AQA GCSE Uses of nuclear radiation(Physics)
Uses of nuclear radiation
Nuclear Radiation can be used to medicine for:
1. Exploration of Internal organs
2.Control or destruction of unwanted tissue
Exploration of Internal Organs
Tracers
Some radioactive isotopes such as iodine-131 can be used as tracers. A tracer is a substance that is used to trace the flow of a substance around the body, or through an organ.
The patient is given a solution of iodine-131 to consume. After absorption the iodine-131 will accumulate in the thyroid gland.
The amount of iodine-131 absorbed by the thyroid gland can indicate the level of thyroid activity. If too much iodine-131 is taken up, then the thyroid is overactive. If too little iodine -131 is taken up then the thyroid is under active.
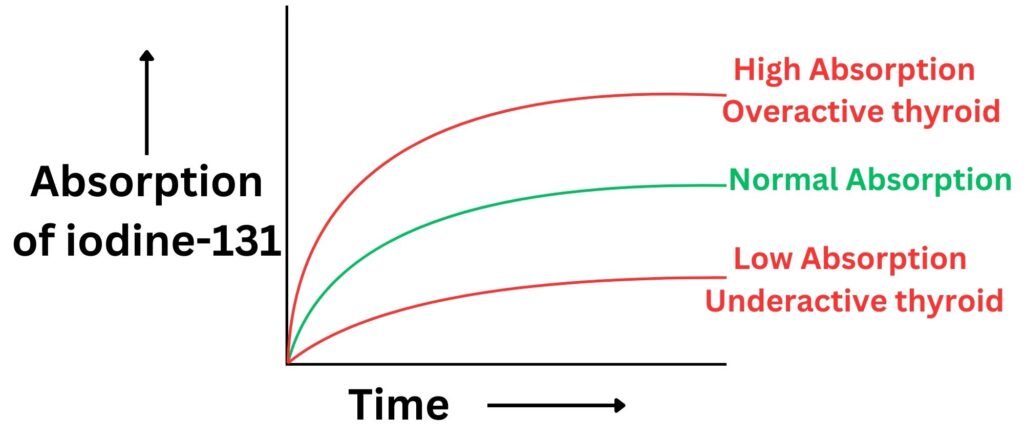
Iodine-131 is used because:
1. It is a gamma emitter, so it can be detected outside of the body
2. It has a half life of 8 days this long enough for its function, but it decays quickly into stable product. This means the person will not be exposed to ionising radiation for a long period of time.
Imaging of organs
Iodine-131 can also be used in imaging of body organs, by using a gamma camera. In this case the iodine-131 is injected into the body. A gamma camera is then placed next to the organ we want to view. The gamma camera will detect the gamma rays and display an image of the organ.
Below is an image of a gamma camera. The patient lies on the bed, which moves to the left. The scanner at the top of the unit will detect the gamma rays from one of the patient’s body organs.

Below is a scan from a gamma camera:

The red/orange regions are warm regions, whilst blue or green regions are cool regions.
Cancerous tumours are normally warm regions. However, some body tisses are metabolically active, so they will show up naturally as warm regions. It needs special Radiographer training to interpret these scans.
You do not need to be able to interpret these scans, you just need to be aware that nuclear medicine can be used for imaging, including detection of cancerous tumours.
Control or destruction of unwanted tissue
Cancer is uncontrolled cell division, which leads to the formation of a tumour. This tumour is often harmful, so we need to control, or destroy this unwanted tumour to treat the person.
Radiotherapy uses radiation to kill cancerous cells and therefore remove the tumour.

The person lies on the machine, a narrow radiation beam then directed through the tumour to kill the tumour. The angle of the radiation beam is changed, so that the cancerous cells receive the highest dose of radiation and healthy cells receive the minimum dose of radiation.
Image below shows a gamma ray passing through the brain.

Gamma is often used because it is highly penetrating, so it can easily reach the cancerous tumour.
Medical equipment for surgeons is often sterilised using gamma rays. The equipment is placed into a plastic bag and irradiated with gamma radiation to kill any bacteria that might be present on the surgical equipment.

Risks of using nuclear Radiation.
Nuclear radiation is ionising, every time a person is exposed to ionising radiation, it will increase the chance of a DNA mutation and possible later development of cancer.
The chance of nuclear radiation causing cancer is very tiny, but the benefit of carrying out a body scan, or using radiotherapy to treat cancer is large in comparison.
So, often the benefits of nuclear radiation outweigh the risks.
If cancer is suspected a body scan with a gamma camera needs to be carried out to find out if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This is so doctors know which parts of the body to treat. If they didn’t know where else the cancer might have spread, only part of the cancer might be treated.
Practice Questions
1.State two uses of nuclear radiation in medicine
2. Define the term tracer
3. What is radiotherapy?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque