AQA GCSE Half Life(Physics)
Half Life
There are two possible definitions, either is suitable:
The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for the number of nuclei of the isotope in a sample to halve.
The time it takes for the count rate (or activity) from a sample containing the isotope to fall to half its initial level.
The one you would choose, depends on the situation. If the the data is showing the number of nuclei decreasing, then use the first one. If the data shows the count rate decreasing, then the 2nd one would be used.
Half life graphs
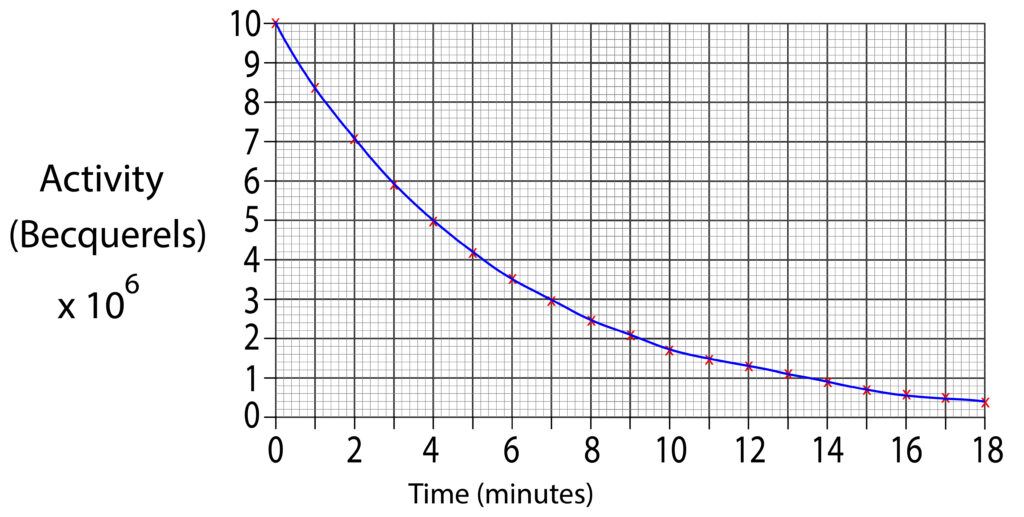
At the start the first activity reading is 10 x 106 Bq.
To find the half life, we will halve this value which is 5 x 106 Bq. Then draw a horizontal line from axis at 5 x 106 Bq to graph line. Finally, continue to draw the line, but downwards toward the time axis.
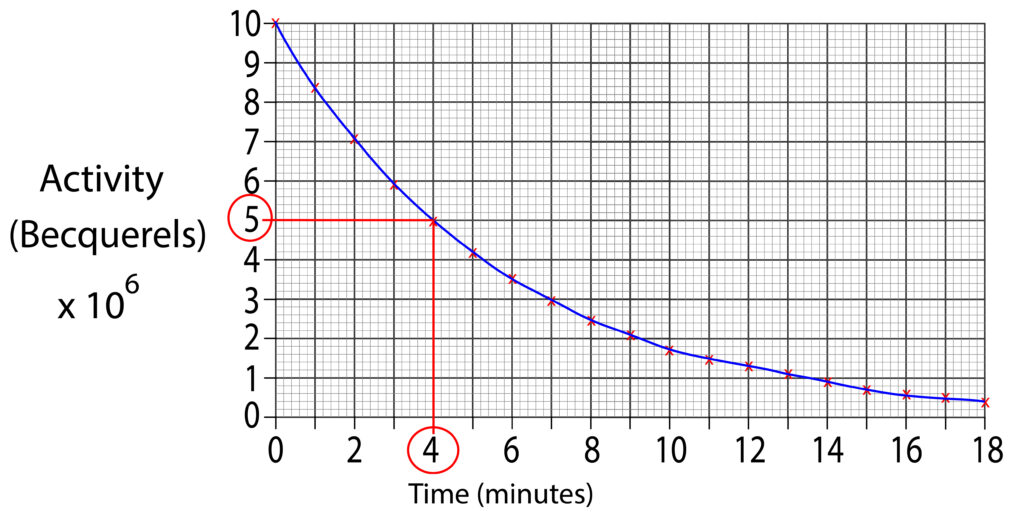
The line is shown in red, the half life for this isotope is 4 minutes.
Sometimes, you need to show constant half life on a graph, so the process needs to be repeated. As shown in the graph below.
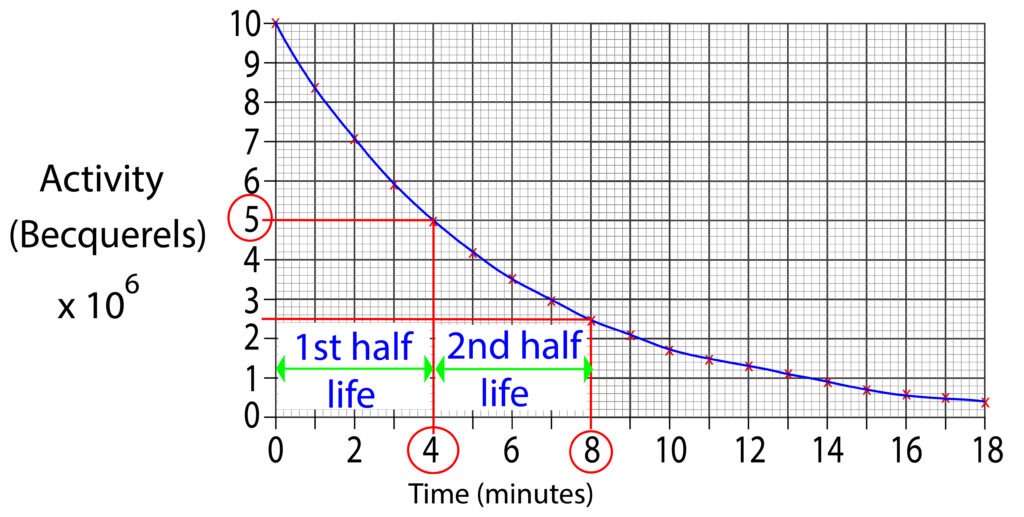
The graph above shows two half lives. Each half life is 4 minutes.
1st half life starts at 0 minutes and ends at 4 minutes.
2nd half life starts at 4 minutes and ends at 8 minutes.
This shows us that each isotope has a constant half life.
This means that for this isotope, every 4 mintes the count rate will halve.
Tip: In the exam, draw the lines onto the graph with a ruler, there is often a mark for this!
Practice Questions
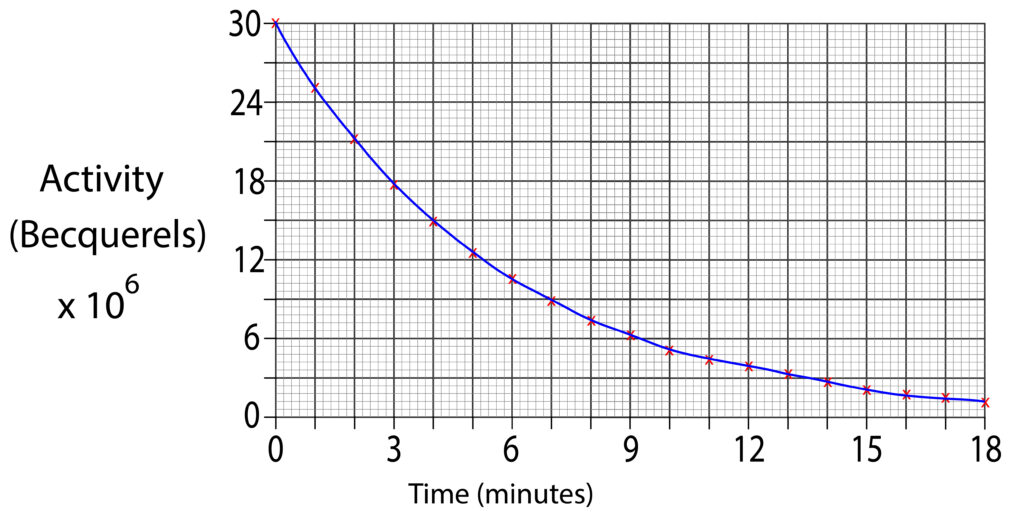
1.Using the graph below estimate the half life for the sample.
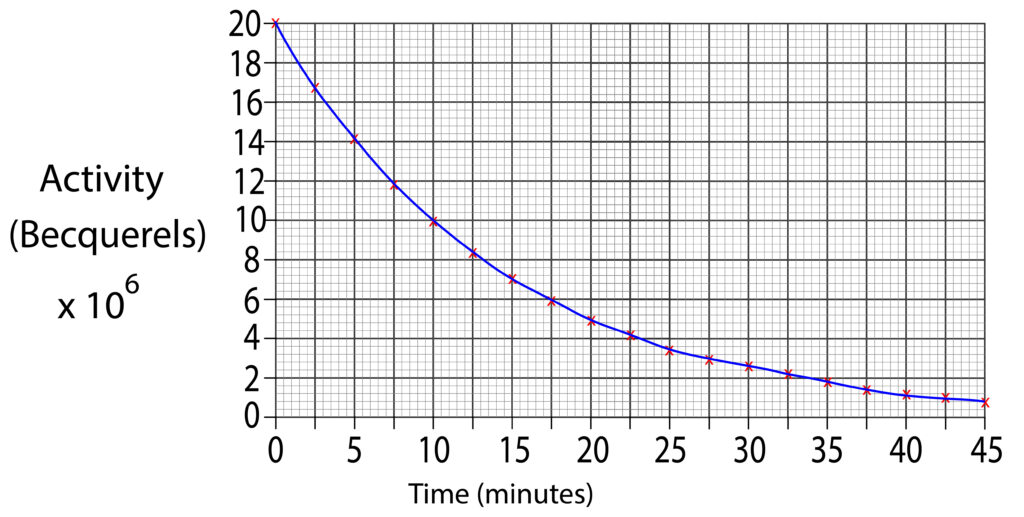
2. Using the graph below estimate the half life for the sample
3. Use the data in the table below to plot your own graph and calculate the half life.
| Time (seconds) | Activity (counts per second) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 241 |
| 30 | 212 |
| 60 | 188 |
| 90 | 165 |
| 120 | 145 |
| 150 | 127 |
| 180 | 112 |
| 210 | 99 |
| 240 | 87 |
| 270 | 76 |
| 300 | 67 |
| 330 | 59 |
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque