AQA GCSE The magnetic field of the Earth(Physics)
The magnetic field of the Earth
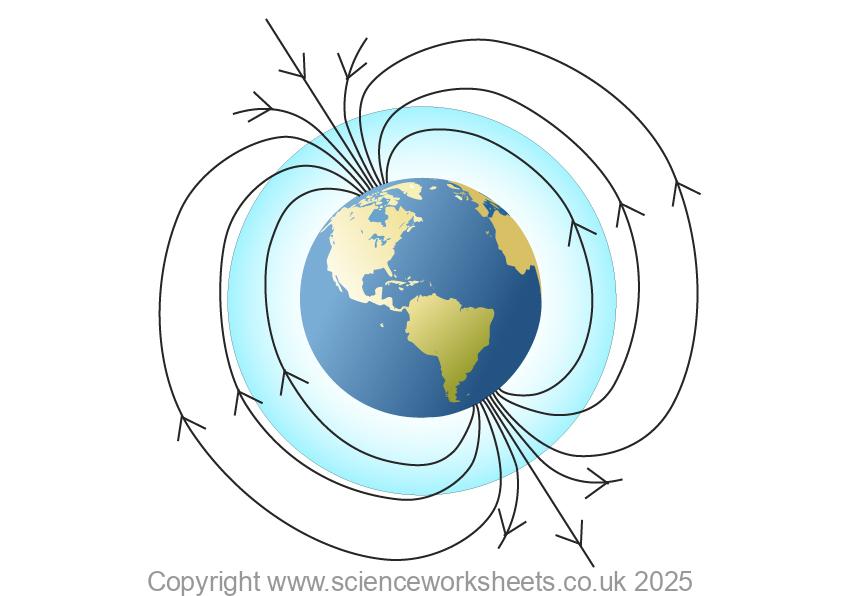
Our Earth has a magnetic field.
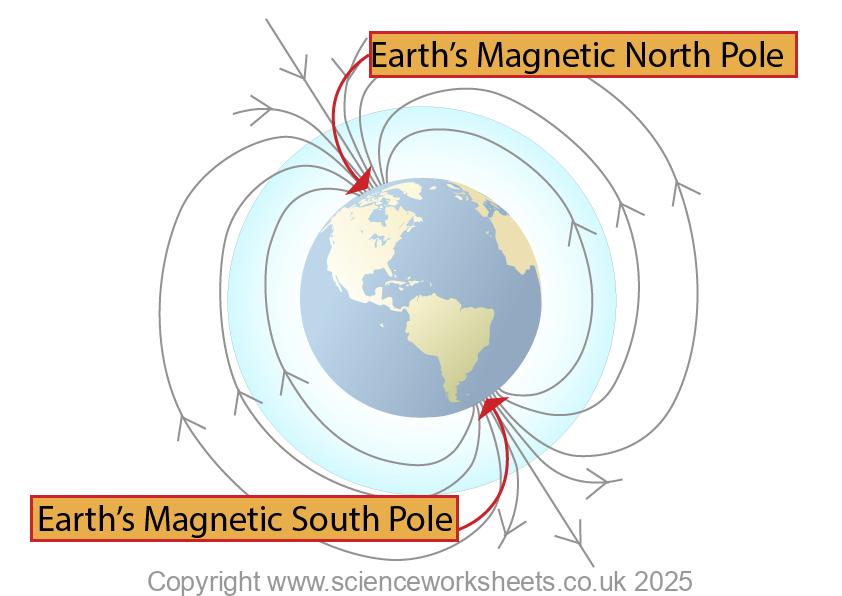
Poles of the Earth’s Magnetic Field
The Earth has two magnetic poles:
1.Earth’s Magnetic North pole(near geographical north pole)
“Earth’s magnetic north pole” is based on geography, not magnetism. Navigators noticed that the compass needle’s north end pointed north, so they named that area the magnetic north and this name has stuck.
Magnetically, it’s a south pole because it attracts the north end of magnets. This is why sometimes you will see it labelled as a south pole.
It can be slightly confusing.
2.Earth’s Magnetic South pole(near geographical south pole)
These are shown in the diagram below.
Magnetic Compass
A compass needle will always point in the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field.
A compass has a needle that is magnetised. This means it has a north end and a south end.
The North end of the compass needle will point towards the Earth’s magnetic North pole, near the geographical north pole.

Evidence that the behaviour of a compass proves the core of the Earth is magnetic
A compass needle will always point in the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field.
The direction the compass needle points is evidence that Earth itself acts as a giant magnet.
If Earth were not magnetic, the needle wouldn’t have a preferred direction to align with, and the compass would be useless for navigation.
The compass needle points toward magnetic poles but not at, the geographic poles. This suggests that Earth’s magnetic field has a two-pole structure, like a bar magnet. This indicates a central, powerful magnetic source, which leads scientists to infer that the core is magnetic.
Practice Question
1. The Earth has two magnetic poles, state the name of these two poles
2. The south end of a compass needle will point in which direction?
3. Outline the evidence which suggests that the Earth’s core is magnetic
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque