AQA GCSE Nuclear Equations(Physics)
Nuclear Equations
There are 3 main types of nuclear equations:
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma decay
Alpha Decay
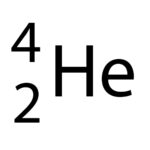 Alpha particle contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons
Alpha particle contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons
An alpha particle is written as a helium nucleus seen in the picture to the left.
When an unstable nucleus undergoes an alpha decay the structure of the nucleus changes because an alpha particle is released. As the number of protons in the nucleus will change, it means that a new element is formed.
The new daughter nucleus, in this case lead, Pb will have less mass and less charge.
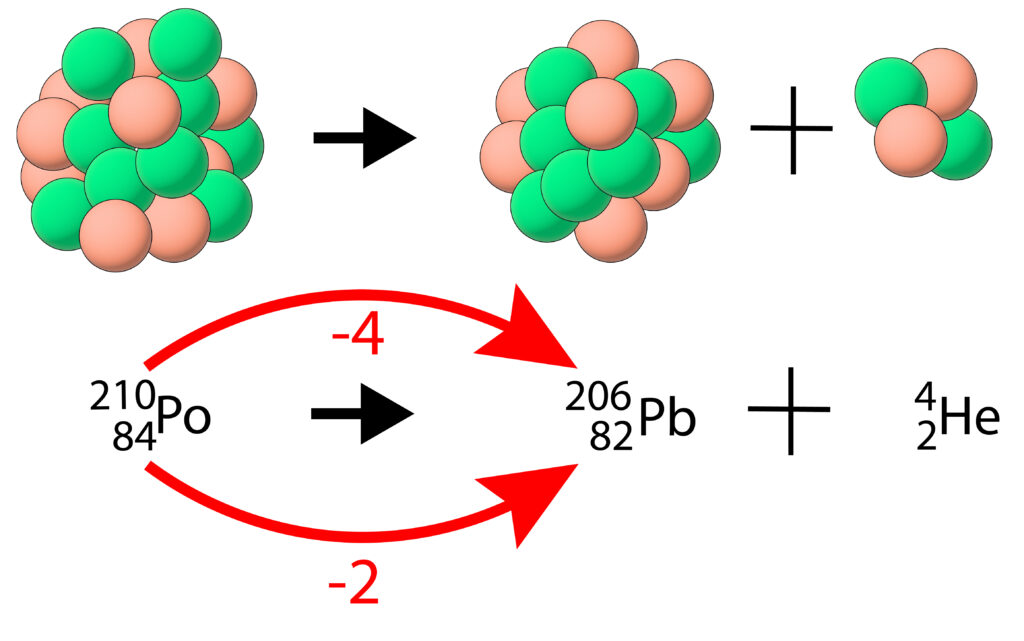
Subtract 4 from the mass number(top number) and 2 from atomic number(bottom number).
Then look up the symbol for the new element, in this case it will be the symbol for 82, which is Pb.
Finally add on an alpha particle which is represented by a helium nucleus.
Beta Decay
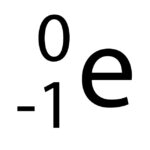 A beta particle, or electron is represented in Physics using the symbol on the left.
A beta particle, or electron is represented in Physics using the symbol on the left.
During a beta decay a neutron turns into a proton and a high speed electron is emitted from the nucleus.
This means that both the mass and the charge of the nucleus will change. As the proton number or atomic number changes, so will the element.
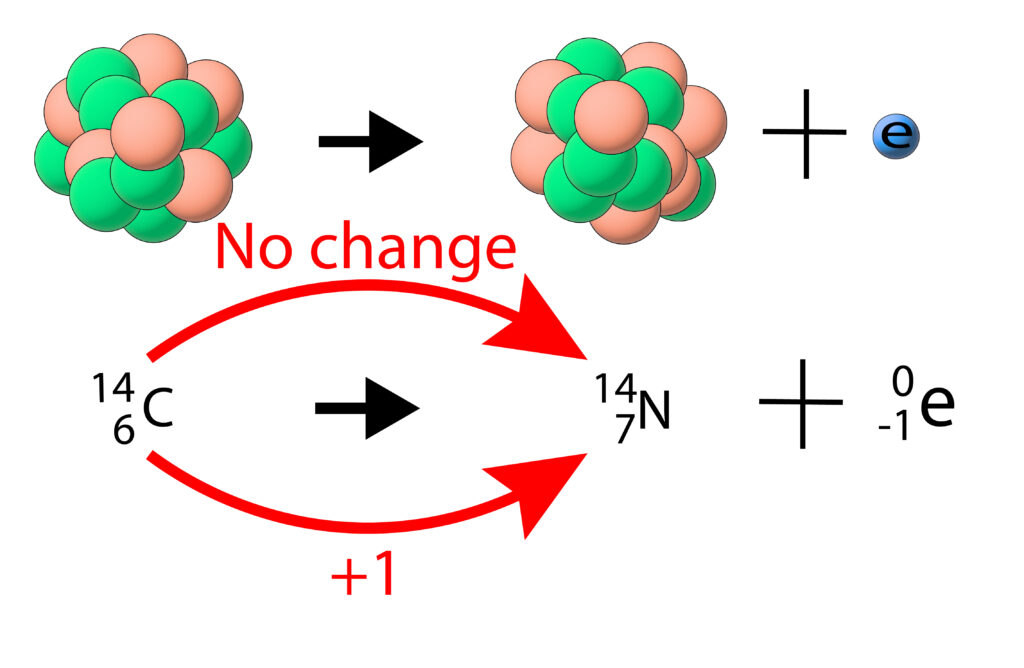
The mass number (top number) stays same
The atomic number (bottom number) increases by one, as a neutron turns into a proton.
Look up the symbol for the new atomic number. In this case it is nitrogen, N.
Add an electron onto the end.
The mass of the nucleus decreases because of the emitted electron.
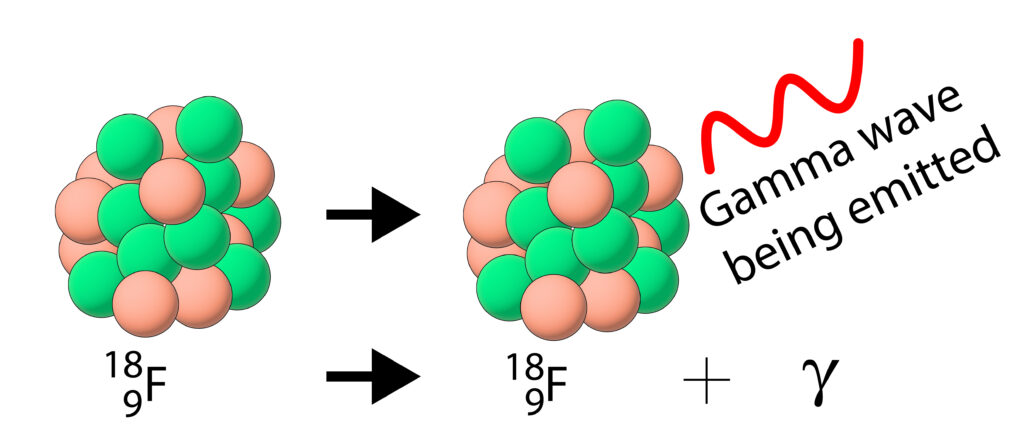
Gamma Decay
During gamma decay, the mass or charge of the nucleus does not change.
Instead the nucleus emits gamma radiation and the nucleus has less energy after the gamma decay
Practice Questions
1. Complete the following decay equations for a single alpha decay

2. Complete the following decay equations for a single beta decay

Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque