AQA GCSE Magnetic Fields(Physics)
Magnetic Fields
A magnetic field is a region of space where a force due to magnetism is experienced by a magnetic material or magnet.
Magnetic materials include iron, steel, cobalt and nickel.
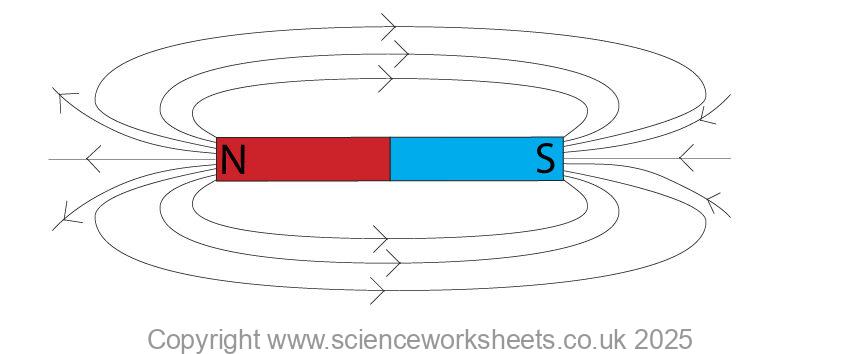
Strength of the magnetic field.
The magnetic field is always strongest at the poles of the magnet where the field lines are closest together.
Strength of magnetic field also depends on distance. The further from the magnet, weaker the magnetic field as the field lines are further apart.
Force and Magnetic Field
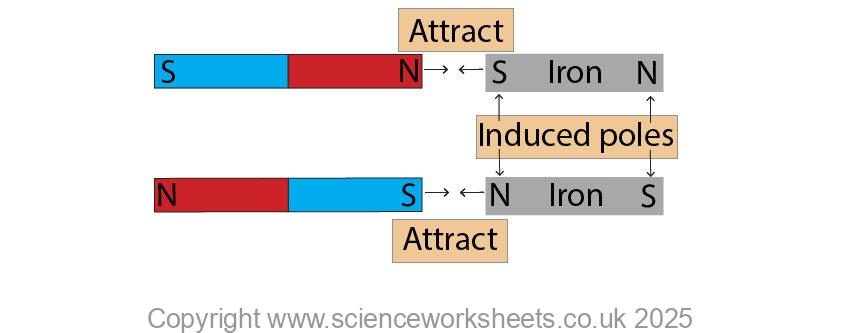
A magnet will only ever exert a non contact force of attraction on a magnetic material.
When unmagnetised iron is placed near the poles of a magnet, it become magnetised and is then attracted to the magnet.
Direction of the Magnetic field.
The direction of the magnetic field at any point is given by the direction of the force that would act on another north pole placed at that point.
Lets break this statement down into easier terms
When you are near a magnet, the magnetic field points in the direction a compass needle (the north end) would point.
This can be seen in the diagram below where the compass needle (north end) points towards the south pole of the permanent magnet.

The direction of a magnetic field line is from the north (seeking) pole of a magnet to the south(seeking) pole of the magnet. This is shown in the diagram above
Practice Question
1.Define the term magnetic field.
2. Describe how you could indicate the strength of a magnetic field when drawing the magnetic field lines on a piece of paper
3.State the direction that the magnetic field lines travel in
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque