Answers to AQA GCSE Comparing Transverse and Longitudinal waves(Physics)
Practice Question
1.Draw two line diagrams to show the difference between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave
Longitudinal wave line diagram:
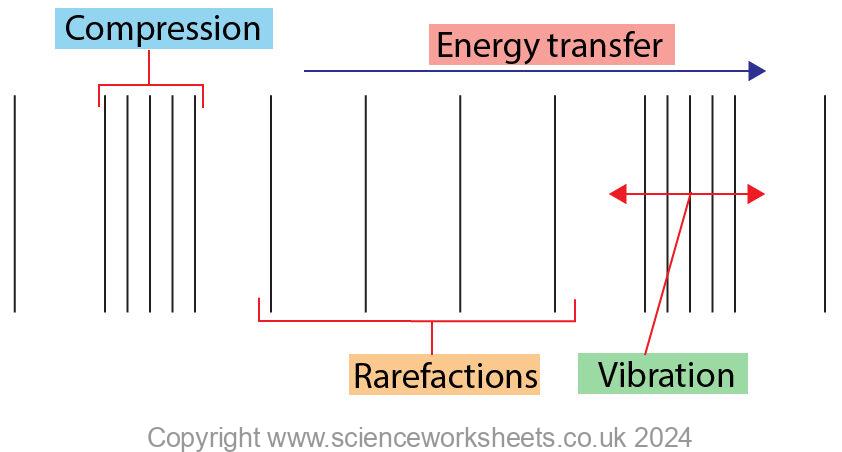
Transverse wave line diagram:

2. State 3 ways that longitudinal waves and transverse waves are different
Any 3 from the table below
| Characteristic | Transverse wave | Longitudinal wave |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wave vibrates at 90 degrees to the direction in which the wave transfers energy | Wave vibrates along the direction in which the wave transfers energy |
| Line diagram contains | Peaks/Crests and Troughs | Compressions and Rarefactions |
| Travel through | Solids and vacuum (but not fluids) | Solids, liquids, gases |
| Medium needed | No (electromagnetic waves can travel in space) Some other transverse waves would need a medium to travel through | Yes (cannot travel in a vacuum) |
| Density | Always same | Density can change |
| Particle motion | Parallel to wave direction | Perpendicular to wave direction |
| Pressure | Pressure is always the same | Regions of high pressure and regions of low pressure |
3. State 3 ways that longitudinal waves and transverse waves are similar
Any three of the following:
Both transfer energy and information, but not matter
Both Have Wavelength, Frequency, and Amplitude
Both follow the wave speed equation; wave speed = frequency x wavelength
Both can be reflected and refracted
Both have wavefronts
Both can be absorbed.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque