AQA GCSE Mains Electricity(Physics)
Mains Electricity
UK Mains electricity is 230 Volts, 50 Hertz and is Alternating Current (AC).
Alternating means that it will continuously change direction as shown below.
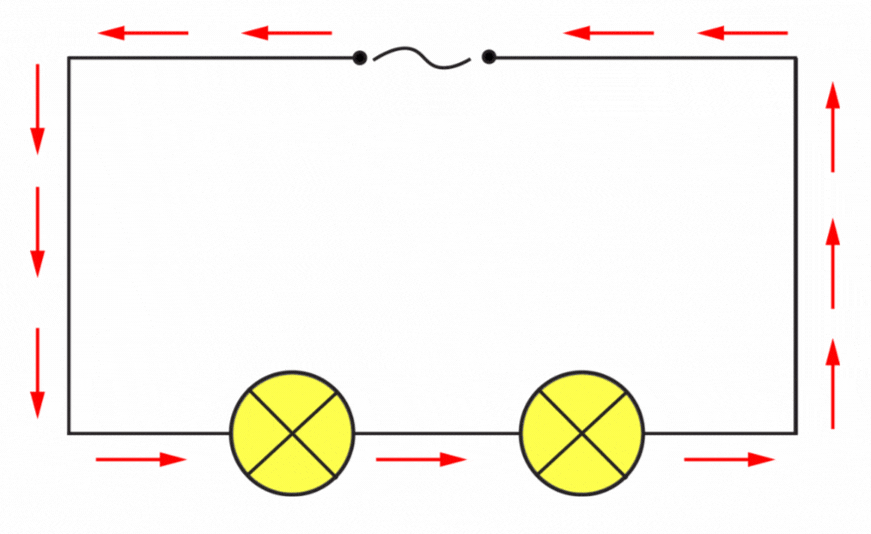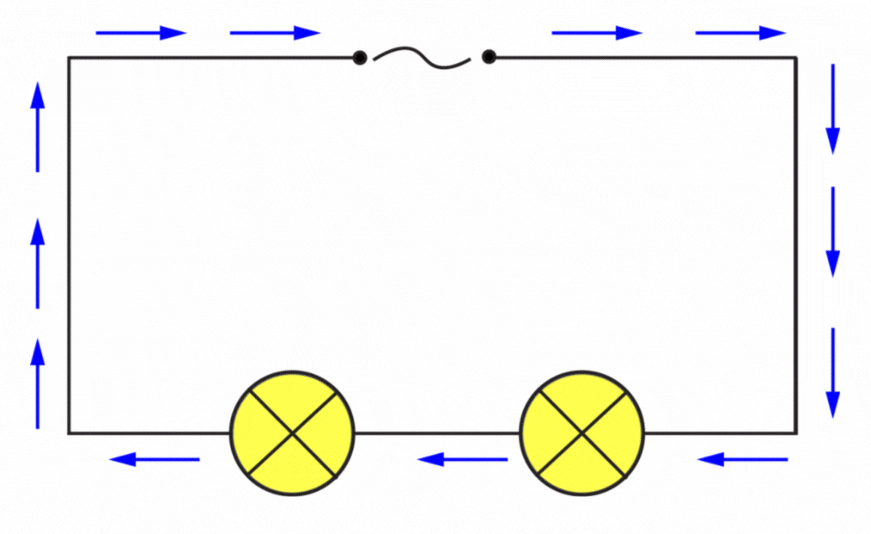
UK Electricity is 50 Hz, this means that the direction changes 50 times per second, so the generator that is producing this electricity, rotates at a rate of 50 times per second!
Different countries will use a slightly different frequency. USA uses 60Hz.
UK Mains Plugs
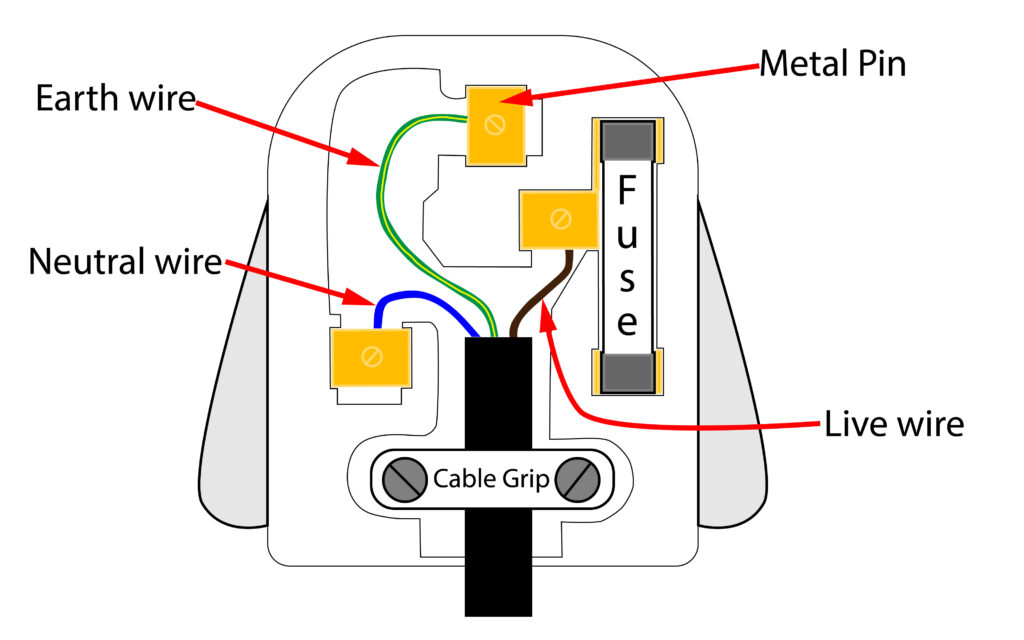
In the above plug 3 core cable is used, so it contains Live(brown), Neutral(blue) and Earth wire (green-yellow).
Electrical appliances with a metal case need an Earth wire. Appliances with a plastic case are said to be double insulated, they only need two core wire (live and neutral).
Role of the wires
Live wire will carry the alternating potential difference from the mains supply to the appliance. Remember it alternates at 50 times per second in UK. UK Electricity is 50 Hz.
Neutral wire will complete the circuit, it should be earthed at 0V at the local substation. In some cases the potential difference of the neutral wire is almost 0V. Without the neutral wire the circuit is incomplete, so it is needed!
Earth wire is Earthed at 0V, it should not carry a current. It will carry a current if the appliance becomes faulty. If the live wire were to break, make contact with electrical case, charges flow onto the case. So, case becomes live.
The Earth wire connects the metal case to Earth, allowing these charges to flow to Earth.
This would prevent an electric shock if someone touches the case.
See our dedicated page on Earth wires.
Practice Questions
1.Describe the difference between two core and three core wire
2. State the colours of the following wires:
Live
Neutral
Earth
3. Explain why both the live and neutral wire is needed for an electrical appliance to work.
4. State the function of the cable grip in the plug.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque