Answers to AQA GCSE Velocity time graphs and acceleration curved lines(Physics)
Practice Questions
1.A car’s velocity-time graph shows a curve that starts at zero velocity and increases non-linearly over time, eventually reaching a uniform velocity. Sketch a velocity time graph to show this motion.
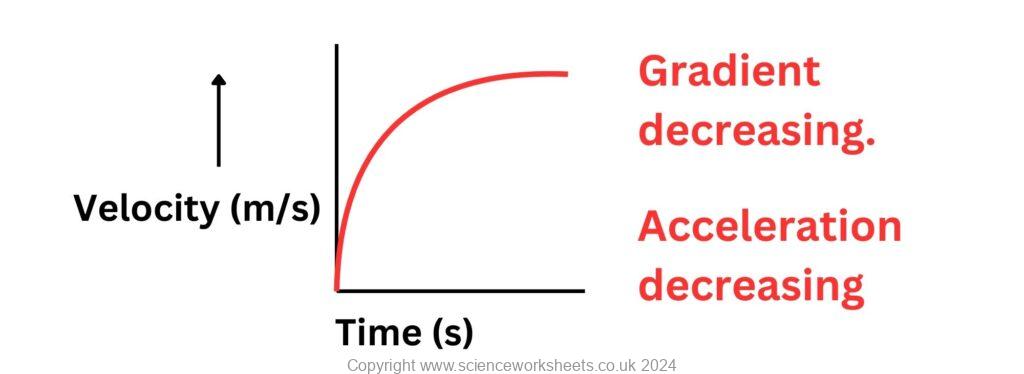
2. If the curve on a velocity-time graph becomes steeper over time, how would you describe the change in acceleration?
If the gradient increases over time, then the acceleration will increase over time.
3. If a curved velocity-time graph crosses the time axis, what does this indicate about the motion of the object?
If the velocity time graph line crosses the time axis, then the direction of the object changes. If the object was previously moving forwards, once the line crosses the time axis, the object will now move in the opposite direction e.g. backwards.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque