AQA GCSE Series Circuit Calculations(Physics)

Example 1

In the circuit above calculate the current,I flowing in the circuit.
V = IR,
So, I = V/R
I = 6/2 = 3A
Example 2

In the circuit above calculate the resistance of the resistor on the right.
First we need to find the total resistance of the whole circuit, using the potential difference across cell and reading on ammeter.
V = IR
R = V/I, R = 6/2 = 3 ohms
In a series circuit, total resistance is the sum of the individual resistors. So, if the total resistance is 3 ohms and the resistor on the left is 0.8 ohms, then the resistor on the right is 3-0.8 = 2.2 ohms.
Example 3
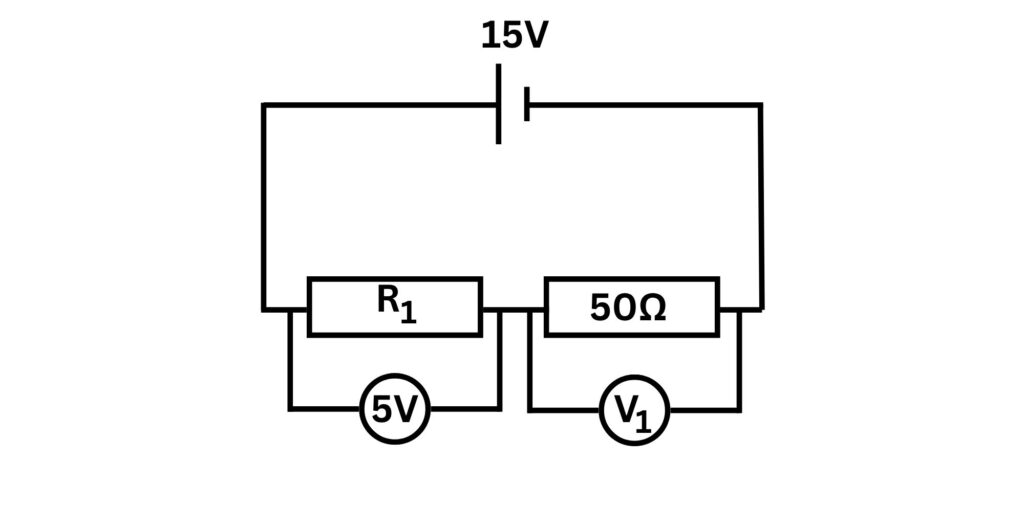
In the circuit above calculate V1 and R1
In a series circuit the potential difference is shared between the components. So 15V = 5V + V1. Therefore, V1 = 10V.
We can now work out the current flowing through the 50 ohm resistor, using V = IR
I = V/R, I = 10/50 = 0.2A
In a series circuit, current is the same at all points. This means that a 0.2A current will also flow through R1.
V = IR, so R1 = V/I
R1 = 5/0.2 = 25 ohms
Practice Questions
1.Calculate the resistance of the bulb in the circuit below

2. Calculate the current flowing through the circuit below with the two resistors.

3. In the circuit below, calculate V1 and R1

Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque