AQA GCSE Current and Electrical Charge(Physics)
Electric current is the flow of charge around a circuit.
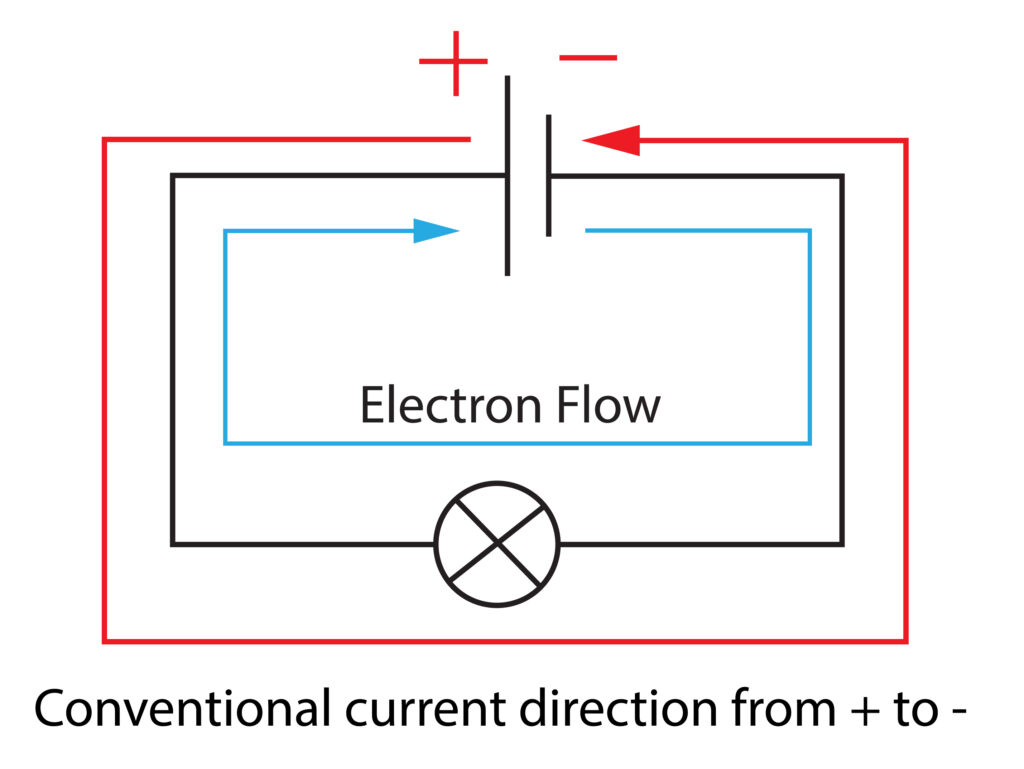 The cell or battery of a circuit makes these charges flow around the circuit. Conventional current flow is from positive to negative, electron flow however is from negative to positive.
The cell or battery of a circuit makes these charges flow around the circuit. Conventional current flow is from positive to negative, electron flow however is from negative to positive.(There is a reason for the difference, but you don’t need to know it!)
The cell or battery makes the charges flow around the circuit, the potential difference or voltage provides the energy to push and pull the charges to flow around the circuit.
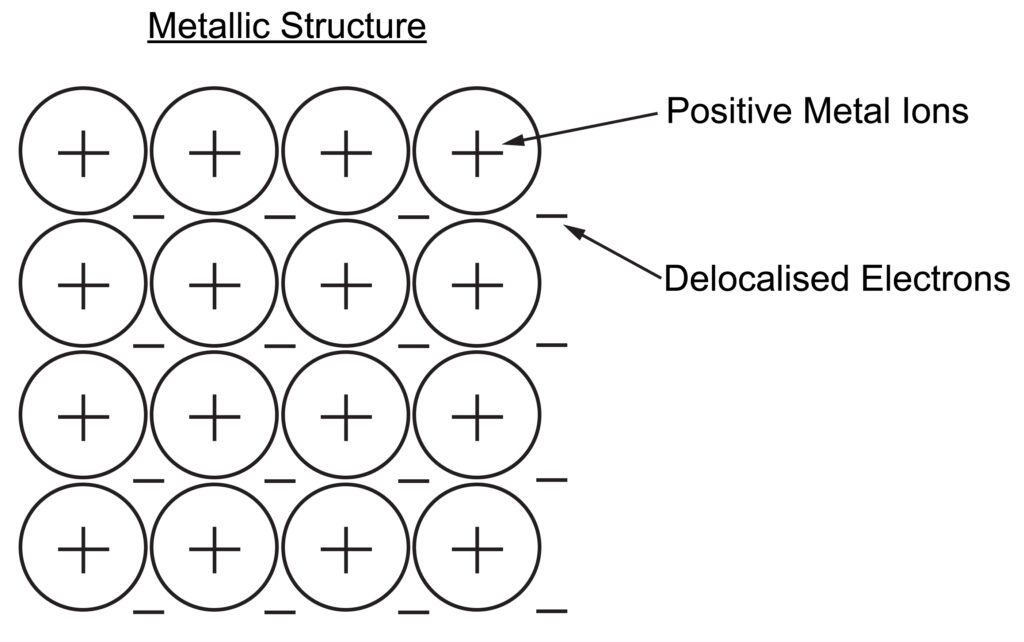
Metallic structure is a giant structure made up of positive metal ions and delocalised electrons. These delocalised electrons (free electrons) are able to move through the structure, carrying charge.
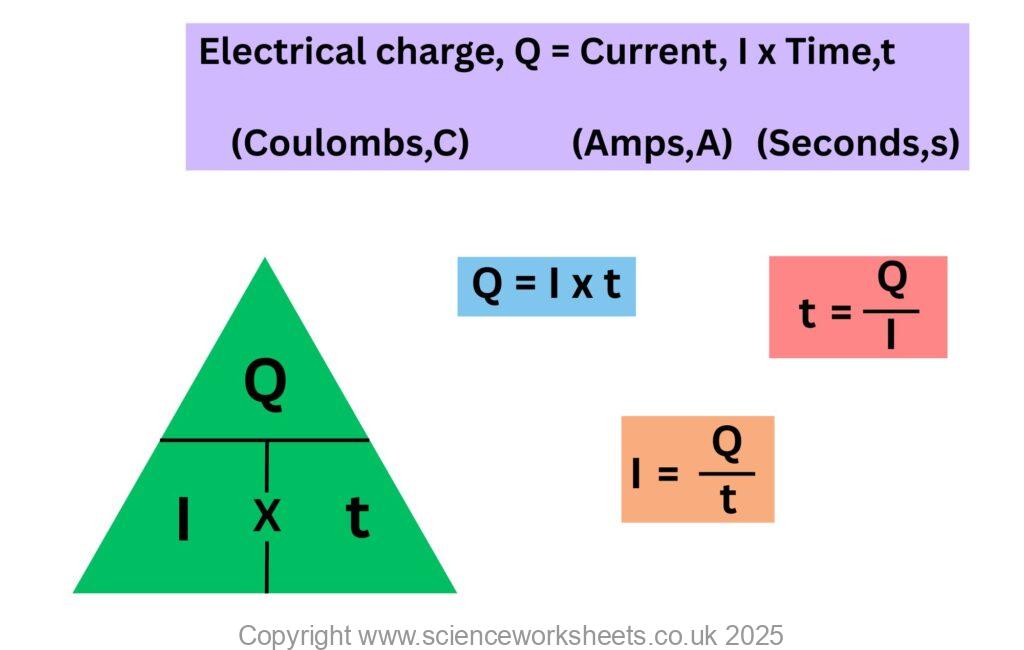
Electric Charge
At GCSE electrical charge is defined on 1 amp flowing for 1 second, which means that a total charge of 1 coulomb is transferred.
Practice Questions
1.State which direction conventional current flows.
2. What makes the current flow around a circuit?
3. Why is copper a good conductor of electricity?
4. Describe metallic structure.
5. A 3 amp light bulb is switched on for 2 minutes. Calculate the total electrical charge transferred.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque