Answers to AQA GCSE Elastic Potential Energy (Physics)
Answers to Practice Questions
1.Describe the relationship between the spring constant and the elastic potential energy.
Relationship is directly proportional, so as the spring constant increases, so does the elastic potential energy. This means that as spring constant increases, so does elastic potential energy.
2. A steel spring has a spring constant of 15N/m and when compressed its length decreases by 0.4m Calculate the elastic potential energy stored in the spring when it is compressed.
Ee = 1/2 x k x e2
Ee = 1/2 x 15 x 0.42
Ee = 1/2 x 15 x 0.16
Ee = 1.2J
3. A resistance band has a spring constant of 30N/m. During an exercise its length is increased from 0.7m to 1.1m. Calculate the elastic potential energy stored in the resistance band.
Extension,e = 1.1m-0.7m = 0.4m
Ee = 1/2 x k x e2
Ee = 1/2 x 30 x 0.42
Ee = 1/2 x 30 x 0.16
Ee = 2.4J
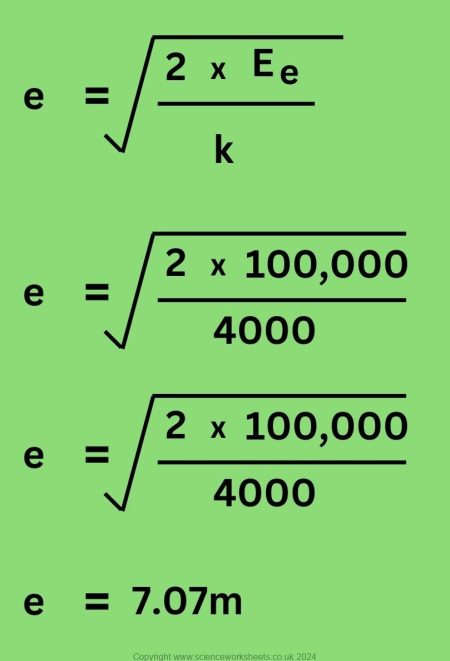
4. A catapult has 100kJ of elastic potential energy stored and its spring constant is 4000N/m. Calculate the extension that the catapult is experiencing.
100kJ = 100,000J
Need more questions, see our worksheets.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque