Answers to AQA GCSE Terminal velocity(Physics)
Practice Question
1. Define the term terminal velocity
Terminal velocity is achieved when an object has a constant speed in one direction and the forces acting on the object are balanced.
2. Explain what is meant by resultant force
Resultant force is the overall force. It can also be a single force that takes account of all the forces acting on an object.
3. When an object is dropped in a fluid, why does it accelerate downwards?
Force of gravity acts of the object, making it accelerate downwards.
4. Using the velocity time graph shown above, predict the appearance of the next stage in the graph, when the ball hits the ground. You can sketch your predicted graph on a piece of paper
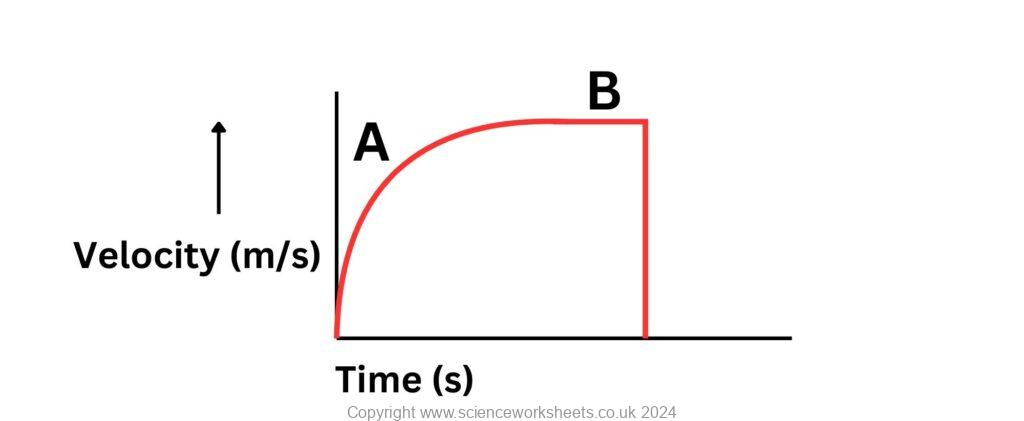
When the ball hits the ground, the velocity will become 0m/s. So, the line will go vertically downwards
5. Use the image below to answer the following question


5a. Describe and explain how force 1 and 2 will change as time increases using the graph above.
You can reference these changes to stage A and B which are labelled on the graph.
Include key words such as acceleration and velocity in your answer.
Force 1 = Engine or driving force
Force 2 = Drag forces
A- Force 1>force 2, so car accelerates forwards and velocity increases. However, as velocity increases, force 2 will increase and therefore acceleration will decrease, which is why the gradient of the velocity time graph decreases.
B- Force 1 = force 2, so acceleration is zero and the car is at terminal velocity.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque