AQA GCSE Newton's 1st Law(Physics)
Newton’s 1st Law
Newton’s 1st law states:
An object will remain at rest or continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by an external force.
This means if the resultant force acting on an object is zero then:
1.if the object is stationary, the object will stay stationary
2. If the object is currently moving, then the object continues to move at the same speed, in the same direction. So, object continues to move at the same velocity.
Stationary Objects and Newton’s 1st Law
Below is a stationary box on a table. The box will remain stationary because the forces acting on the box are balanced. So, the resultant force is 0N.
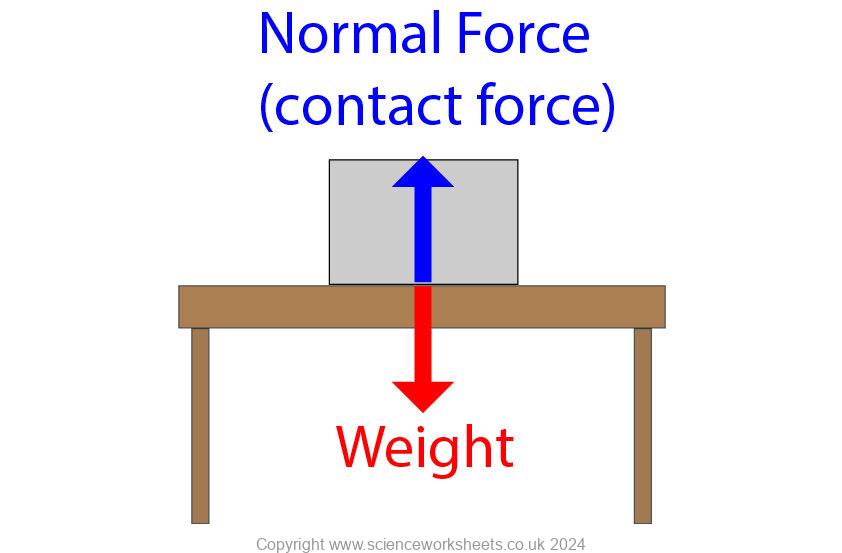 It is important to remember under Newton’s 1st law that the forces are acting on a single object.
It is important to remember under Newton’s 1st law that the forces are acting on a single object.
What happens if the object is subjected to a resultant force?
If the object is subjected to a resultant force, then the object can change its speed, shape or direction.
Moving Objects and Newton’s 1st Law.
Below is an image of a ball that is falling at constant speed. The ball has a 5N weight which acts downwards, and an air resistance of 5N which acts upwards. Both forces cancel out to give a resultant force of 0N.
As the object was previously falling, it will continue to fall downwards at a constant speed.
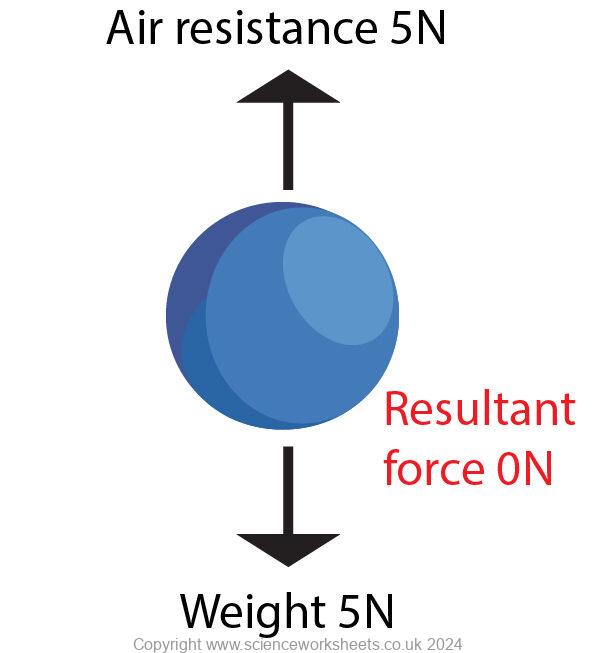
Example of an object being subjected to a resultant force
When a car is at rest, it stays stationary unless a resultant force acts on it.

When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the engine provides a forward force that is greater than the opposing forces (like air resistance and friction).

This resultant force causes the car’s velocity to change — it starts moving and accelerates forward.
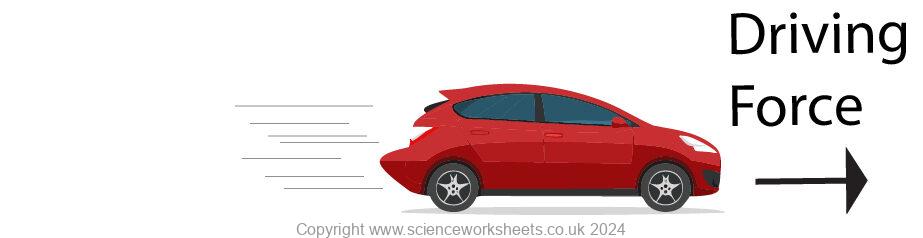
This demonstrates Newton’s First Law because the car only changes its velocity (from stationary to moving) when a resultant force acts on it.
Inertia and Newton’s 1st Law.
Inertia is the tendency of objects to continue in their state of rest or of uniform motion.
Imagine you’re sitting in a car that is moving at a constant speed. Suddenly, the driver slams on the brakes.
When the car stops abruptly, your body tends to keep moving forward at the same speed because of inertia.
This illustrates Newton’s First Law because:
Your body remains in motion (moving forward) until an unbalanced force (like the seatbelt) acts on it to stop you.
Practice Question
1.State the definition of Newton’s 1st law.
2.What does Newton’s First Law of Motion state about an object at rest?
a) It will start moving on its own.
b) It will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
c) It will accelerate constantly.
d) It has no forces acting on it.
a) A car accelerating on a straight road.
b) A book lying on a table.
c) A skydiver falling at terminal velocity.
d) Both b and c.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations
Drawing ray diagrams for a concave lens
Drawing Ray Diagram to produce a virtual image for a convex lens
Drawing ray diagram to produce a real image for a convex lens.
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
Seeing Coloured Objects Part 2
Viewing objects through coloured filters
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque