AQA GCSE Perfect Black Body(Physics)
Perfect Black Body
Black surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation.
We can define a perfect black body as:
An object that absorbs all of the radiation incident on it
This means that a perfect black body will not reflect or transmit any radiation.
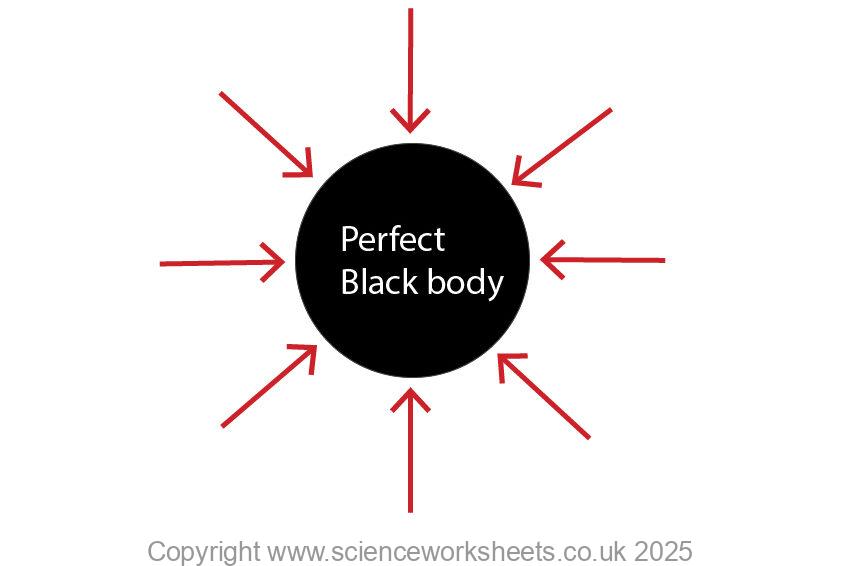
In the diagram below the black sphere is acting as a perfect black body absorbing all of the incident radiation and transmitting or reflecting none.
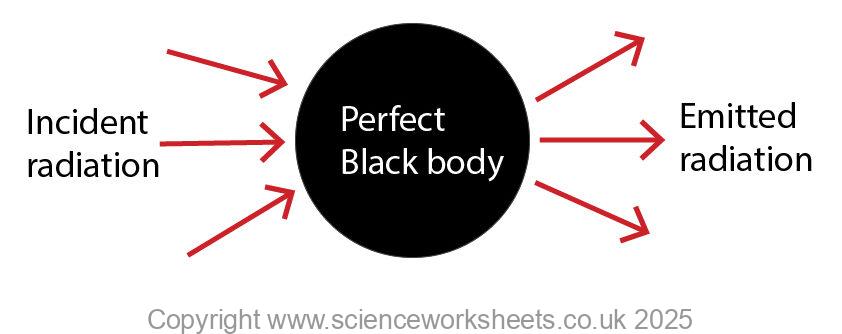
Perfect black bodies as emitters.
Any body that is a good absorber, is also a good emitter.
This means that a perfect black body is also the best possible emitter of radiation.
When the black body absorbs the incident radiation, its temperature increases, as a result it will then emit radiation.
Perfect Black Body and Temperature
The temperature of a perfect black body depends on the rate of absorbtion of incident and the rate of emitted radiation.
Rate of energy absorbed > Rate of energy emitted then temperature increases
Rate of energy absorbed = Rate of energy emitted then temperature is constant
Rate of energy absorbed < Rate of energy emitted then temperature decreases
Practice Question
1.Define the term perfect black body
2.In the table below tick the boxes next to the correct statements for a perfect black body
| Statement | Tick if correct |
|---|---|
| Absorbs all of the incident radiation | |
| Can reflect radiation | |
| Can transmit radiation | |
| Is the best possible emitter |
3. A perfect black body has a constant temperature. What can you deduce about the incident and emitted radiation for the perfect black body?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque