AQA GCSE Magnets(Physics)
Magnets
A magnet has two poles, a north pole(N) and a south pole(S).

Magnets and Forces
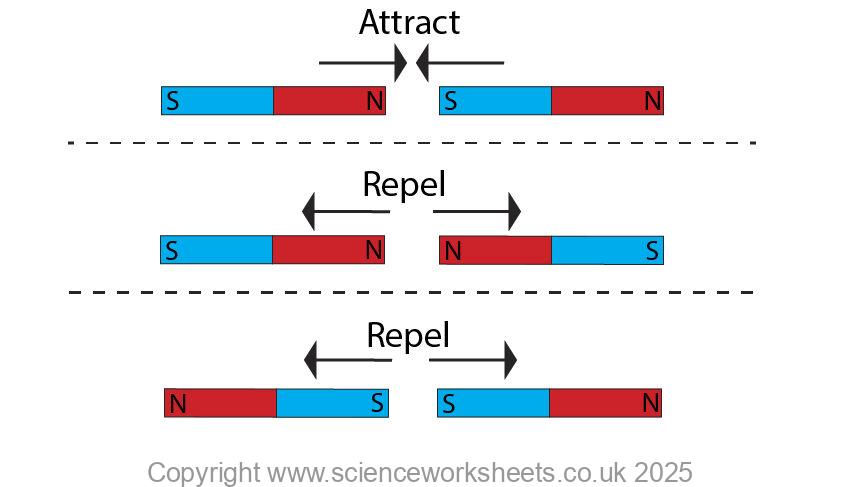
When two magnets are near each other, they will exert forces on each other.
Unlike poles such as north and south will experience a force of attraction.
Whilst like poles north and north, or south and south will experience a force of repulsion.
The force involved here is a non contact force. Other non contact forces include force of gravity, or electrostatics.
Permanent magnets
A permanent magnet will produce its own magnetic field.
A magnetic field is a region of space where a force due to magnetism is experienced by a magnetic material. Magnetic materials include iron, steel, cobalt and nickel.
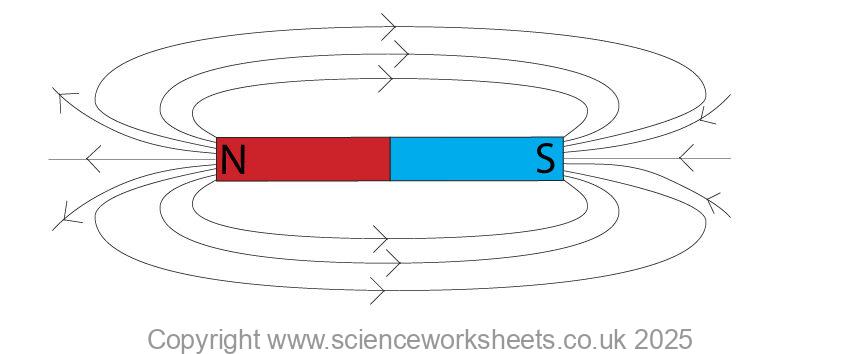
Steel, which is an alloy of iron, is a permanent magnet. Steel is often described as magnetically hard, so its hard to magnetise, but will retain its magnetism. This is why it is used for permanent magnets.
The bar magnets that you use in school will be made of steel.
Induced Magnetism
Induced magnetism occurs when a magnetic material is placed into a magnetic field and it becomes magnetic.
Magnetic materials include iron, nickel, cobalt or steel.
Iron is magnetically soft, this means it is easily magnetised. So, iron is used as a temporary magnet.
If unmagnetised iron is placed next to a bar magnet, within the bar magnets magnetic field, then the iron becomes magnetised.
Notice that induced magnetism always causes a force of attraction because the induced magnetic material will attract to the permanent magnet.
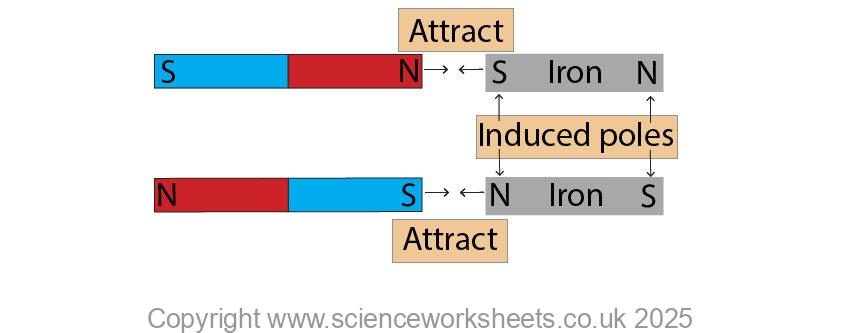
If the piece of magnetised iron is moved out of the magnetic field of the bar magnet, then the magnetised iron will demagnetise.
Practice Question
1.State the name of the type of force that occurs between two permanent magnets.
2. Describe the difference between a permanent magnet and an induced magnet.
3. Define the term magnetic field
4. State the names of the four magnetic materials
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque