AQA GCSE Displacement and Distance(Physics)
Distance and Displacement have different meanings
| Distance | Displacement | |
|---|---|---|
| Scalar/Vector | Scalar | Vector |
| Definition | How far an object travels or moves | How far an object travels or moves in a certain direction |
| Units | Metres (m) | Metres (m) |
Distance
As distance is a scalar quantity, it has a magnitude only, no direction.
In the diagram below the football is kicked and passes between several players before it reaches the other goal. During its journey it travels 250m.
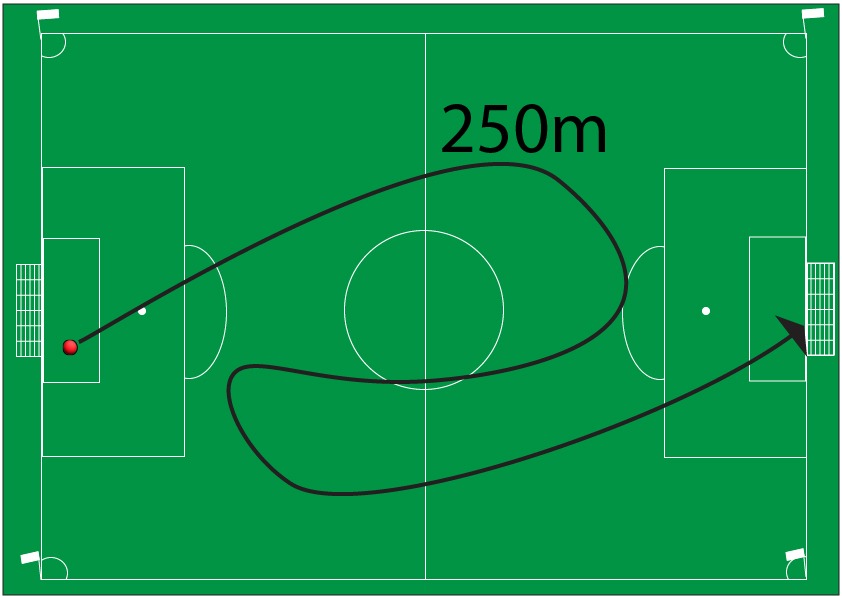
Displacement
Displacement is the distance travelled in a certain direction. The rule here is that it has to be a straight line from where the object starts to where it finishes. In the diagram below you can see displacement of the football shown. The total displacement is 105m in an East direction.
The original 250m arrow which represents distance has been left in place, so you can compare the difference between displacement and distance
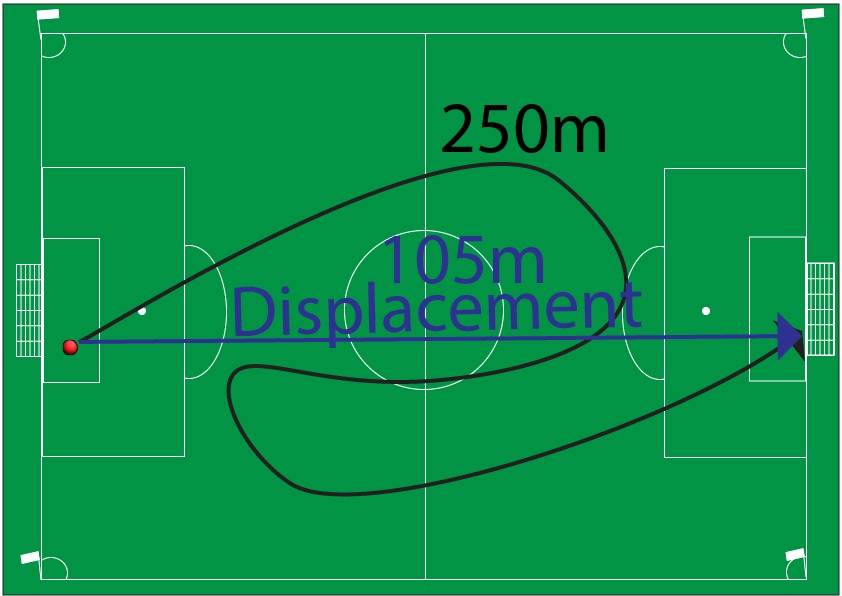
Notice how the displacement arrow in purple is a single straight line from start to finish.
Practice Questions
1. Define the terms distance and displacement
2. Is distance a scalar or vector quantity?
3. Is displacement a scalar or vector quantity?
4. Explain why the displacement for the football in the above diagrams is 105m, but the distance travelled is 250m.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque