AQA GCSE Calculations for Transformers part 2 (Physics)
Calculations for Transformers
As a simplification, we can assume that a transformer is 100% efficient, if the power into the transformer is equal to the power out from a transformer.
Power in = Power out
Power = Potential difference,V x current, I

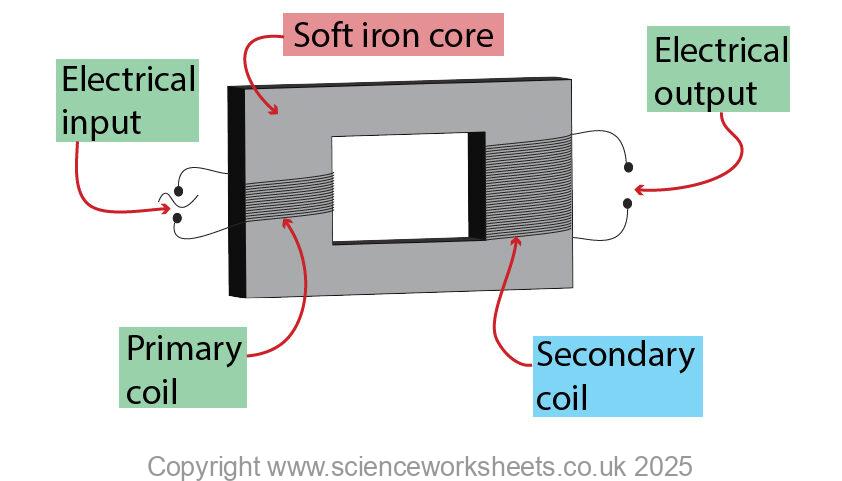
Rearranging the equation:

Example calculation
A transformer has a primary potential difference of 240 V and a primary current of 2 A.
If the secondary potential difference is 48 V, what is the secondary current?
Is = (Vp x Ip)/Vs
Is = (240 x 2)/48
Is = 10A
Practice Questions
1.A transformer has a primary potential difference of 100 V and a primary current of 0.3 A.The secondary potential difference is 20 V.
What is the secondary current, assuming the transformer is 100% efficient?
2.A transformer supplies a secondary coil with a current of 8.0 A at 50 V. The primary coil is supplied with 230 V and carries a current of 2.0 A.
(a) Calculate the input power and output power of the transformer.
(b) Determine the efficiency of the transformer.
(c) Suggest one reason why the efficiency is less than 100%.
3.A phone charger contains a transformer that steps the mains voltage down to 5 V for charging. A current of 0.5A runs from the transformer to the phone.
(a) What is the current supplied by the primary coil if the secondary current is 2.0 A?
(b) Explain why the current is different on each side of the transformer.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque