AQA GCSE Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction(Physics)
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a large and unstable nucleus.
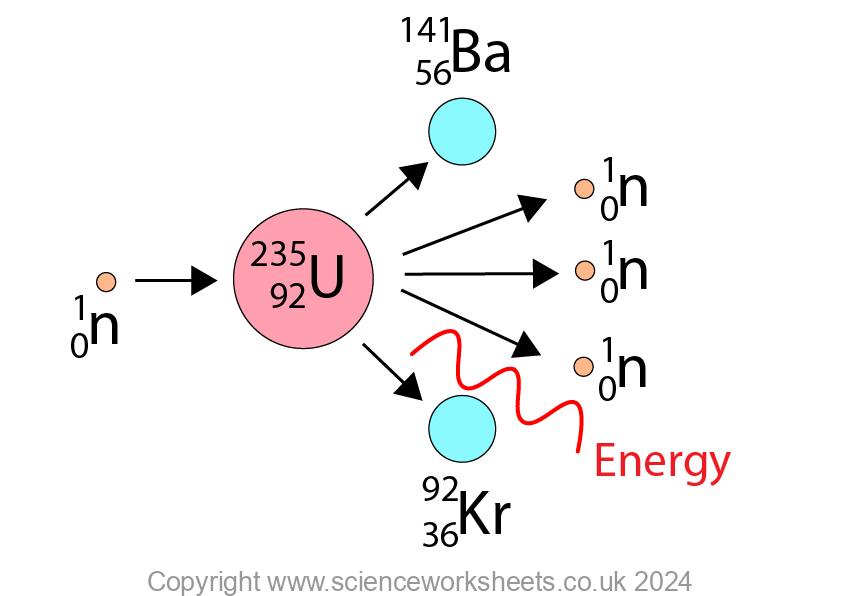
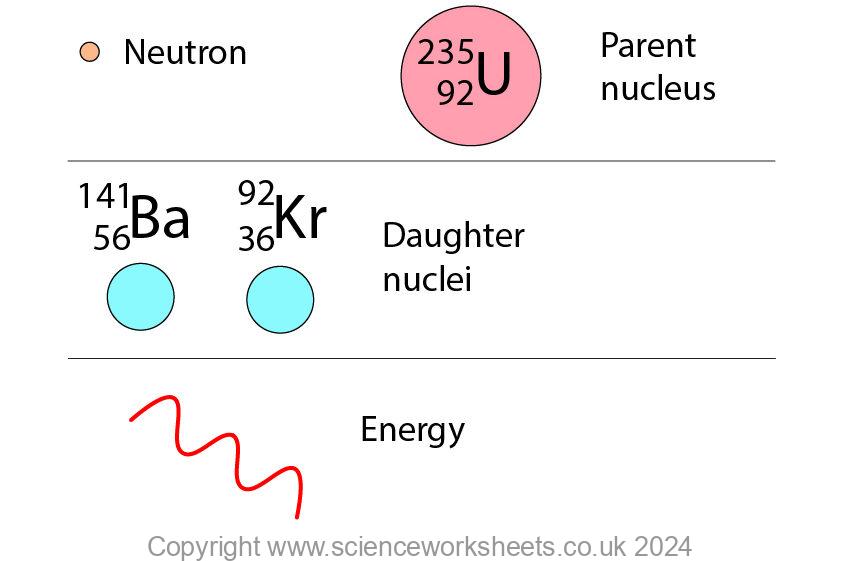
During the nuclear fission reaction, 2 or 3 neutrons are produced. These neutrons can go on and cause further fission reactions. This is known as a chain reaction.
Nuclear Fission Chain Reactions.
A chain reaction is shown in the diagram below:
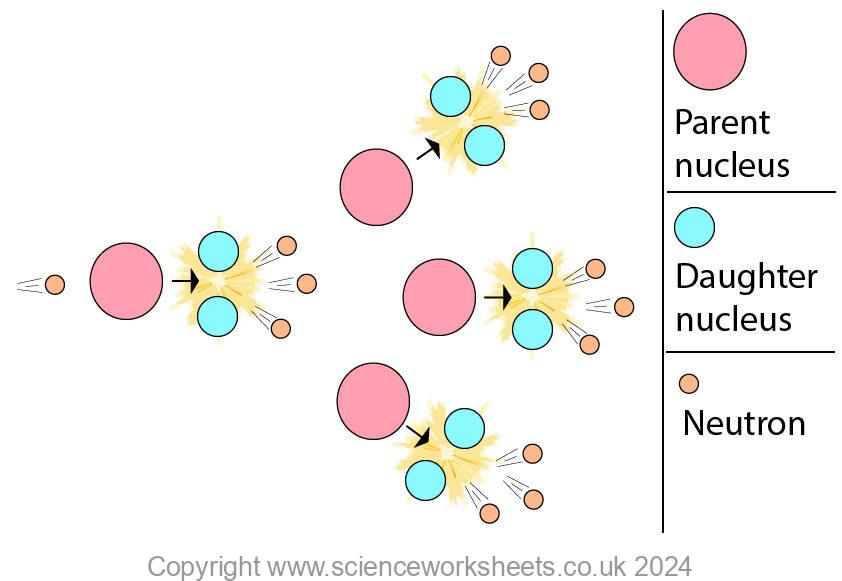
The first fission reaction on the left produces 2 daughter nuclei and 3 neutrons. Each of these 3 neutrons will go on and cause further fission reactions.
These 3 neutrons will end up producing 9 neutrons and so on. Very quickly a lot of neutrons can be produced.
Controlling Nuclear Fission
This nuclear fission reaction needs to be controlled, otherwise it will go out of control as a lot of neutrons can be produced very quickly.
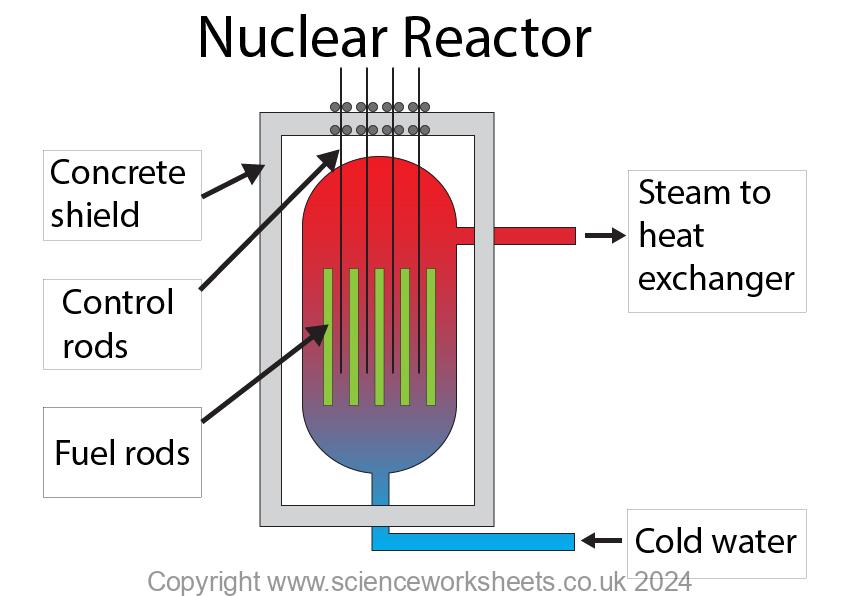
In nuclear reactors, where nuclear fission occurs control rods are used to absorb excess neutrons. Every time fission occurs, 2 of the neutrons are absorbed. This means that only 1 neutron is produced for every 1 neutron used.
If the excess neutrons are not absorbed, then the reaction will go out of control and it will lead to an explosion

This is what happened at the Chernobyl nuclear power station. Since the explosion in the nuclear reactor a protective dome shield has been built over the reactor to prevent the radiation being released.
In nuclear weapons, the fission reaction is delibrately made to go out of control in order to cause a massive explosion. So, a nuclear bomb is an example of an uncontrolled nuclear fission reaction. The two atomic bombs that were used on Hiroshima and Nagasaki were both nuclear fission bombs.
Practice Questions
1. Define the term Nuclear Fission
2.Explain what a chain reaction is and why it occurs
3.Describe how a chain reaction is controlled within a nuclear reactor
4.State the consequence of not controlling a chain reaction
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque