AQA GCSE Background Radiation(Physics)
Background Radiation
Background radiation, is low level ionising radiation that is all around us, all the time.
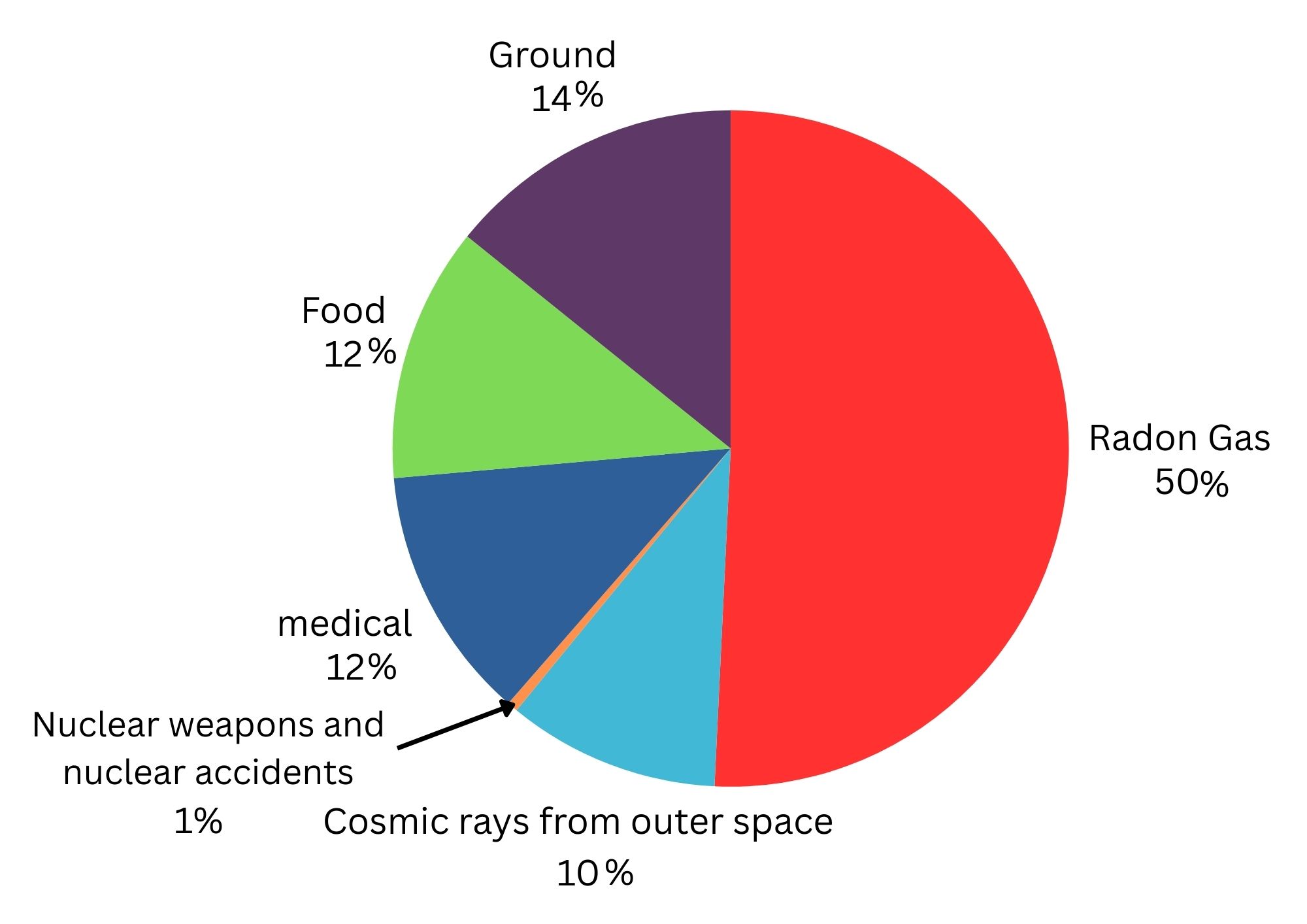
There are different sources of background radiation:
1. Natural sources such as radon gas from rocks and cosmic rays from outer space
2. Man made sources such as the fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents such as Chernobyl.
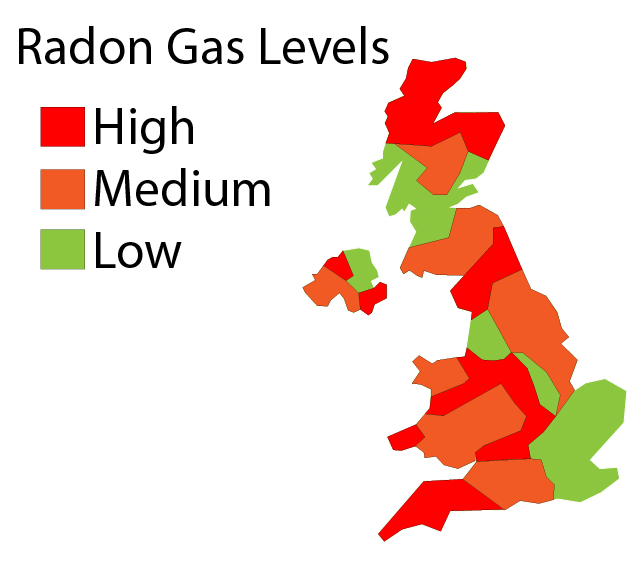
Level of background radiation or radiation dose received will depend on the location. Below is a radon gas map of the UK:
Occupation can also affect the level of background radiation or dose that a person is exposed to. Airline pilots are exposed to more cosmic rays due to flying.
Measuring background radiation
A geiger tube, connected to a geiger counter can be used to measure the background radiation

Radiation Dosage
The dosage of radiation that a person receives is measured in Sieverts.
A sievert takes into account the biological effect of the radiation on the body, the amount of radiation absorbed and the potential for harm to tissues.
A sievert is a very large amount of radiation, so in most cases we will use milisieverts, mSv.
2-3mSv per year is the amount of radiation from natural background radiation sources.
Practice Questions
1. Define the term background radiation
2. State 3 possible sources of background radiation
3. State the name of the piece of apparatus that can be used to measure the background level of radiation
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque