AQA GCSE Electric Motors (Physics)
Electric Motors
When a current carrying coil of wire is placed into a magnetic field it will rotate. This is the basis of an electric motor.
We will look at brushed, Direct current motors.
On both sides of the coil, the current flows in the opposite direction. Due to the motor effect, one side of the coil experiences an up force and the other side of the coil will experience a down force. So, the coil of wire will start to rotate as shown below.
Remember you can apply Fleming’s left hand rule to work out which side of the coil will go up and which side goes down!

Split ring commutator
All electric motors that are direct current and have brushes will have a split ring commutator.
A split ring commutator will swap the electrical contacts every half turn. This allows for the coil to continue rotating in one direction 360 degrees.
By “brushed” we mean an electric motor where there are carbon brushes that make contact with split ring commutator. These provide a permanent electrical connection, but allow free rotation.
The split ring comutator, brushes and part of the coil is shown below.
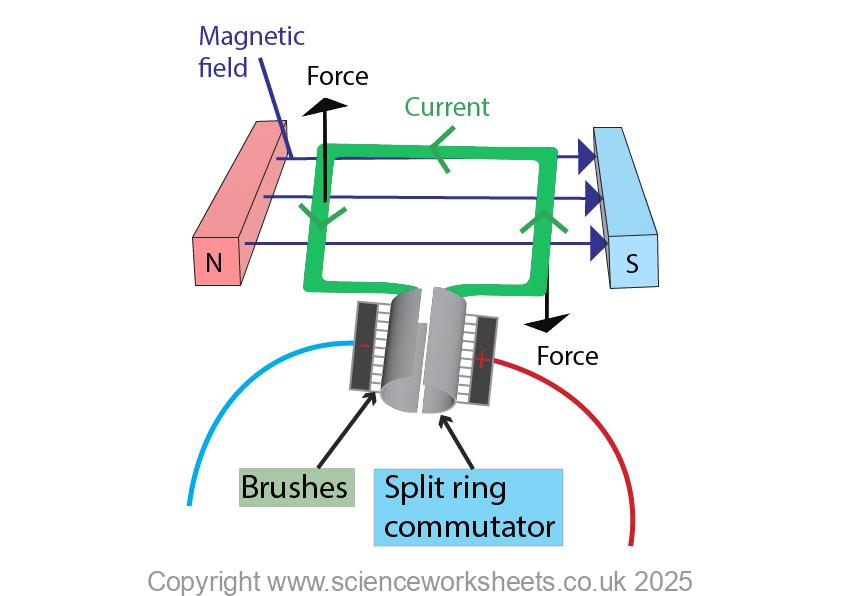
Applying Fleming’s left hand rule to an electric motor
On the left hand side of the coil:
1.Magnetic field is north to south, in this case this will be from left to right. So, first finger will point to the right.
2. Current is coming towards you, so second finger should point towards you.
3. Direction of force is upwards, so your thumb should point towards the ceiling
On the right hand side of the coil:
1. Magnetic field is north to south, in this case this will be from left to right. So, first finger will point to the right.
2. Current is flowing away from you, so your second finger should point towards the wall infront of you.
3. Direction of force is downwards, so your thumb should point towards the floor.
Look at the diagram below, to help to guide you.

Practice Question
1. Expain the function of the split ring commutator in an electric motor
2. Explain the function of brushes in an electric motor
3. Suggest what would happen if an alternating current were connected to a direct current brushed motor
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque