AQA GCSE Calculating Speed(Physics)
Calculating Speed
Speed is the distance travelled by an object in one second.
To calculate speed, we need to measure both the distance and the time period.
Measuring Distance
There are different ways that we can measure distance

Ruler can be used for short distances, measuring tape for medium distances and the trundle wheel for long distances.
Measuring Time
There are several ways that we can measure the time period
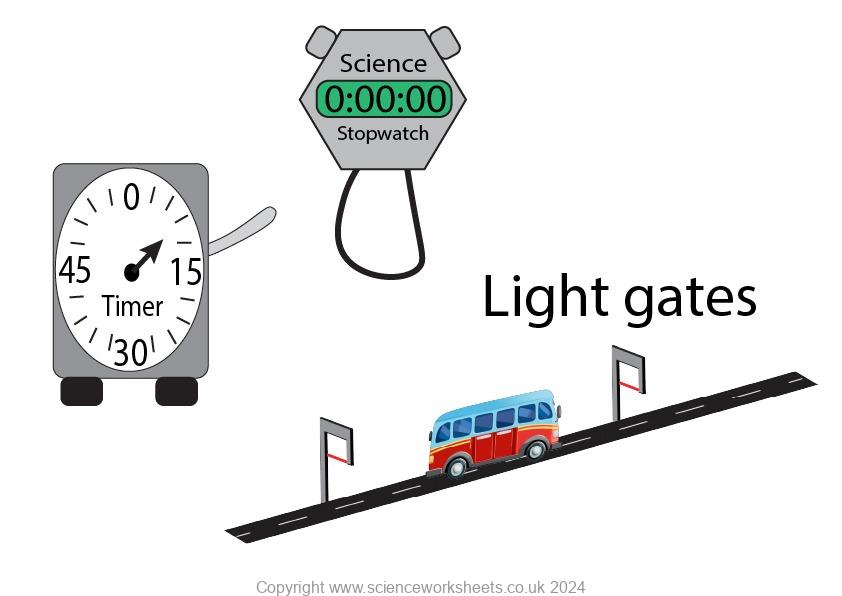
Both the stopwatch and the timer you can start and stop to record the time period.
The light gates work slightly differently. Each light gate has a laser beam. In this case when the toy bus goes through the red laser beam it is recorded.
So, the light gates will record the time taken for the bus to travel from the 1st light gate, to the second light gate.
Calculating Speed.
The formulae are shown below:
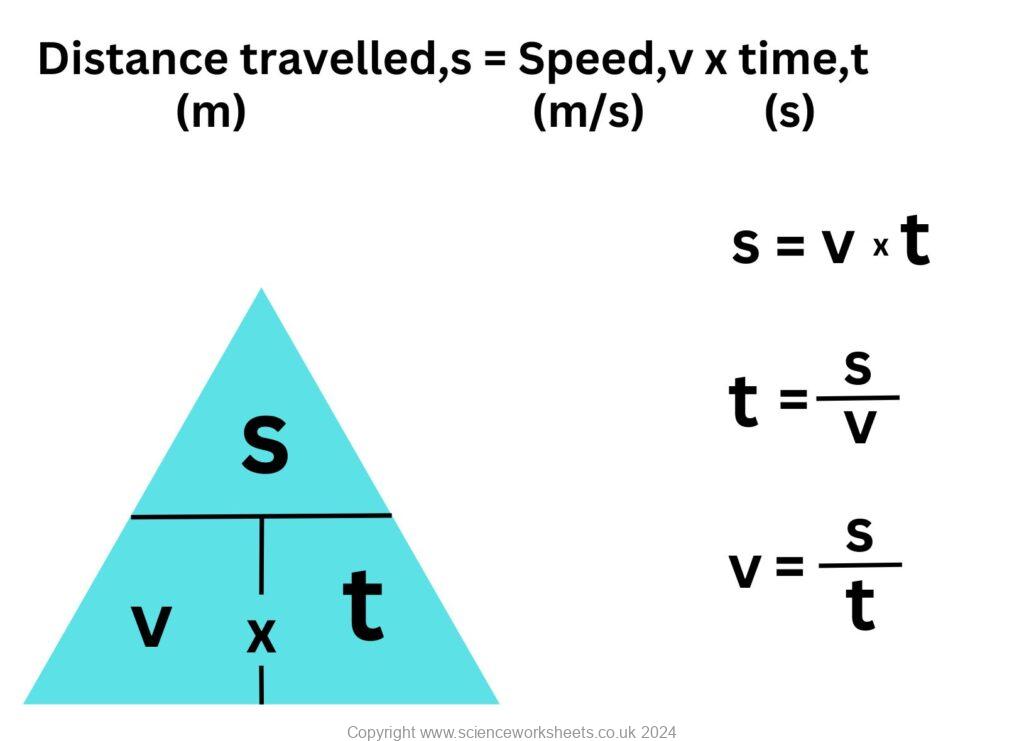
Sample Questions
1. A football travels 30m in 2.5 seconds. Calculate the speed of the football.
Check that both of the units are SI units. In this case they are, distance is in metres, time is in seconds. So, we can use the formula directly
Speed = distance/time
Speed = 30m/2.5 seconds
Speed = 12m/s
2. A car is travelling at 12m/s for a total time period of 2 minutes. Calculate the distance travelled.
2 minutes = 120 seconds
Distance = Speed x time
Distance = 12m/s x 120 seconds
Distance = 1440m
3. How long does it take a person walking 2m/s to travel a distance of 1.5km.
1.5km = 1500m
Time= Distance/speed
Time = 1500m / 2m/s
Time = 750 seconds
Practice Questions
1.Define the term speed.
2.State 3 ways to measure distance
3. State 3 ways to measure time
4. State the formula for speed
5. A bird flies a distance of 250m in 15 seconds, calculate the speed.
6. A man walks from his house to a shop which is 500m away from his house. Then he walks back to his house covering the same distance. This journey took him 15 minutes. Calculate his speed.
7.A barrel is pushed over a distance of 0.6km at a speed of 2m/s. Calculate the time taken to push the barrel.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque