AQA GCSE The Solar System(Physics)
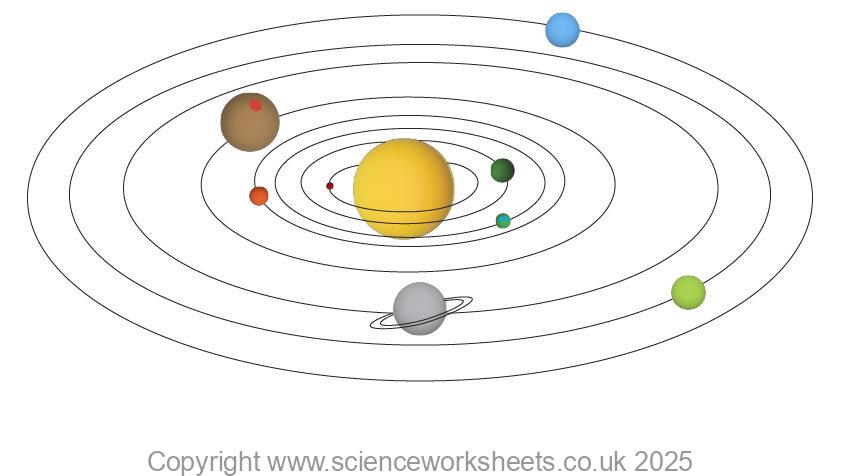
The Solar System
Our Solar system is found within the Milky way galaxy
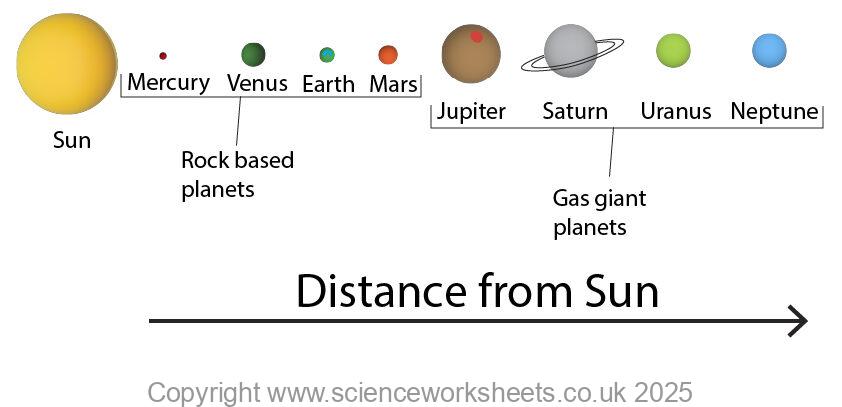
Our Solar system is made up of:
1 Star called the Sun
Eight planets
Dwarf planets
Natural satellites such as Moons which orbit planets.
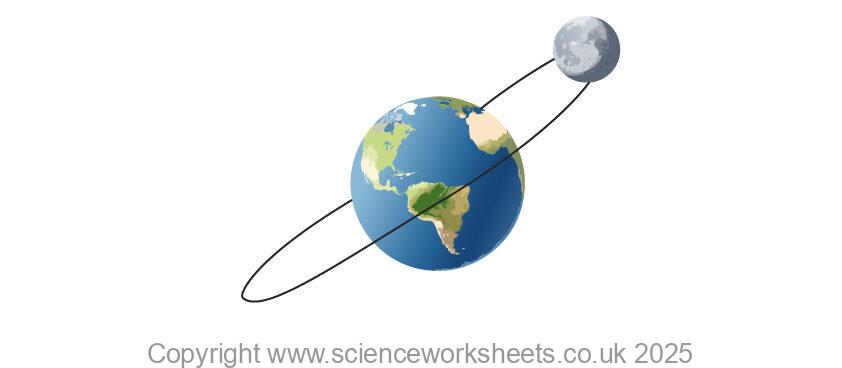
Moons
Some planets have moons. A moon is a natural satellite, so it orbits a planet.
Our Earth has 1 moon. A diagram of Earth and its Moon are shown below. The Moon orbits at an angle to the Earth
Mercury and Venus have no moons in orbit around them.
According to NASA, Saturn has 274 moons!
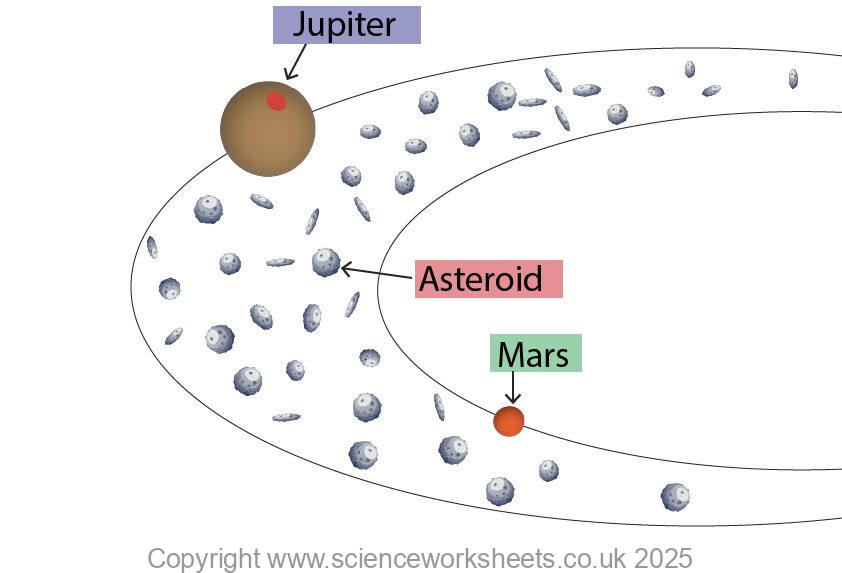
Asteroids
Asteroids are lumps of rock that are floating in space. There is an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
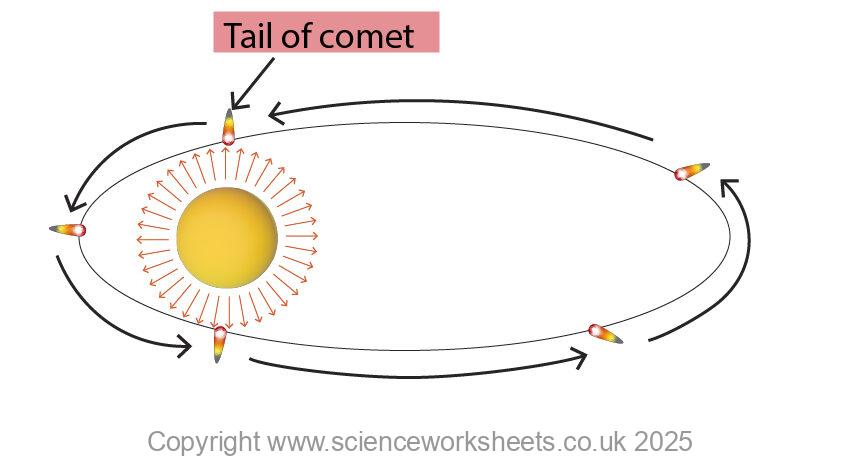
Comets
Comets are a frozen rock which contains dust and ice. They have a highly elliptical orbit around the Sun.
The solar radation emitted from the Sun, forms a solar wind which melts the ice on the comet, causing it to form a tail, which always points away from the Sun.
When the comet goes into deep space it will refreeze.
Due to the Sun’s gravity the Comet moves faster when it is nearer the Sun and slower when further from the Sun.
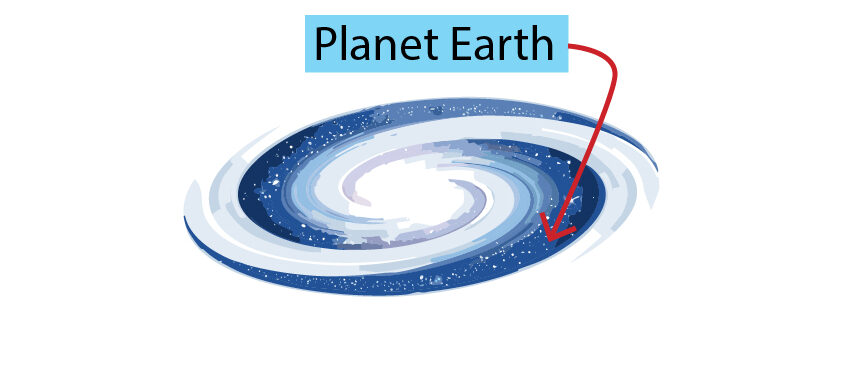
Milky Way Galaxy.
Planet Earth is found in the Milky Way Galaxy.
Within the Universe, there are billions of galaxies. The Milky Way is just one of these galaxies.
The Milky Way Galaxy is made up of billions of stars, including our Sun.
Our Solar system and planet is on the outer edge of the Milky way galaxy
Practice Questions
1.List the names of the planets in order from the Sun
2. Describe the composition of a comet.
3. Where is our solar system located within the Universe?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque