Answers to AQA GCSE Changes in energy, Specific Heat Capacity(Physics)
Answers to Practice Questions
1. Aluminium has a specific heat capacity of 900J/kg°C. Calculate the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a 2.5kg aluminium block from 20°C to 65°C.
ΔE = m x c x Δθ
Δθ = 65-20 = 45°C
ΔE = 2.5 x 900 x 45
ΔE = 101250J
2. Gold has a specific heat capacity of 130J/kg°C. Calculate the amount of energy needed to raise to the temperature of a 10g gold ring from 20°C to 600°C.
ΔE = m x c x Δθ
Convert 10g into kg, so 10g = 0.01kg
Δθ = 600-20 = 580°C
ΔE = 0.01 x 130 x 580
ΔE = 754 J
3. 10kJ of energy is transferred 1.5kg of material Y to raise its temperature by 20°C. Calculate the value of the specific heat capacity of Y.
ΔE = m x c x Δθ
10kJ = 10,000J
Rearrange equation to make c the subject.
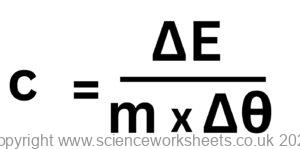
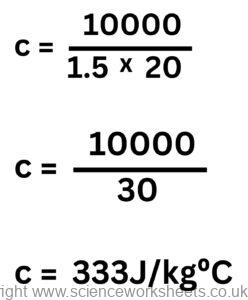
4. Material G has a specific heat capacity of 650J/kg°C. 25kJ of energy is supplied to material 900g of material G to raise its temperature from 20°C. Calculate the final temperature of material G.
25kJ = 25000J
900g = 0.9kg
ΔE = m x c x Δθ

Need more questions, see our worksheets.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque