AQA GCSE Calculations for Transformers part 1 (Physics)
Calculations for Transformers
The relationship of the potential differences across the primary and secondary coils of a transformer Vp and Vs depends on the relationship of the number of turns on each coil, np and ns .
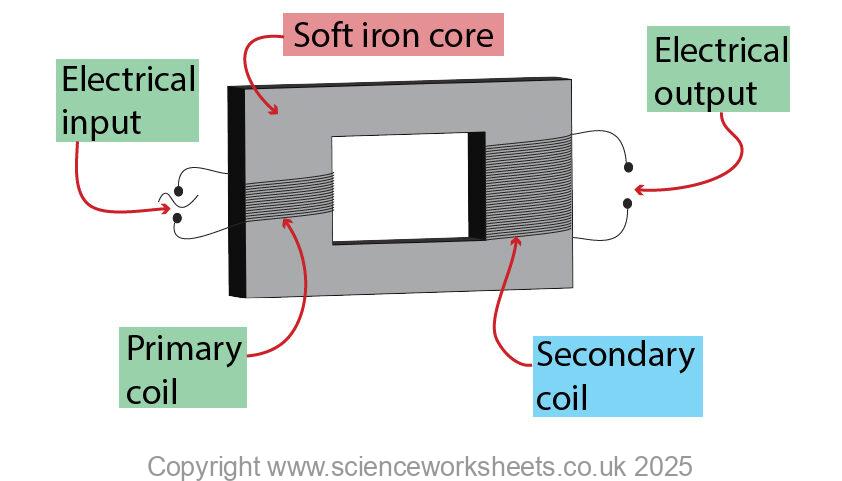

Vp = Potential difference across primary coil
Vs = Potential difference across secondary coil
Np = Number of turns on primary coil
Ns = Number of turns on secondary coil
We can rearrange this equation into this more useful format by cross multiplication

We have rearranged the equation into the four possible rearrangements that come from the cross multiplied equation above

Example calculation
230V alternating potential difference is applied across the primary coil of a transformer which has 460 turns. The secondary coil has 1840 turns.
Calculate the potential difference across the secondary coil.

Practice Questions
1. A transformer has 200 turns on the primary coil and 1000 turns on the secondary coil.If the input voltage is 240 V, calculate the output potential difference.
2. An electric toothbrush charges using a transformer. The charger is plugged into a 230 V mains socket and the coil inside the base has 920 turns. The coil inside the toothbrush has 40 turns.
What is the potential difference induced across the toothbrush coil?
3.A machine in a factory requires 500 V to operate and is connected to a transformer coil with 1250 turns. The transformer’s other coil is connected to the 230 V supply.
How many turns are on the coil connected to the mains?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque