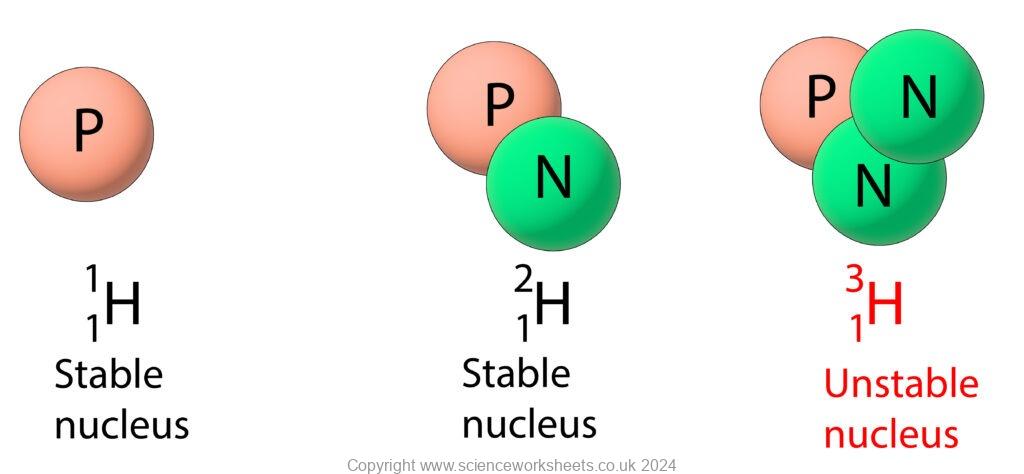
Stable nuclei: This has the correct ratio of protons to neutrons, so the nucleus is stable
Unstable nuclei: This has an incorrect ratio of protons to neutrons, so the nucleus is unstable and will undergo radioactive decay
Hydrogen has three isotopes. The first two isotopes are stable, but the third isotope is unstable. So, hydrogen-3 will undergo radioactive decay to become more stable
What happens during radioactive decay?
During radioactive decay an unstable nucleus will emit radiation to try to become more stable.
The radiation emitted could be one of the following:
1.Alpha particle (Helium nucleus: 2 protons and 2 neutrons)
2.Beta particle (an electron)
3.Gamma wave (electromagnetic wave)
4. Neutron
Emission of a gamma wave
Some nuclei will emit a gamma wave (electromagnetic wave) during radioactive decay.
Fluorine-18 is a gamma emitter
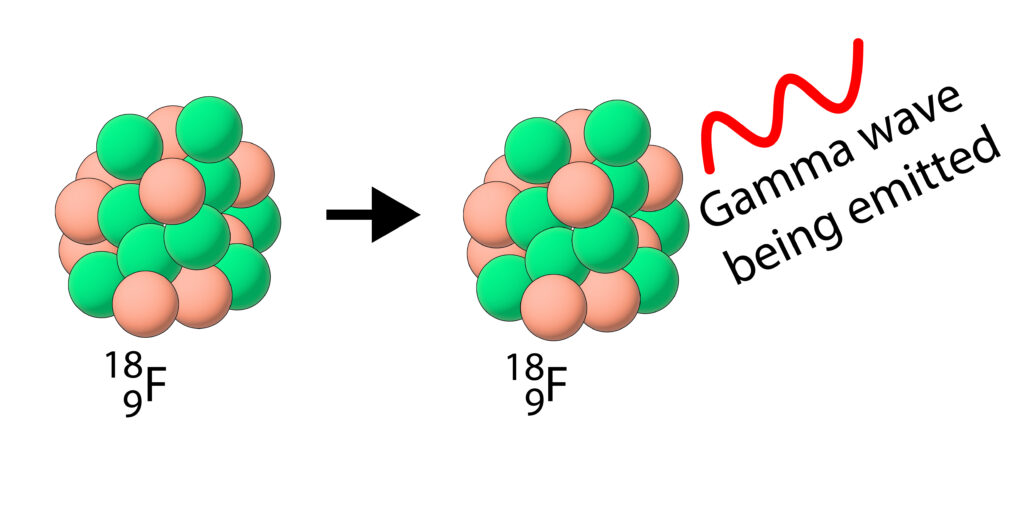
During the gamma decay, the particles in the nucleus do not change, but a gamma wave is emitted and the nucleus now has less energy than before, so it is more stable.
Emission of an Alpha, Beta or Neutron particle.
During some types of radioactive decay a particle can be emitted such as alpa, beta or a neutron.
Alpha Emission
An alpha particle is a helium nucleus, so it contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Polonium-210 commonly undergoes alpha decay to emit an alpha particle (helium nucleus)
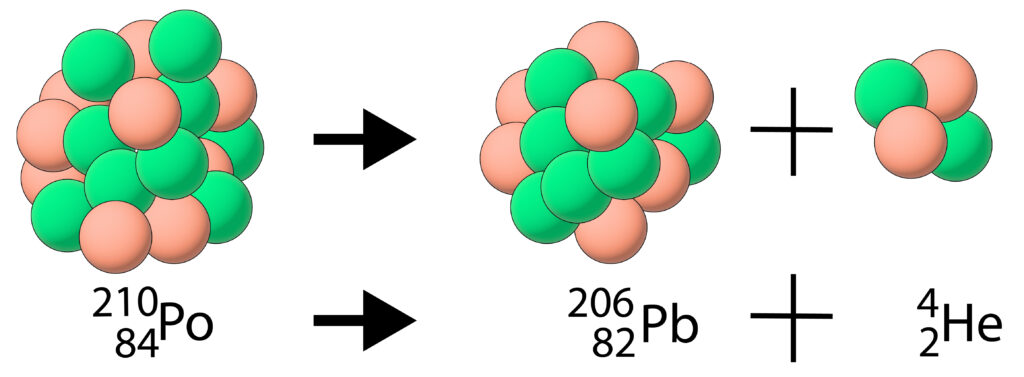
Notice that due to the loss of the alpha particle, the nucleus has changed. As the number of protons have decreased by two, the element has changed from Polonium(Po) to Lead(Pb).
Beta Emission
A beta particle is an electron. During a beta decay a neutron turns into a proton and an electron is emitted.
Beta decay tends to occur when there are too many neutrons in the nucleus.
Remember what we said earlier, nuclei are unstable if the ratio of protons to neutrons is not correct!
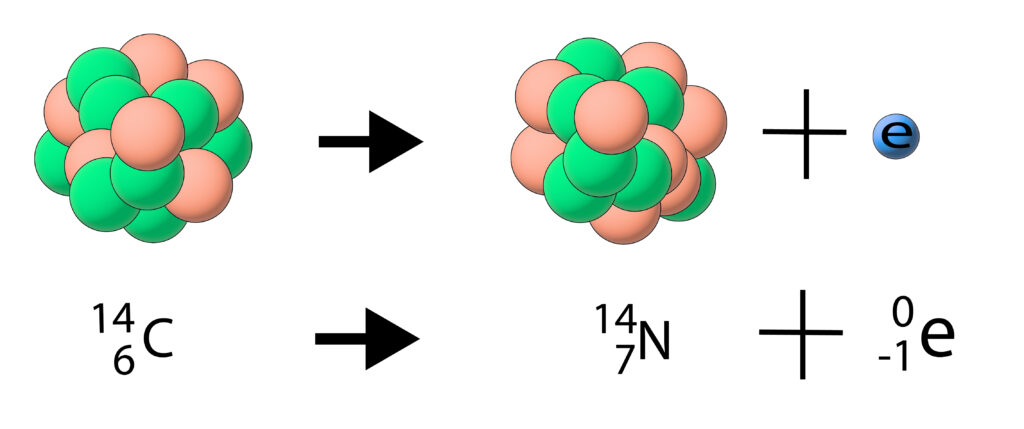
During the beta decay a neutron turns into a proton and an electron is released.This means that the nucleus has changed as there is now one more proton and one less neutron.
Neutron emission
Neutron emission can occur in nuclear reactors. where neutrons are released through nuclear fission.
However, there are other ways that neutron emission can occur such as an alpha particle colliding with a nucleus to make the nucleus unstable and then emit a neutron.
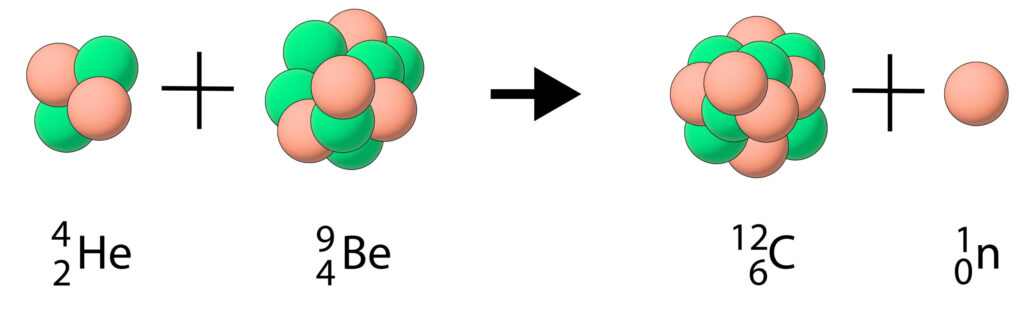
An example of neutron emission is an alpha particle colliding with beryllium-9 to form carbon-12 and emit a neutron.
When does radioactive decay occur?
Radioactive decay is a random process. It can occur any time.
Practice Questions
1.Explain why Carbon-12 does not undergo radioactive decay, but carbon-14 will undergo radioactive decay.
2. State what can be emitted during radioactive decay
3.Describe how the nucleus changes during the following decay types:
3a. Alpha emission
3b. Beta emission
3c. Gamma emission
4.State why it is not possible to predict when radioactive decay will occur.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque