AQA GCSE Nuclear Fission(Physics)
Nuclear Fission
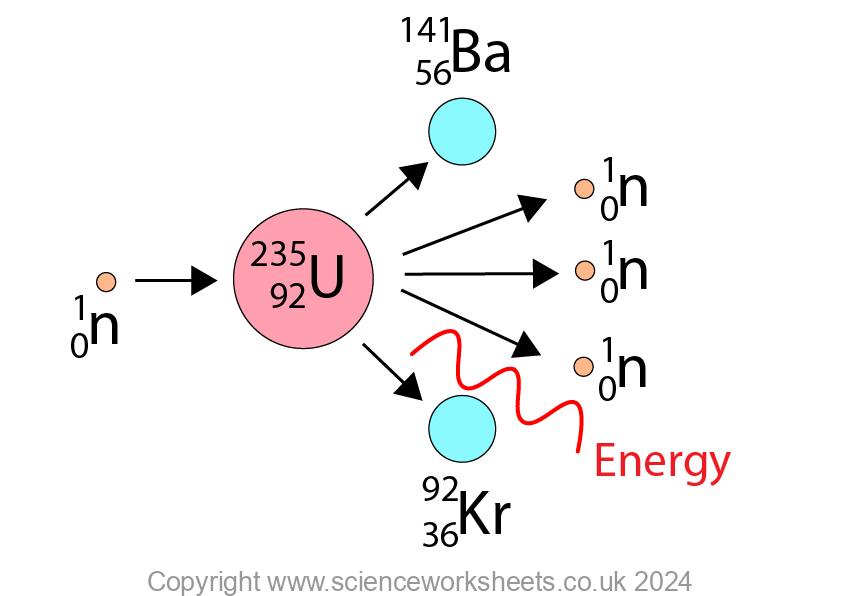
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a large and unstable nucleus.
As a result of nuclear fission this large nucleus will split to form daughter nuclei, 2 or 3 neutrons and energy released.

Types of nuclear fission
There are two types of nuclear fission:
1.Induced fission
2. Spontaneous fission
Induced Fission
In induced fission, the nucleus of an atom absorbs a neutron, which makes the nucleus unstable. This unstable nucleus then undergoes nuclear fission.
Induced fission occurs in nuclear reactors where Uranium-235 nuclei absorb neutrons, then undergo fission to release energy.
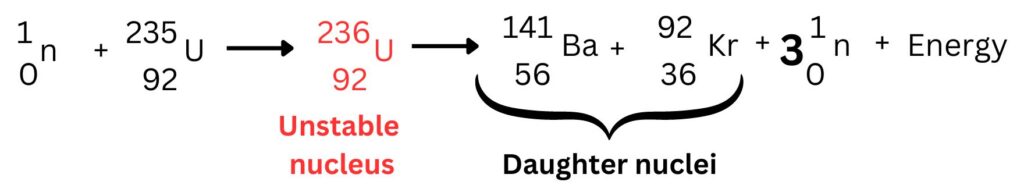
To simpify this the unstable nucleus in the red can be removed from the equation. This has been included above to aid your overall understanding.
Spontaneous Fission
This is when the nucleus undergoes nuclear fission without absorbing a neutron. This type of fission is rare, but still possible.
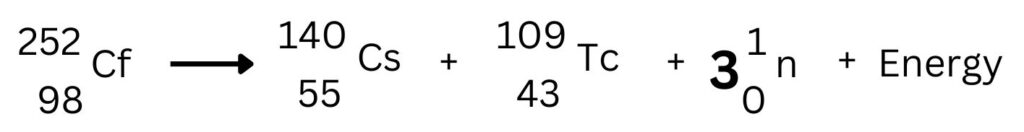
Practice Questions
1.Define the term nuclear fission
2. State the names of the two types of nuclear fission
3. State where nuclear fission takes place in industry
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque