AQA GCSE Ionisation(Physics)
Ionisation
Ionisation is the process where an atom will form an ion.
An ion is a charged atom.
Atoms are electrically neutral because they contain equal numbers of protons and electrons. Each proton has a +1 charge, each electron -1 charge.
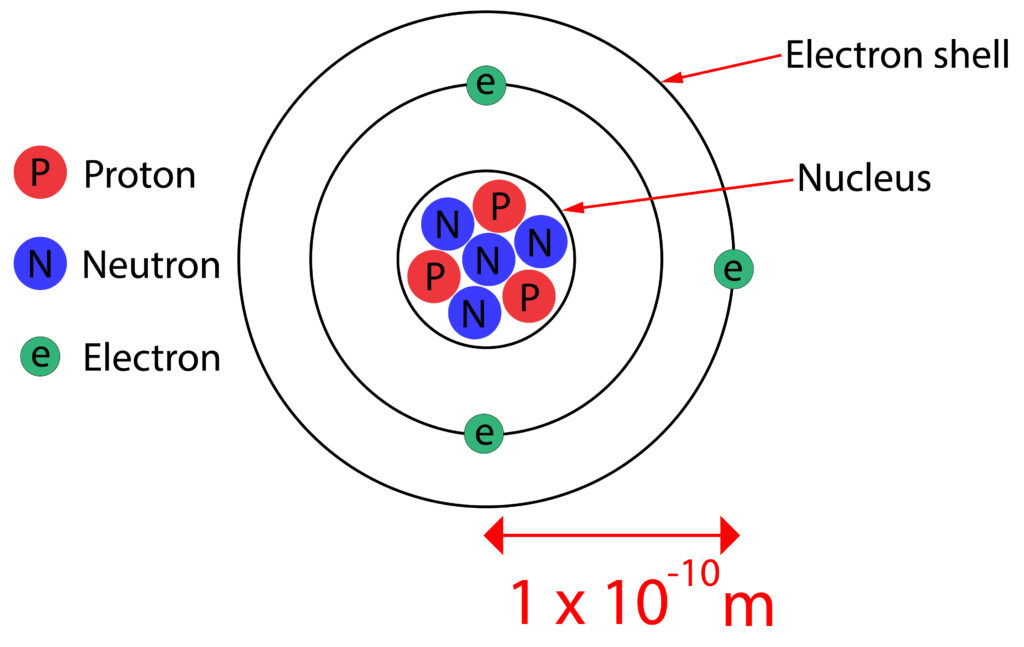
Atoms can lose or gain electrons to form ions. The element above is Lithium, if it loses one electron from its outer shell it will have 3 protons and only 2 electrons, so it will form a +1 ion.
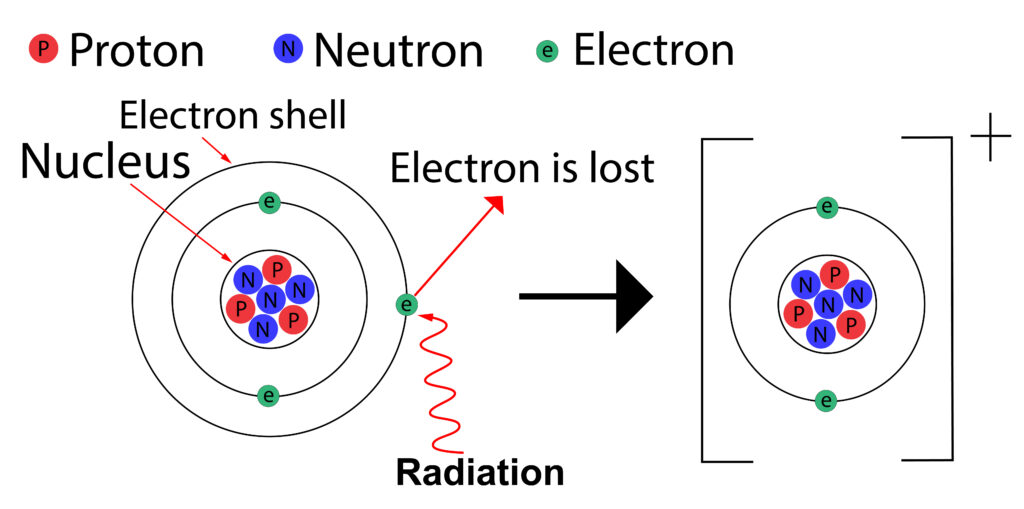
If radiation strikes the electron, it can knock an electron off of an atom causing the formation of an ion, this is known as ionisation.
Practice Questions
1. What is meant by the term ionisation?
2. Explain why atoms are electrically neutral
3. How would an atom change if it were to for a 2+ positive ion?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque