AQA GCSE Motion of gas particles(Physics)
Motion of gas particles
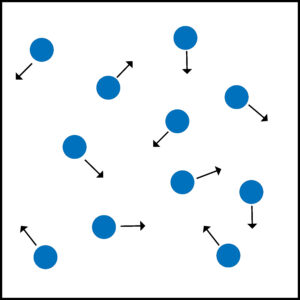
Gas particles move in random directions.
This can be modelled using Brownian motion
Browian Motion
Brownian motion is the erratic, random movement of particles in a fluid, as a result of continuous bombardment from molecules of the surroundings medium.
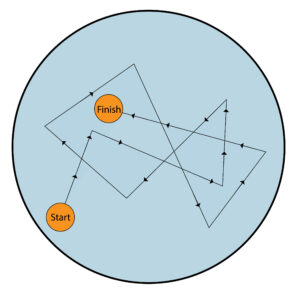 An example of brownian motion is dust particles in a liquid. The dust particle shown by the orange circle moves in random directions from start to finish because small water molecules are colliding with the dust particle.
An example of brownian motion is dust particles in a liquid. The dust particle shown by the orange circle moves in random directions from start to finish because small water molecules are colliding with the dust particle.
Temperature of a gas and Kinetic Energy
The temperature of the gas is related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
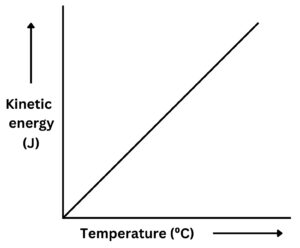
As temperature increases, so does the average kinetic energy of the particles. There is a directly proportional relationship between temperature and average kinetic energy.
Temperature and Pressure of a gas at constant Volume
Gas pressure is caused by moving gas particles colliding with the walls of the container and exerting a force. This force exerted is gas pressure.

As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the gas particles will increase, so they move faster, colliding with the walls of the container more often, resulting in more collisions per unit time. Therefore, as temperature increases gas pressure increases.
This does make the assumption that during the temperature increase, volume is constant.
The graph below shows the relationship between temperature of a gas and gas pressure
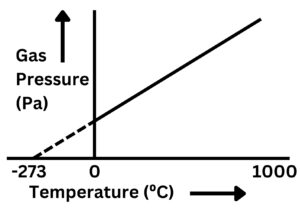
As gas temperature increases, gas pressure increases. There are several reasons why the line is dotted below 0C. However, this goes outside the bounds of GCSE and you should only focus on the general trend for your exams.
Practice Questions
1.Describe Brownian motion and provide an example.
2. How is the temperature of a gas related to the kinetic energy of its molecules?
3. Describe and explain the relationship between gas temperature and pressure at constant volume.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque