AQA GCSE Introduction to Electromagnetic waves(Physics)
Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves.
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber.
A transverse wave will vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction in which it transfers energy.
We will talk about how they transfer energy from a source to an absorber later, this can be complicated! This will be the next page.
All electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, they do not need a medium to travel through.
When electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum, they all travel at the same speed 3 x 108m/s.
All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed through air as well.
Electromagnetic Spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic (EM) radiation.
The electromagnetic spectrum is called a continuous spectrum because it consists of an unbroken range of wavelengths and frequencies, without any gaps between them. As shown below:
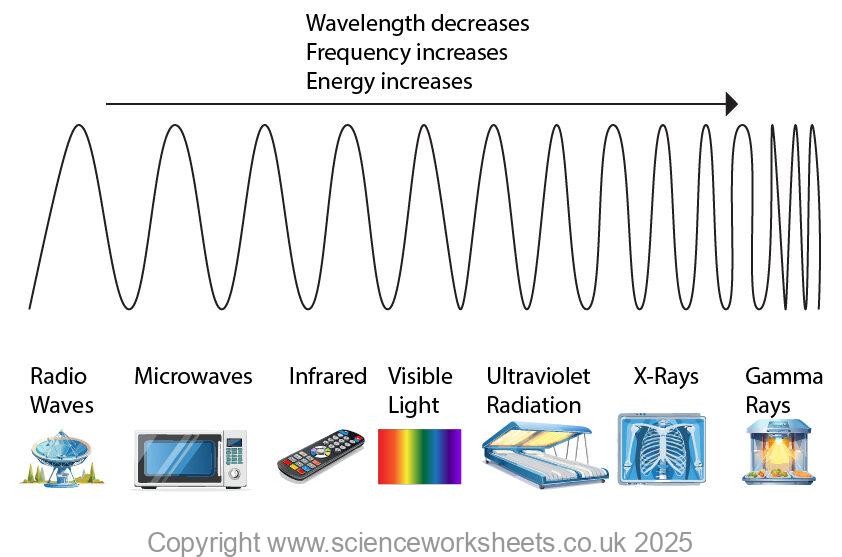
Visible light
We can use our eyes to detect the presence of visible light.
Visible light is a tiny part of the electromagnetic spectrum, so we can only detect a very limited range of electromagnetic waves with our eyes.
There are other animals which can detect a wider range of electromagnetic waves.
Practice Question
1.State the definition of Electromagnetic waves.
2. A radiowave and a visible light ray are emitted from the same point on the Earth, both travel in the same direction. Which one will reach their destination first?
3. What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque