AQA GCSE Isotopes(Physics)
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element, with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
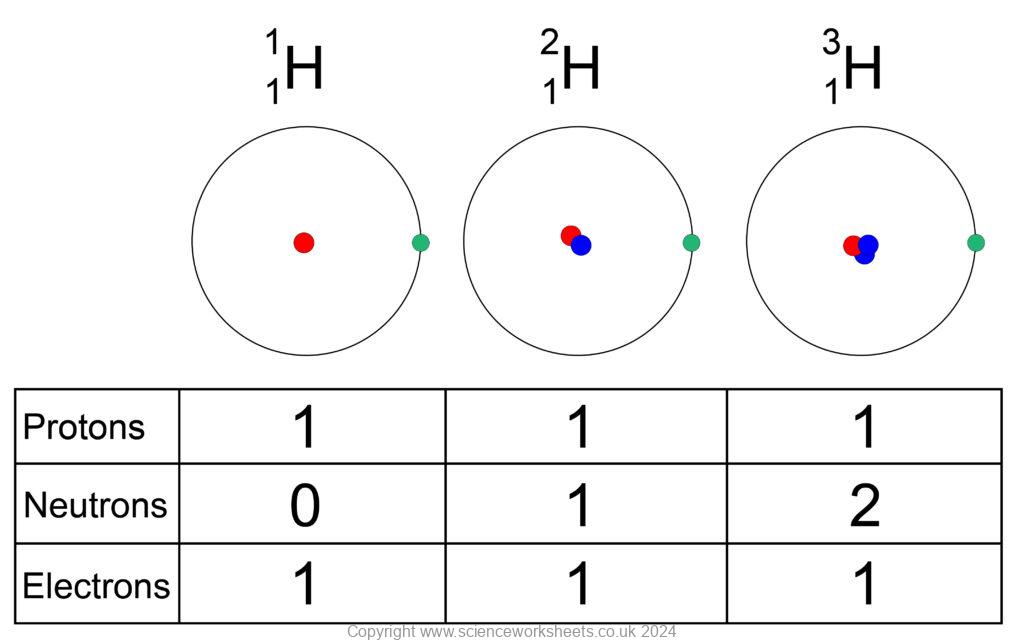
Properties of Isotopes
All isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties, because they all have the same number of electrons in the outer shell.
The isotopes for hydrogen above have different physical properties. As they have a different number of neutrons, their mass varies.
On the left is hydrogen-1, with a mass of 1 (1 proton)
In middle is hydrogen-2 with a mass of 2 (1 proton and 1 neutron)
On right is hydrogen-3, with a mass of 3. (1 proton and 2 neutrons)
Radioactivity and Isotopes.
Some isotopes are radioactive, this is because they have an unstable nucleus.
Hydrogen-3 (Tritium) has an unstable nucleus, so it tries to undergo radioactive decay to become more stable.
For a nucleus to be stable there has to be the correct ratio of protons to neutrons. If the ratio is not correct, then the nucleus will be unstable.
Copper and chlorine exceptions?
Copper has a mass number of 63.5 and Chlorine has a mass number of 35.5.
Using the rule we learnt on previous page:
Neutrons = Mass number – atomic number
Copper has a mass number of 63.5, atomic number 29.
Chlorine has a mass number of 35.5, atomic number 17.
Copper would appear to have 34.5 neutrons and chlorine would appear to have 18.5 neutrons.
It is not possible to have half a neutron.
This effect is caused by isotopes.
Chlorine has two isotopes. A natural sample of chlorine contains 75% chlorine-35 and 25% of chlorine-37. We can average the mass numbers for the isotopes to calculate 35.5 as shown below.
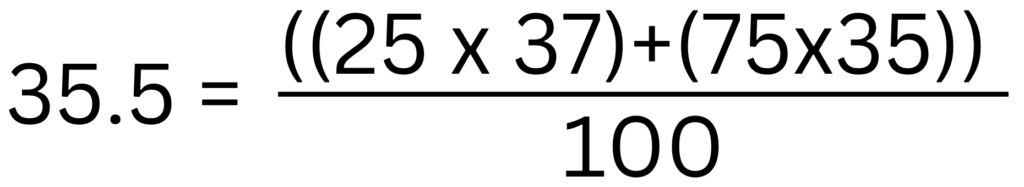
Practice Questions
1. State the definition of an isotope
2. State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in carbon-14
3. Explain why carbon-13 is not radioactive, but carbon-14 is radioactive
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque