AQA GCSE Sound Waves and the Ear(Physics)
Sound waves and the Ear.
Remember on the previous page, we learnt that sound waves travelling through a solid caused vibrations in the solid.
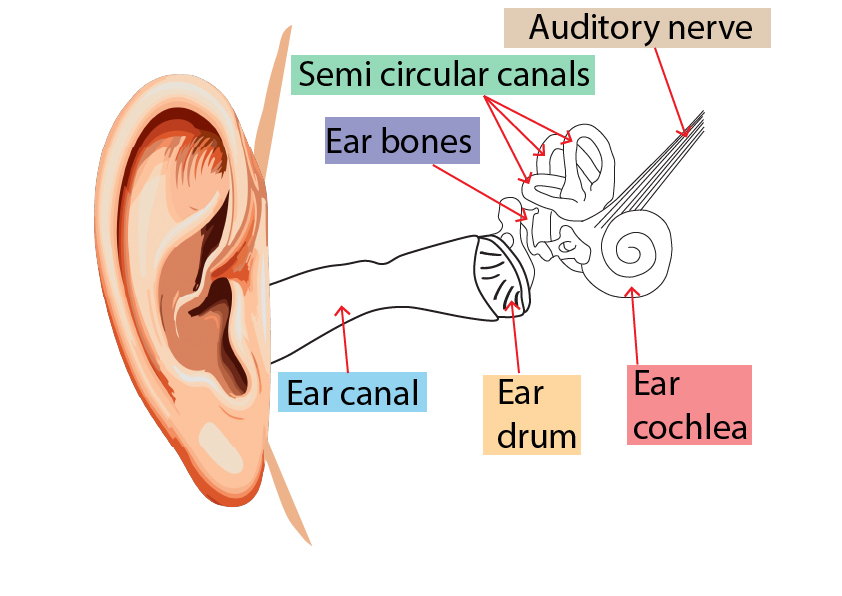
When the sound wave enters the ear, it passes along the ear canal and hits the ear drum, causing the ear drum to vibrate. Other parts of the ear will also vibrate, eventually leading to an electrical impulse being sent along the auditory nerve to the brain.
Converting wave disturbances between sound waves and vibrations in solids
When sound waves hit a solid object such as the ear drum, it will cause the ear drum to vibrate at the same frequency.
Process: Sound waves in the air reach the ear canal and strike the ear drum, causing it to vibrate.
Conversion: The vibrating ear drum transfers the energy to the ossicles (tiny bones in the middle ear), which amplify the sound and pass the vibrations to the cochlea in the inner ear.
Relevance: This allows humans to perceive sound.
Human Audible Hearing Range.
The human audible hearing range is from 20Hz to 20,000Hz.
This audible range is limited because when the sound waves are converted into vibrations of solids, the vibrations can only work over a restricted range of frequencies.
The eardrum and ear bones have specific resonant frequencies. They respond best to sounds within a certain range (typically 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz).
Extremely low-frequency sounds (below 20 Hz) do not produce significant vibrations in these structures, making them harder to detect.
High-frequency sounds (above 20,000 Hz) may not effectively transfer through the ossicles or may not stimulate the cochlea properly.
Practice Question
1. What type of wave are sound waves?
2. List the main parts of the human ear involved in hearing.
3. Describe the role of the eardrum in hearing.
4. Define the typical frequency range of human hearing.
5. Explain how sound waves are converted into vibrations in solids.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque