AQA GCSE Radio waves and oscillations(Physics)
Radio waves and oscillations
Radio waves are transmitted from the transmitting aerial to a receiving aerial as shown below.
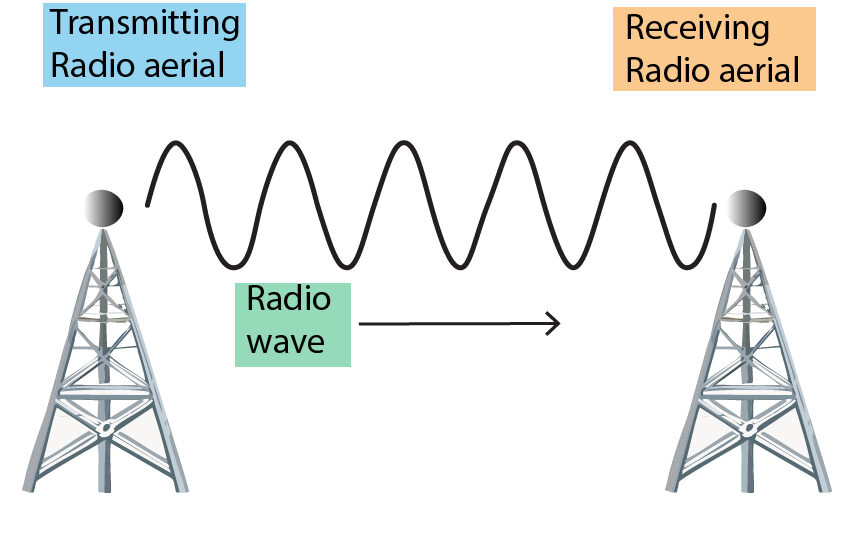
At the transmitting aerial
A high freqency, alternating potential difference is applied across the transmitting aerial, this causes an alternating current to flow in the transmitting aerial.
This current will cause oscillations in charge which flow up and down the transmitting aerial, causing radio waves of the same frequency to be emitted.
The radio waves travel through the air to the receiving aerial.
At the receiving aerial.
The metal aerial will absorb the radio waves. This will cause an alternating current in the receiving aerial that is of the same frequency as the radio waves. So, the radio waves will induce (create) oscillations in the electrical circuit.
Practice Question
1. Explain how a transmission aerial is used to broadcast radio waves
2. Suggest why the sound heard from a radio would be similar to the sound being produced in the studio from where it is broadcast.
3. What is meant by the term oscillations?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque