AQA GCSE Reaction time(Physics)
Reaction time
The reaction time is the time period that occurs when a person sees an event and then reacts to that event.
For humans reaction time is typically 0.2-0.9 seconds.
Ideally, a person needs to have the shortest possible reaction time.
Reaction time is increased by tiredness, alcohol, drugs and distractions.
Measuring Reaction time.
To test the reaction time, one person will drop a standard 30cm ruler and another person will try and catch the ruler. The ruler is dropped without warning, so a true test of reaction time can occur.
The distance from the bottom of the ruler, to where the 2nd person caught the ruler is recorded. The shorter this distance, the shorter the reaction time.
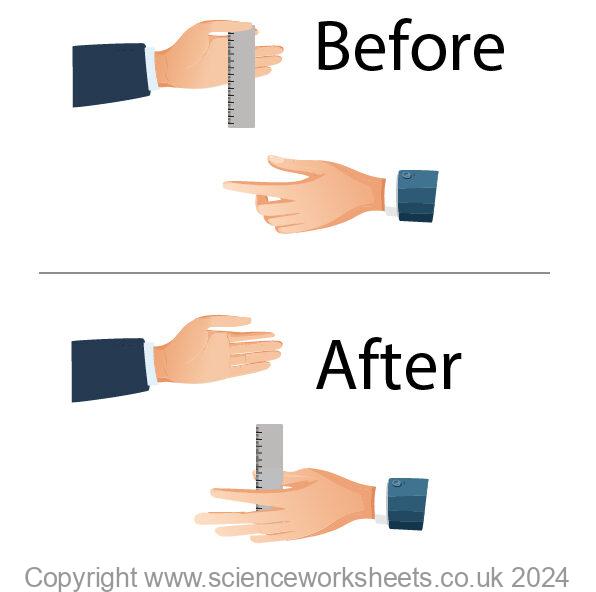
Data for this experiment is recorded below.
The distance is the distance from the bottom of the ruler, to where the person caught the ruler on the scale.
Each person had 3 attempts.
| Name of student | Distance (1st attempt) (cm) | Distance (2nd attempt) (cm) | Distance (3rd attempt) (cm) | Mean distance (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reshma | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| Anvit | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Ben | 5 | 7 | 6 | 6 |
| Donna | 6 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
Anvit had the shortest mean distance, so he had the shortest reaction time.
Bob and Donna both had the longest mean distance, so they had the longest reaction time.
Practice Question
1.Define the term reaction time
2. State the typical value for reaction time for a human
3. Estimate the reaction time value for an adult who has consumed alcohol
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque