AQA GCSE Electromagnetic Circuit Diagrams (Physics)
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a solenoid with an iron core. You need to be able to interpret circuit diagrams like the one below.
In the one below, when the switch is closed, a current flows through the coil, soft iron core becomes magnetised and an electromagnet is formed.
When the switch is open, circuit is incomplete, current stops flowing, soft iron core demagnetises and electromagnet is no longer present.

Electromagnets in scrap yard cranes
When the crane operator pushes a switch to complete the circuit, current flows through solenoid and an electromagnet is formed. This allows the crane to pick up scrap iron.
The iron is then moved to a new location. Crane operator pulls the switch to break the circuit, so current stops flowing, solenoid demagnetises. The crane drops scrap iron.


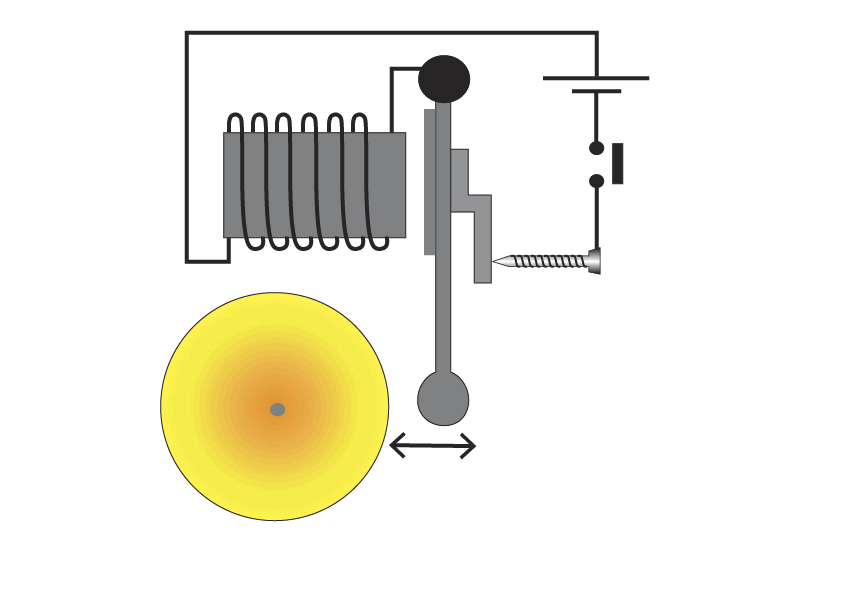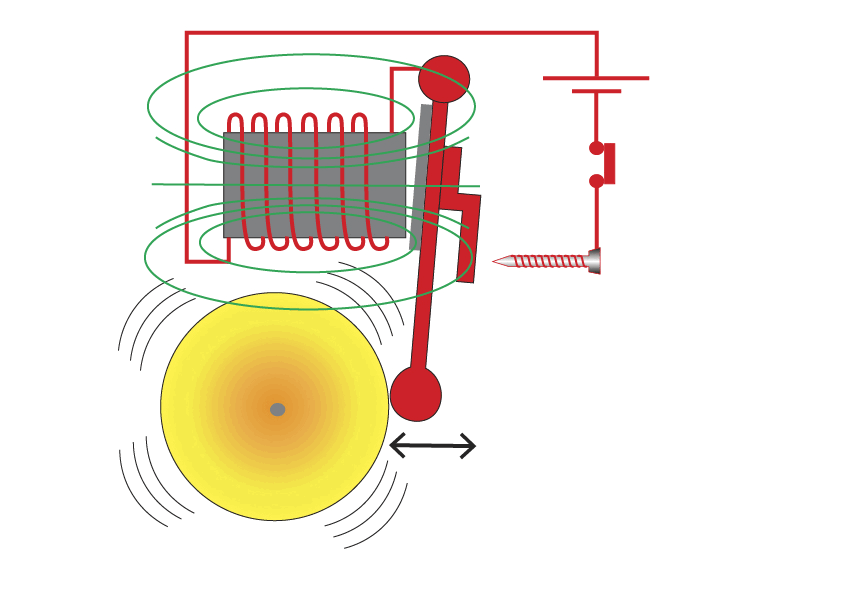
The Electric Bell

1.Switch, when the switch is closed the circuit is complete
2. Once switch is closed, current flows through the coil
3. Electromagnet is formed
4. The iron armature is now attracted to the electromagnet, so iron armature moves to left
5. Striker will hit the bell, as it does the circuit is broken
6. A gap appears between contact screw and the contact plate on the striker. This breaks the circuit, once striker has hit the bell it springs back to reconnect the contact screw and plate. Circuit is complete and process repeats.
As a result the striker will continuously move left and right hitting the bell, whilst switch is closed.
Relays
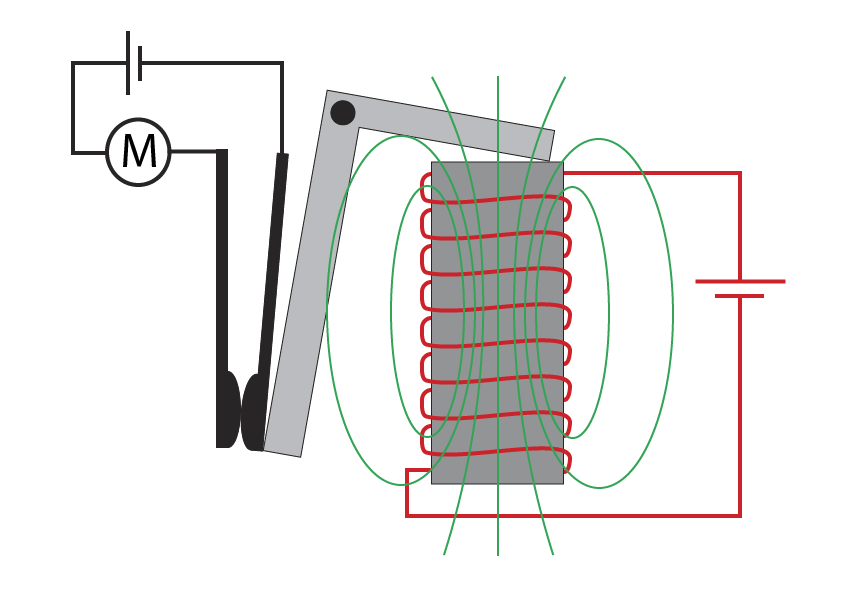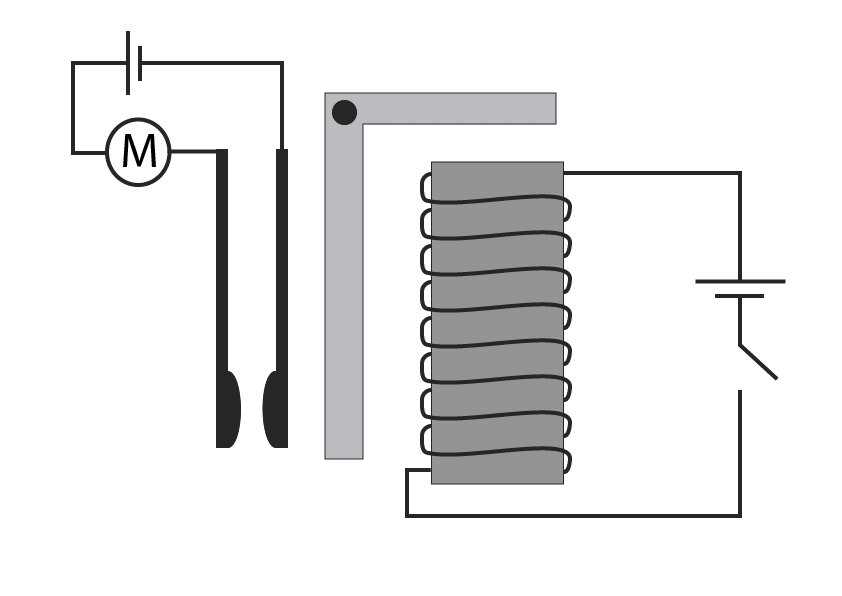
A relay is where a small circuit is used to switch on a larger circuit.
When the switch is closed in the circuit below, the circuit on right is complete, current flows through the coil and a magnetic field forms around solenoid. The newly formed electromagnet attracts the iron armature down.
The iron armature is on a pivot, so as its pulled downwards, the bottom part moves to the left to push the contacts together on the motor circuit. The motor circuit is now complete so the motor will start.
Practice Question
1.Explain how a scrap yard crane works to be able to pick up and drop scrap iron.
2. Below is a circuit diagram of an electromagnetic lock. Suggest how it works to unlock the door
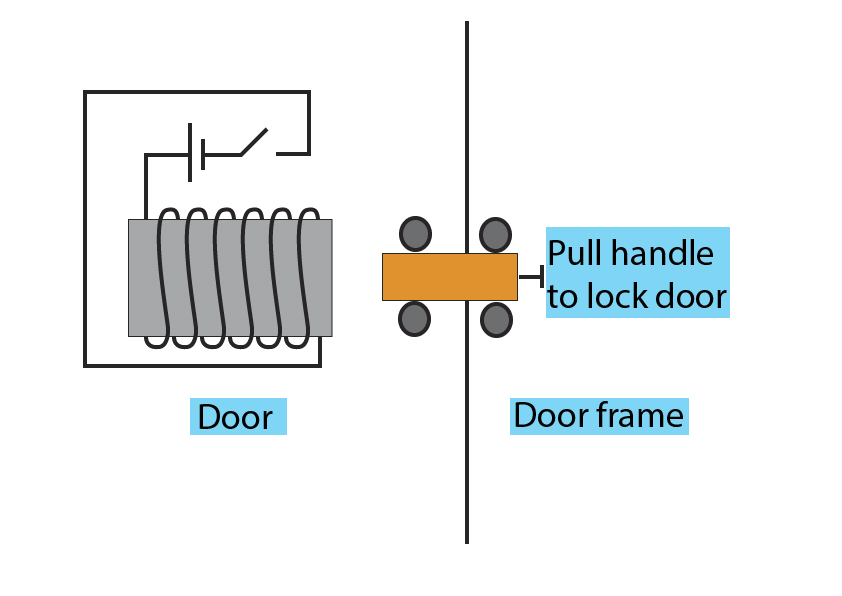
3. Explain how a relay can be used to switch on a larger circuit using a smaller circuit.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque