AQA GCSE Characteristics of Waves(Physics)
Characteristics of Waves
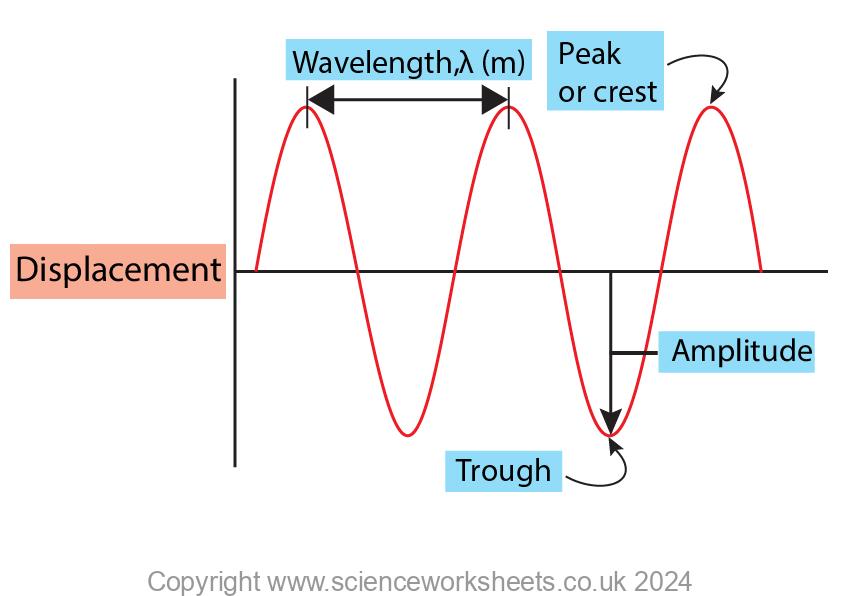
You will need to learn the labels on the diagram below.
If you need to draw a diagram like this in the exam and its hard to draw the curved line, use tiny “x” to mark out the positions first such as peaks and troughs. Then just draw over these, they will help guide you to draw these correctly.
Key definitions
Wavelength is the distance from one point on a wave, to the same point on the next wave. Wavelength is measured in metres.
Amplitude is the maximum displacement of a point on a wave away from its undisturbed position. Amplitude is a measure of the energy of a wave.
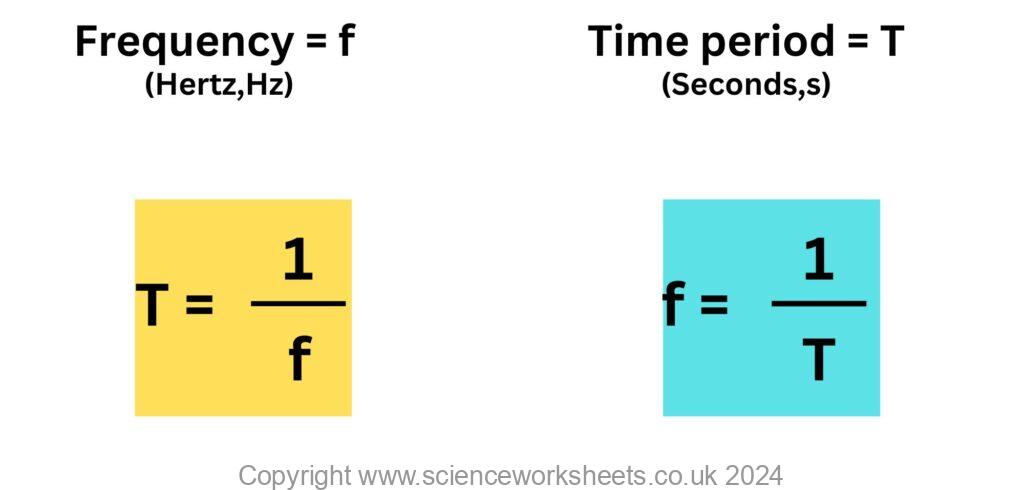
Frequency and Time Period.
Frequency,f of a wave is the number of waves passing a point each second. Frequency has units of Hertz (Hz). 1 wave per second = 1 Hz.
The time period, or period, T is the time taken for each wave to pass a fixed point. Time period is measured in seconds,s.
Both frequency and time period are linked by an equation, see below.
Example calculation
1.A wave has a frequency of 20Hz. Calculate the time period.
T = 1/f
T = 1/20 = 0.05 seconds
2. A wave has a time period of 0.01 seconds. Calculate the frequency
f = 1/T
f = 1/0.01 = 10Hz
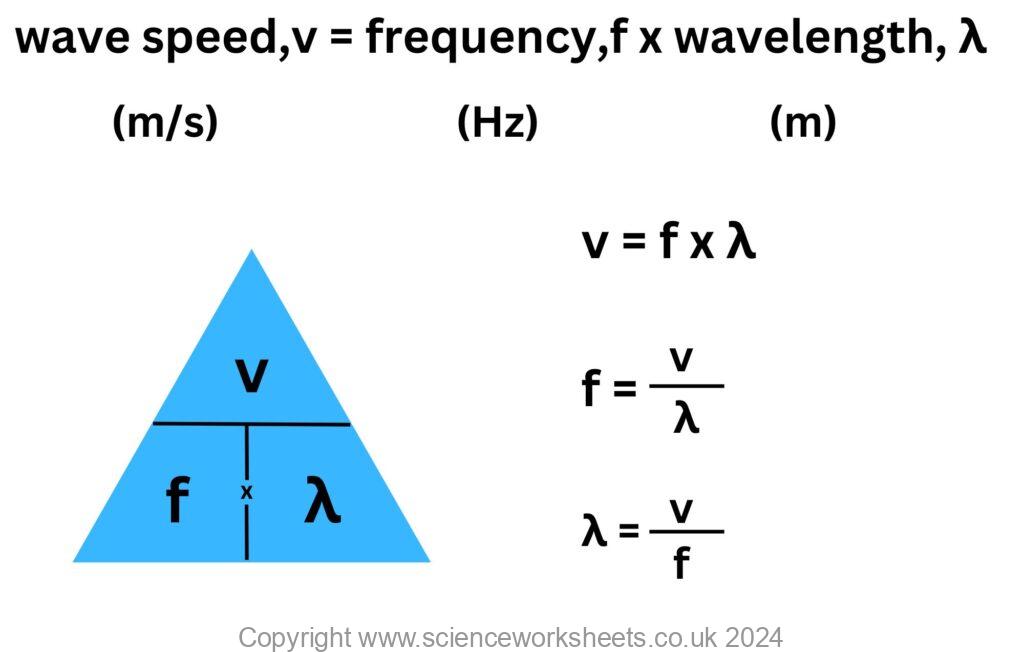
Wave Speed
The wave speed is the speed at which the energy is transferred (or the wave moves) through the medium.
There is an equation that you need to know for wave speed, shown below.
Example Calculation.
A wave has a wave speed of 20m/s and a wavelength of 0.4m. Calculate the frequency of the wave.
f = v/λ
f = 20/0.4 = 50Hz
Combining the equations!
It is possible to combine the equations
v = f x λ and f = 1/T
v = (1/T) x λ
A wave has a time period of 0.2 seconds and a wavlength of 0.8m. Calculate the wave speed
v = (1/T) x λ
v = (1/0.2) x 0.8 = 4m/s
Practice Question
1.State the definition for wavelength
2.State the definition for amplitude
3. State the defintion for frequency
4.State the definition for time period
5. Write the equation which links Time period and frequency
6. Write the equation which links wave speed, frequency and wavelength
7. A wave has a wave speed of 10m/s and a wavelength of 0.1km. Calculate the frequency
8. Calculate the time period of a wave which has a frequency of 1000kHz.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque