AQA GCSE Static Electricity and Sparking(Physics)
Static Electricity and Sparking
Static electricity is caused by the build up of electrical charge on the surface of a material.
Building static charge
As the man walks across the carpet, he builds up static electrical charge due to friction between his shoes and the carpet.
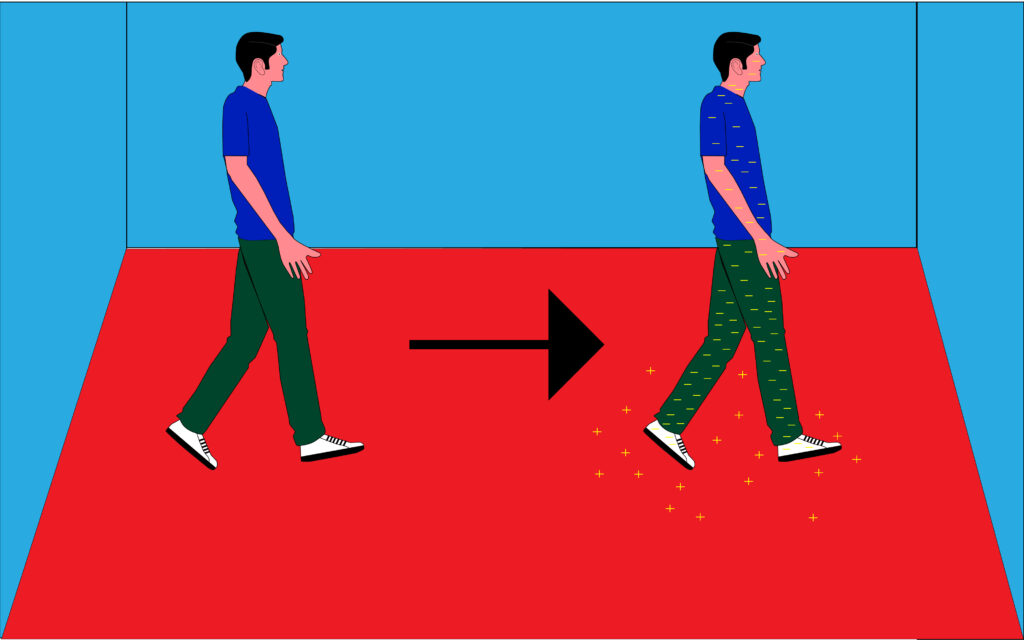
Electrons move from the carpet onto the man. This means that the man now has a negative charge and the carpet has positive charge.
Electric Sparks
Once the man is electrically charged if he touches a metal object such a door handle then he will discharge, causing an electric spark and he can receive a small electric shock.
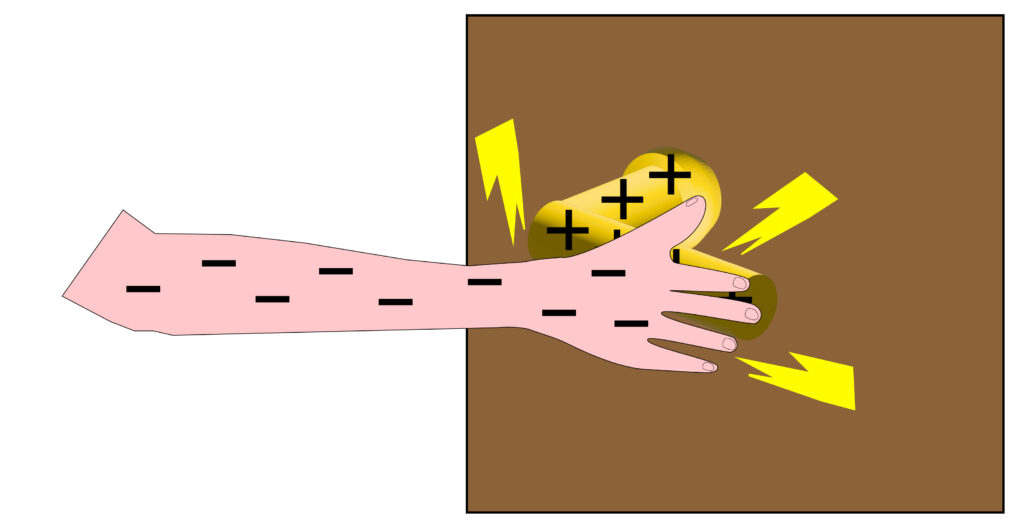
In the diagram above there is a potential difference between the hand and the metal door handle. When the hand touches the door handle, electrons flow from the hand to the door handle, earthing the charge and a spark occurs.
Practice Questions
1. A passenger in a car seat is uncomfortable and keeps moving within the seat to find a more comfortable position. Explain how this can cause the passenger to build up static electrical charge
2. Suggest why lightning occurs in terms of static electricity
3. A man walks on nylon carpet tiles in the gym using his new trainers. When he touches the stainless steel water fountain he receives a small electric shock. Explain why.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque