AQA GCSE Explaining pressure in a column of liquid(Physics)
Explaining pressure in a column of liquid
Pressure in a liquid will increase with depth of the liquid. This is shown by the diagram below.
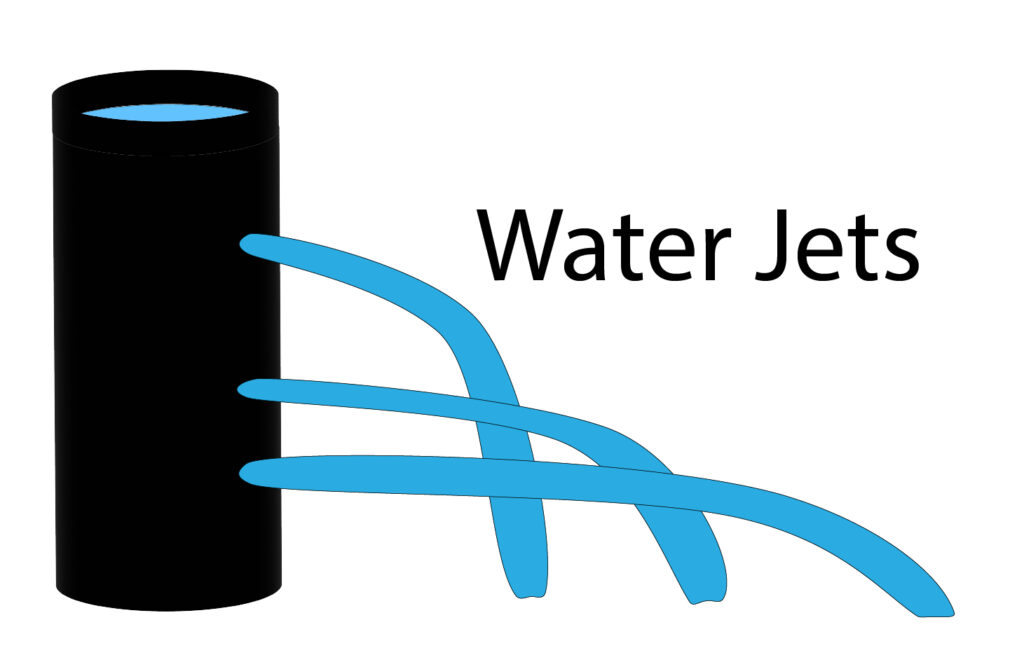
The deeper the hole is from the surface of the water, the further the water jet will travel. As the water jet travels further it must have a greater force, due to the water pressure being greater at increased depth below the surface.
Height from the surface of the liquid and pressure
As the height from the surface of the liquid to the object increases, the pressure exerted on the object by the liquid will also increase.
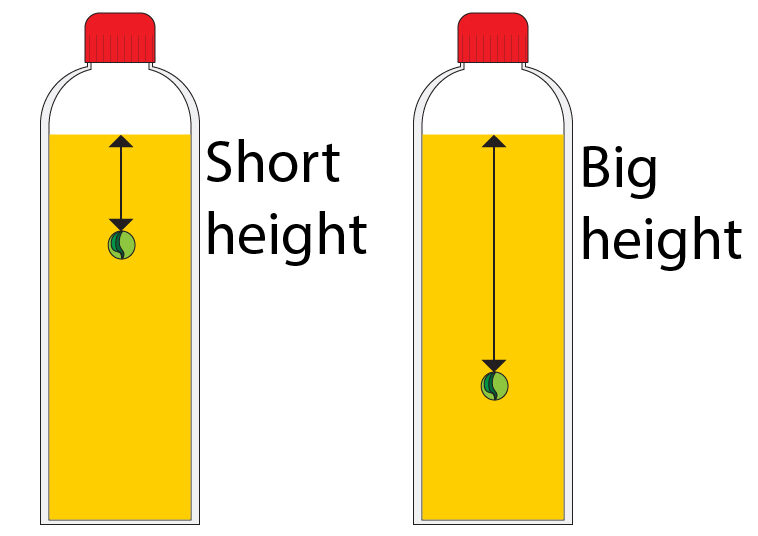
There is a short height between surface of the oil and the marble, so there is less weight of oil above the marble, so less pressure is exerted by the oil onto the marble.
There is a big height between surface of the oil and the marble, so there is more weight of oil above the marble, so more pressure is exerted by the oil onto the marble.
Density of the liquid and pressure
Below is an image of water and liquid mercury. In each liquid a glass marble is suspended. Mercury has a much bigger density than water.
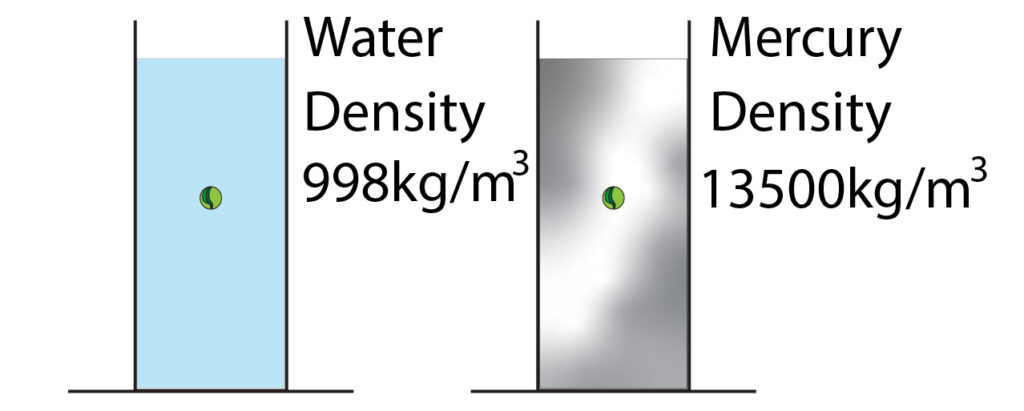
The greater the density of the liquid, the greater the weight of liquid that acts on the marble, so the greater the pressure.
In this case, Mercury has a bigger density than water, so the Mercury will exert more pressure on the marble.
Practice Questions
1. State how the pressure of a liquid changes with depth of the liquid
2.Explain why the pressure of a liquid will change with depth of liquid
3.Use the table below to answer the following questions
| Liquid | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|
| Water | 1000 |
| Oil | 920 |
| Mercury | 13560 |
| Ethanol | 789 |
Select the correct option below which ranks the liquids in order of increasing pressure exerted on a submerged object
a)Oil-Ethanol-Water-Mercury
b)Ethanol-Oil-Water-Mercury
c)Mercury-Water-Oil-Ethanol
d)Water-Mercury-Oil-Ethanol
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque